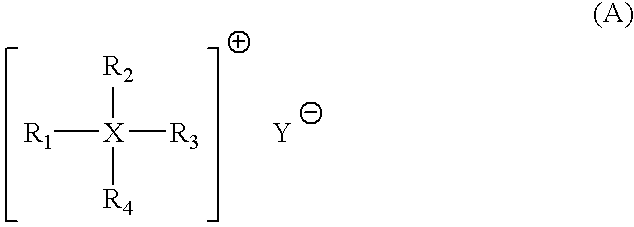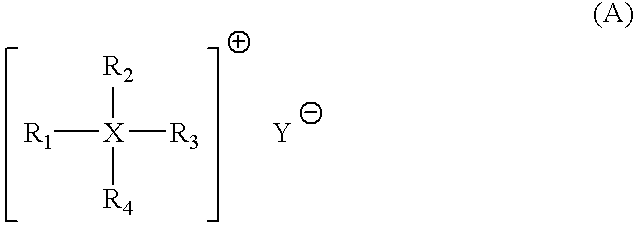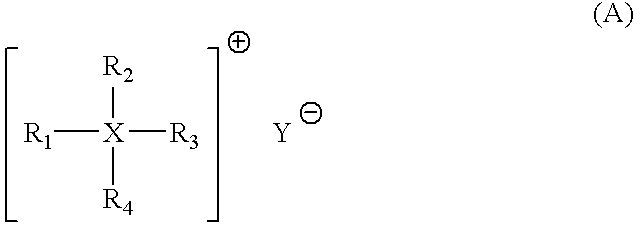Ketone-aldehyde resins having low water content, high thermal stability and yellowing resistance
a technology of ketone aldehyde and low water content, which is applied in the field of ketone aldehyde resins, can solve the problems of high molecular weight, high cost and inconvenience, and adverse effects on properties, and achieves low water content, high thermal stability and yellowing resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0100] Having generally described this invention, a further understanding can be obtained by reference to certain specific examples which are provided herein for purposes of illustration only and are not intended to be limiting unless otherwise specified.
Preparation of a Resin
[0101] The resins are synthesized by charging 1 030 g of cyclohexanone, 210 g of an approximately 30% strength formaldehyde solution, 280 ml of methanol, and 3.8 g of benzyltributylammonium chloride to a three-necked flask with stirrer, reflux condenser, and temperature sensor under nitrogen. The reaction is initiated by adding 8.7 g of a 25% strength sodium hydroxide solution. The temperature of the batch is held below 60° C. by cooling. Then 1 350 g of an approximately 30% strength formaldehyde solution are added over the course of 100 minutes, followed by 25.2 g of a 25% strength sodium hydroxide solution. After stirring at reflux, 100 g of an approximately 30% strength formaldehyde solution are added and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mol % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mol % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mol % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com