Cellular uptake of bioactive agents
a bioactive agent and cellular technology, applied in the field of can solve the problems of epithelial tissue atrophy, limited effectiveness further limited effect of amino acid supplementation, so as to increase the cellular uptake of bioactive agents, reduce the absolute solubility of bioactive agents, and increase the transport (absorption) of bioactive agents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
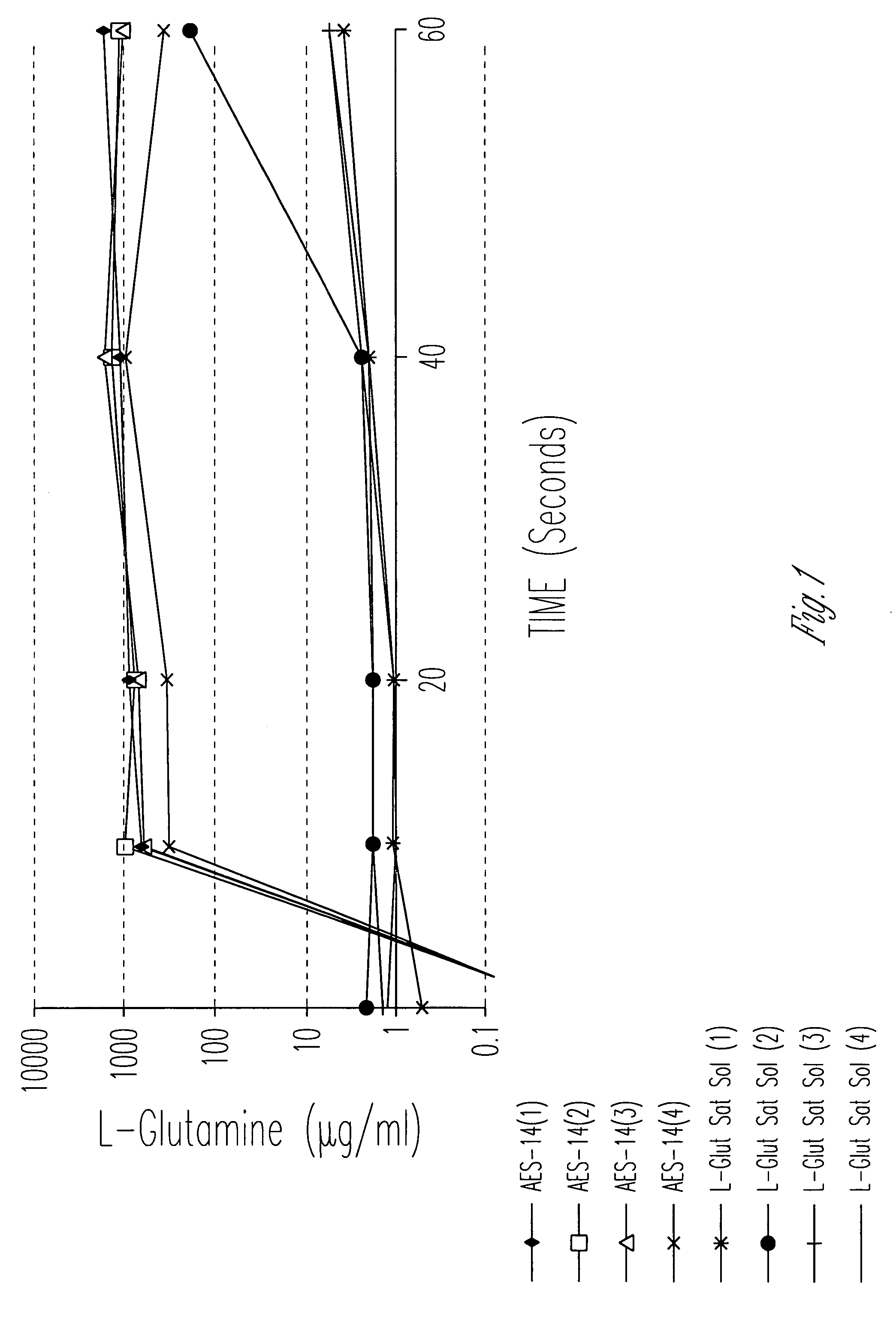
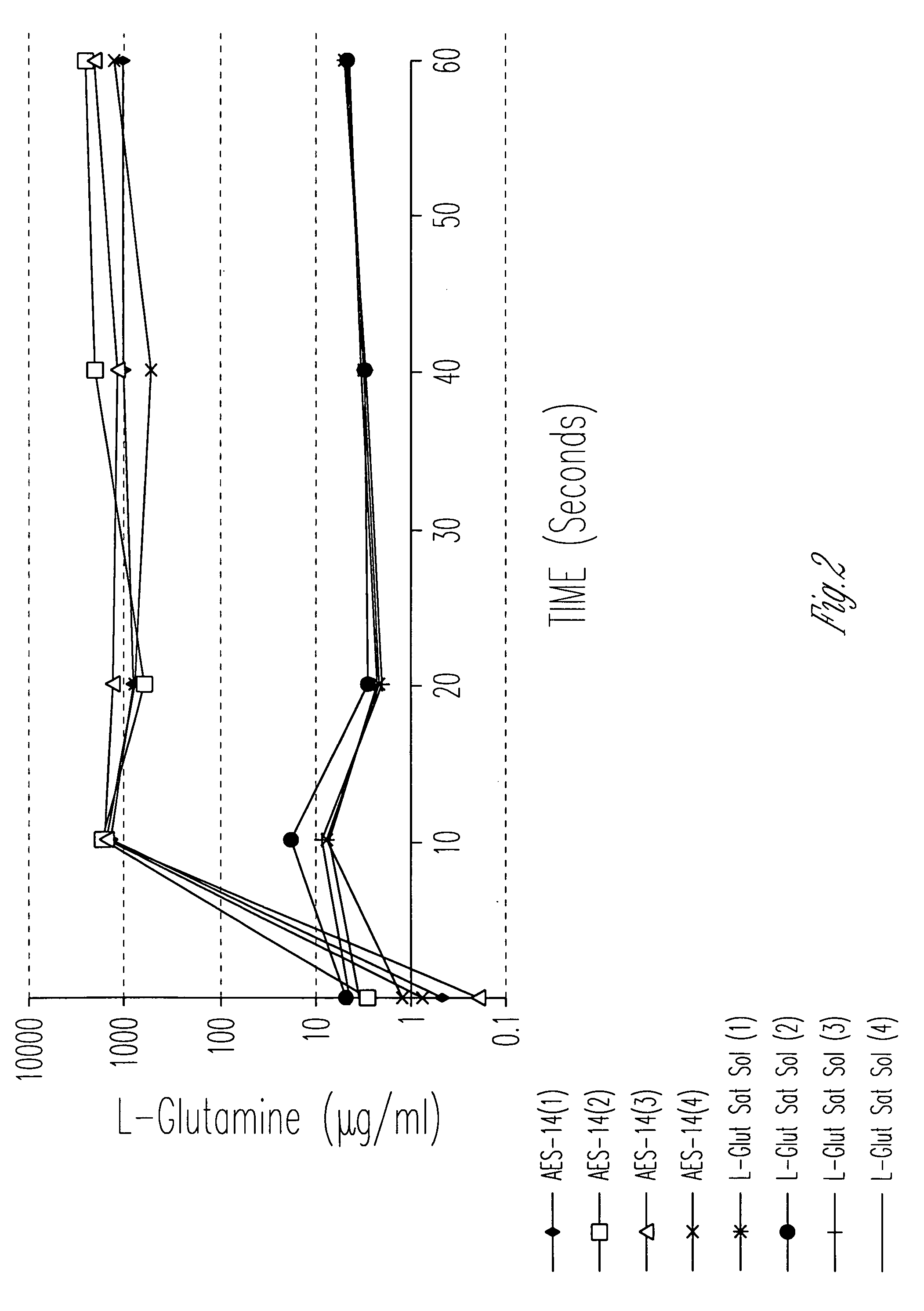
Evaluation of Cellular Uptake of Glutamine in Combination With Sucrose and Sorbitol
[0062] 1. Materials and Methods
[0063] Distilled, deionized water (107 ml) was added to 207 grams of a mixture of sucrose, sorbitol, and glutamine with excipients (Aesgen-14) as listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1Aesgen-14 (AES-14)L-glutamine240.0Kg57.94 w %* 50.00% w / v**Sucrose144.0Kg34.77 w % 30.00% w / v Crystalline Sorbitol13.44Kg3.24 w %2.80% w / vGlycerin14.0Kg2.92 w %2.52% w / vSodium Phosphate2.6Kg0.63 w %0.54% w / vMonobasic (Anhydrous)Avicel Cellulose Gel874.0g0.18 w %0.17% w / vType CL-611Citric Acid (Anhydrous)280.0g0.07 w %0.06% w / vXanthan Gum230.0g0.05 w %0.04% w / vCarrageenan230.0g0.05 w %0.04% w / vArtificial Flavor230.0g0.05 w %0.04% w / vMethylparaben207.0g0.04 w %0.04% w / vPotassium Sorbate Powder180.0g0.04 w %0.04% w / v30% Simethicone Emulsion115.0g0.02 w %0.02% w / v
*Weight percents are expressed as percent of total weight of dry ingredients for reconstitution with water in a 240 ml bottle.
