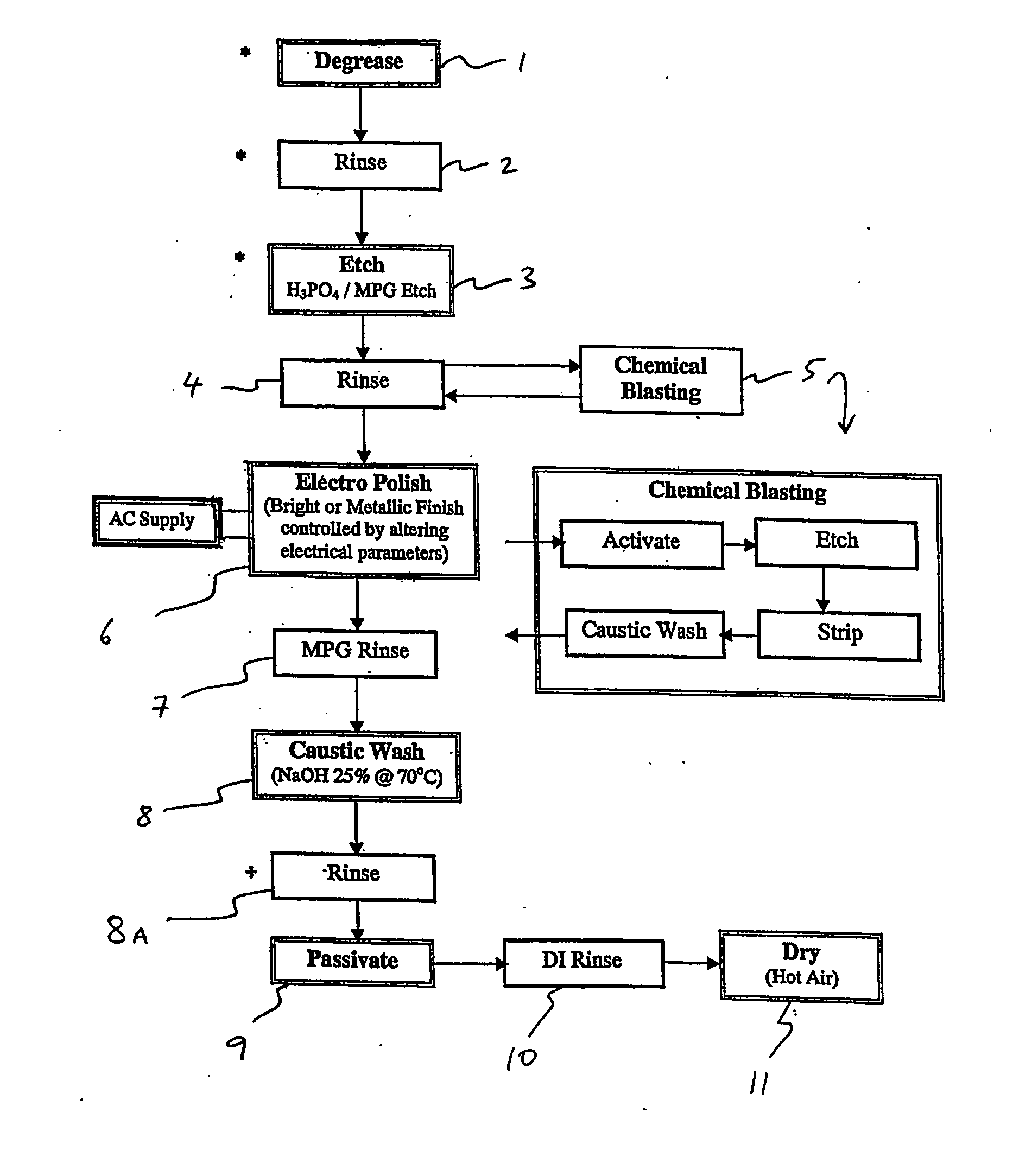
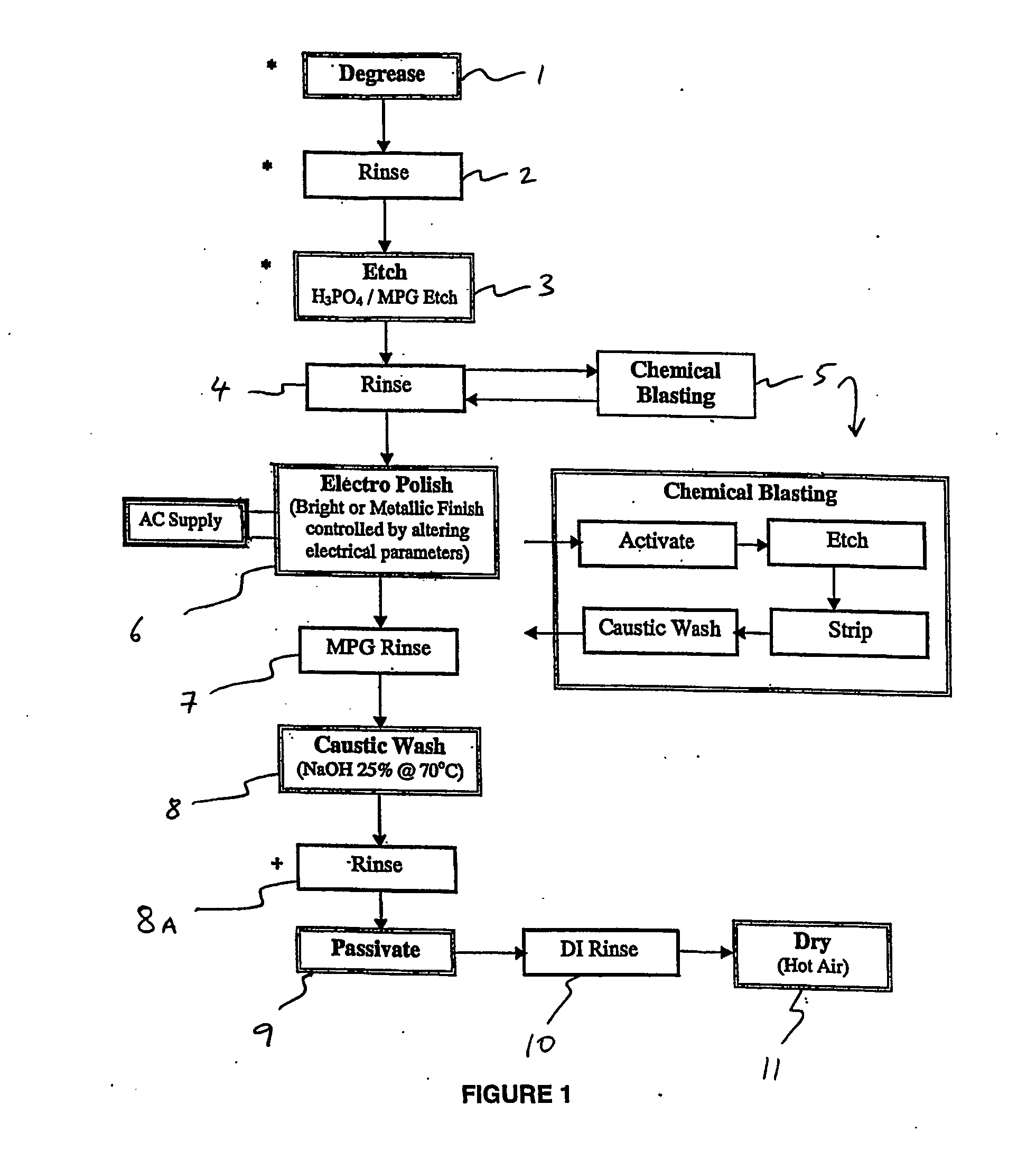
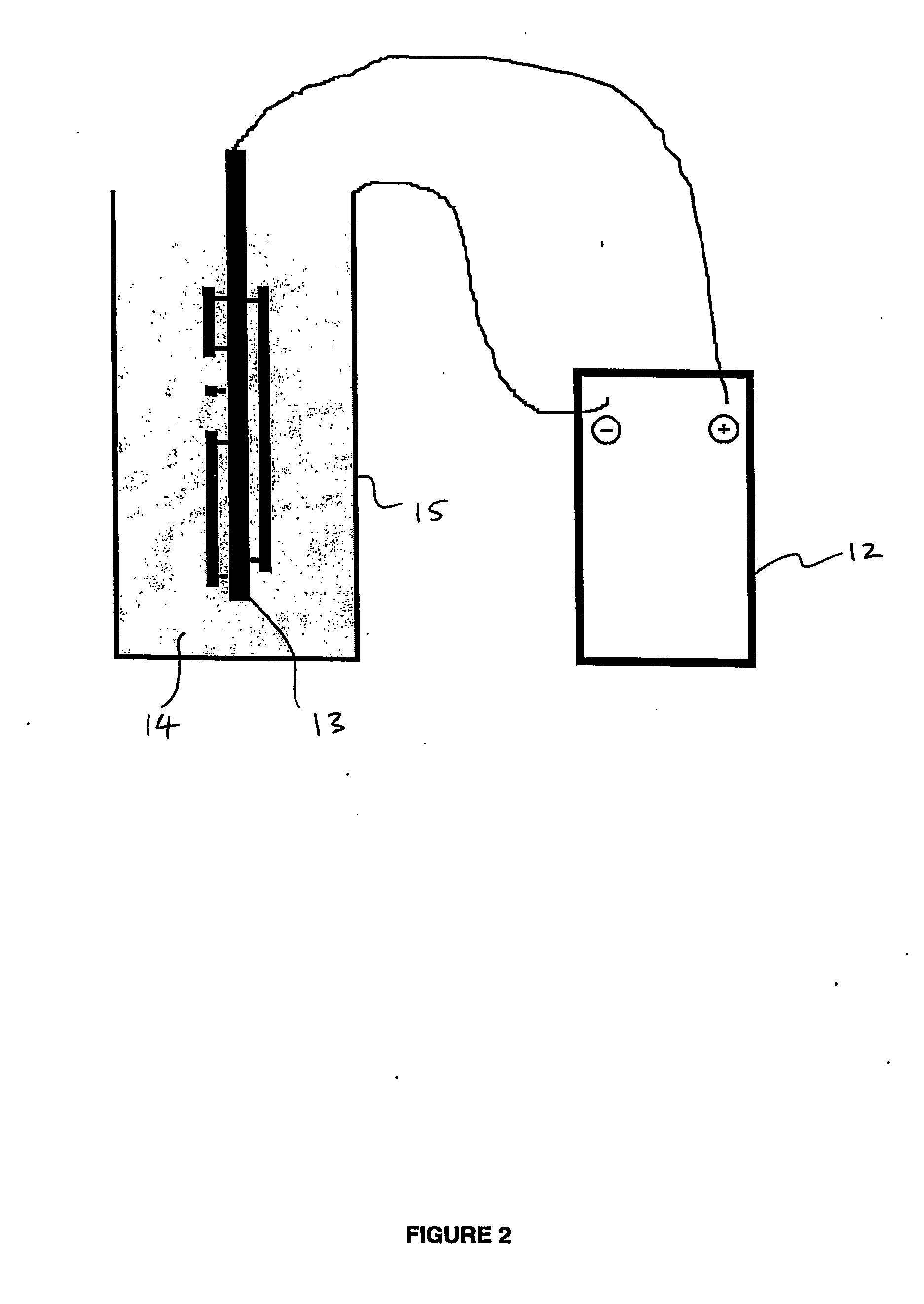
Surface treatment of magnesium and its alloys
a surface treatment and magnesium technology, applied in the direction of anodisation, phosphatisation, chromatisation, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the surface appearance of the surface, obscuring the desired surface finish, and unable to brighten nor polish the metal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0097] A die cast plate, 140 mm×100 mm, 3 mm thick, of AM50 alloy, was brightened, using the following steps: [0098] 1. Degrease in CW25 at 70° C. for one minute [0099] 2. Rinse in water for approximately 30 seconds [0100] 3. Pre-etch in PE3 for 30 seconds [0101] 4. Rinse in water [0102] 5. Electropolish in EP3 solution in two stages—galvanic polish (no imposed AC voltage) for six minutes, followed by an imposed AC voltage of 5 VAC for 20 seconds. [0103] 6. Rinse in monopropylene glycol for 5 seconds [0104] 