**Weight / volum...
example 2
Effect of AES-14 on Drug Uptake and Permeability
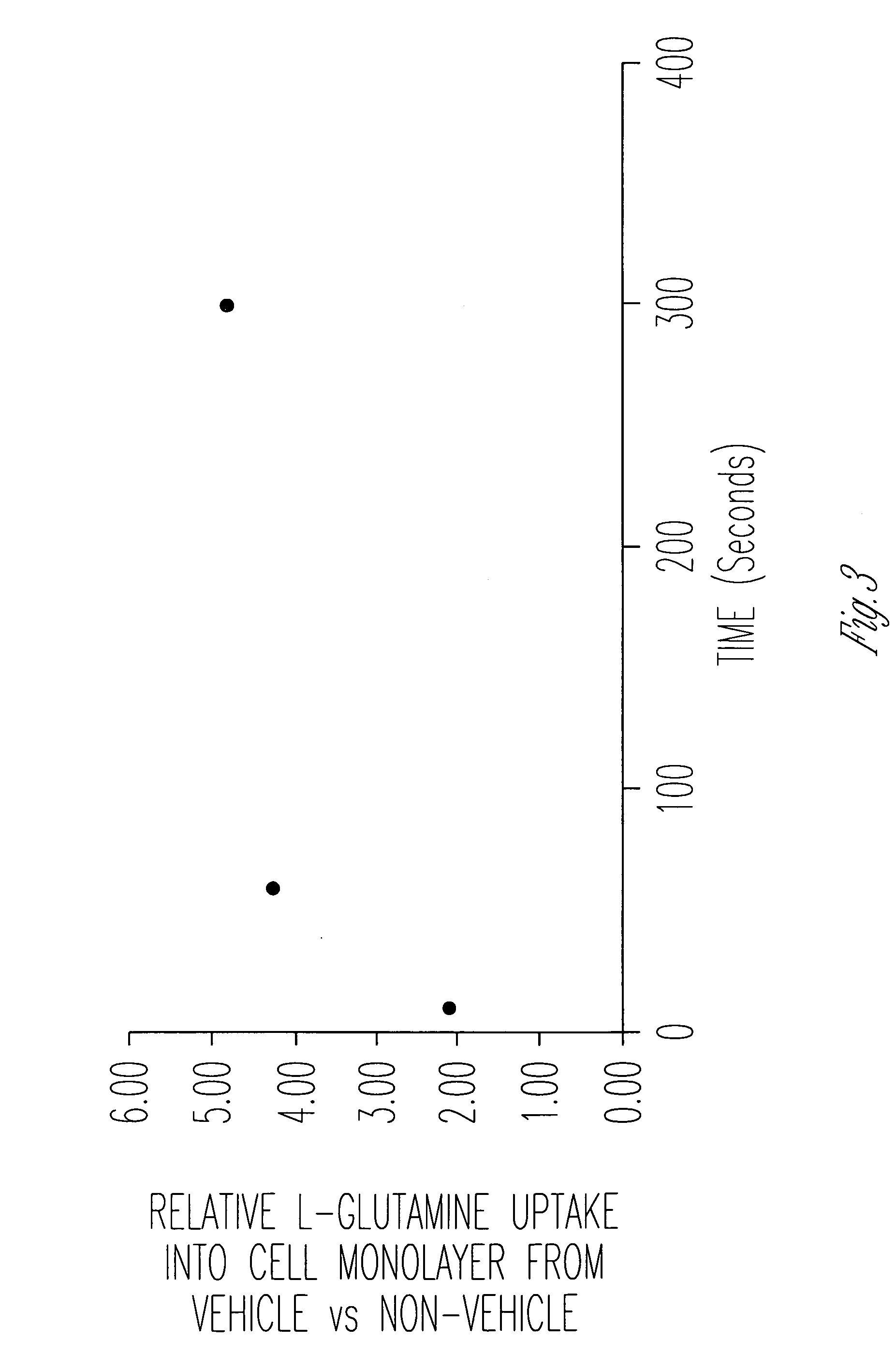
[0072] The cellular uptake and permeability enhancing effect of a pharmaceutical vehicle on four model drugs (L-glutamine, L-asparagine, glycylsarcosine, acyclovir, along with half saturation L-glutamine) across Caco-2 cell monolayers were measured in this experiment. Uptake and permeability of each compound was measured in the apical-to-basolateral direction, with and without vehicle.
Methods
[0073] Materials. Two amino acids (L-glutamine, L-asparagine), a dipeptide (glycylsarcosine), and a therapeutic agent (and acyclovir) with low permeability were studied. Each compound was tritiated. 14C-mannitol was used as an evaluation of monolayer / cell integrity (i.e. as a low uptake / permeability marker).
[0074] Uptake and Permeability Assessments. Compound cellular uptake into and permeability across Caco-2 monolayers was measured. Caco-2 monolayers were grown using a recently developed, rapid culture system, that requires 4 days rather th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com