7. Wash in CW25 for 20 seconds at 70° C. [0105] 8. Rinse in water [0106] 9. Passivate, using potassium permanganate solution, PM1, for 10 seconds [0107] 10. Rinse in water [0108] 11. Dry using hot air
[0109] The result was a very bright finish, having a slight yellow tinge. The die cast structure was plainly visible.
example 2
[0110] A die cast plate of AZ91D alloy having the same dimensions as in example 1 above, was treated using the following processes: [0111] 1. Degrease in CW25, 70° C., for 1 minute [0112] 2. Rinse in water [0113] 3. Pre-etch in PE3 for 30 seconds [0114] 4. Rinse in water [0115] 5. Polish in EP3 solution for 5 minutes, using a galvanic polish (no AC voltage) [0116] 6. Rinse in monopropylene glycol for 5 seconds [0117] 7. Wash in CW25, 70° C. for 20 seconds [0118] 8. Rinse in water [0119] 9. Passivate using PC1 for 30 seconds [0120] 10. Rinse in water [0121] 11. Dry using hot air
[0122] The result was a metallic finish in which casting structures were visible.
example 3
[0123] A die cast plate of AM50 alloy, having the same dimensions as that in examples 1 and 2 above, was treated using the following processes: [0124] 1. Degrease in CW25 at 70° C. for 1 minute [0125] 2. Rinse in water [0126] 3. Pre-etch in PE3 for 30 seconds [0127] 4. Wash in CW25, 70° C. for 30 seconds [0128] 5. Rinse in water [0129] 6. Chemical blast in three steps —1 minute in CB2A solution followed by 7 minutes in CB1 solution and finally, an additional minute in CB2A solution [0130] 7. Wash in CW25, 70° C., 1 minute [0131] 8. Polish in EP3 solution in three steps—one minute using an imposed AC voltage of 5 VAC, 3 minutes without AC voltage, then an additional 20 seconds using an imposed AC voltage as before. [0132] 9. Rinse in monopropylene glycol for 5 seconds [0133] 10. Wash in CW25, 70° C. for 20 seconds [0134] 11. Rinse in water [0135] 12. Passivate in PM1 for ten seconds [0136] 13. Rinse in water [0137] 14. Dry using hot air
[0138] The result was a bright finish, with a h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com