Fused array preform fabrication of holey optical fibers
a technology of optical fibers and preforms, applied in the direction of cladding optical fibers, manufacturing tools, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to describe the optimal design of photonics, wavelength scattering and loss, and inability to allow light of other wavelengths, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing light scattering, reducing optical loss, and high quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
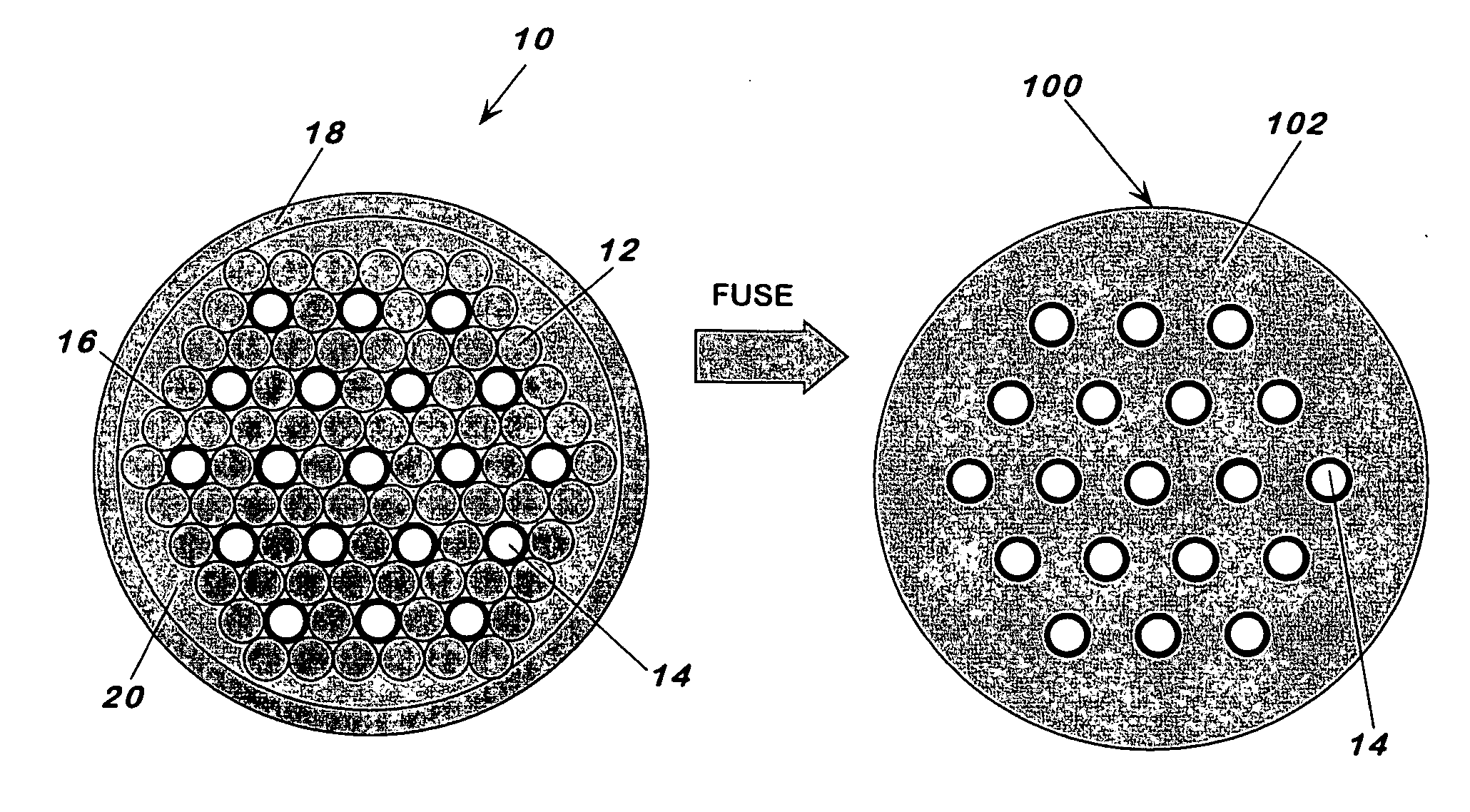
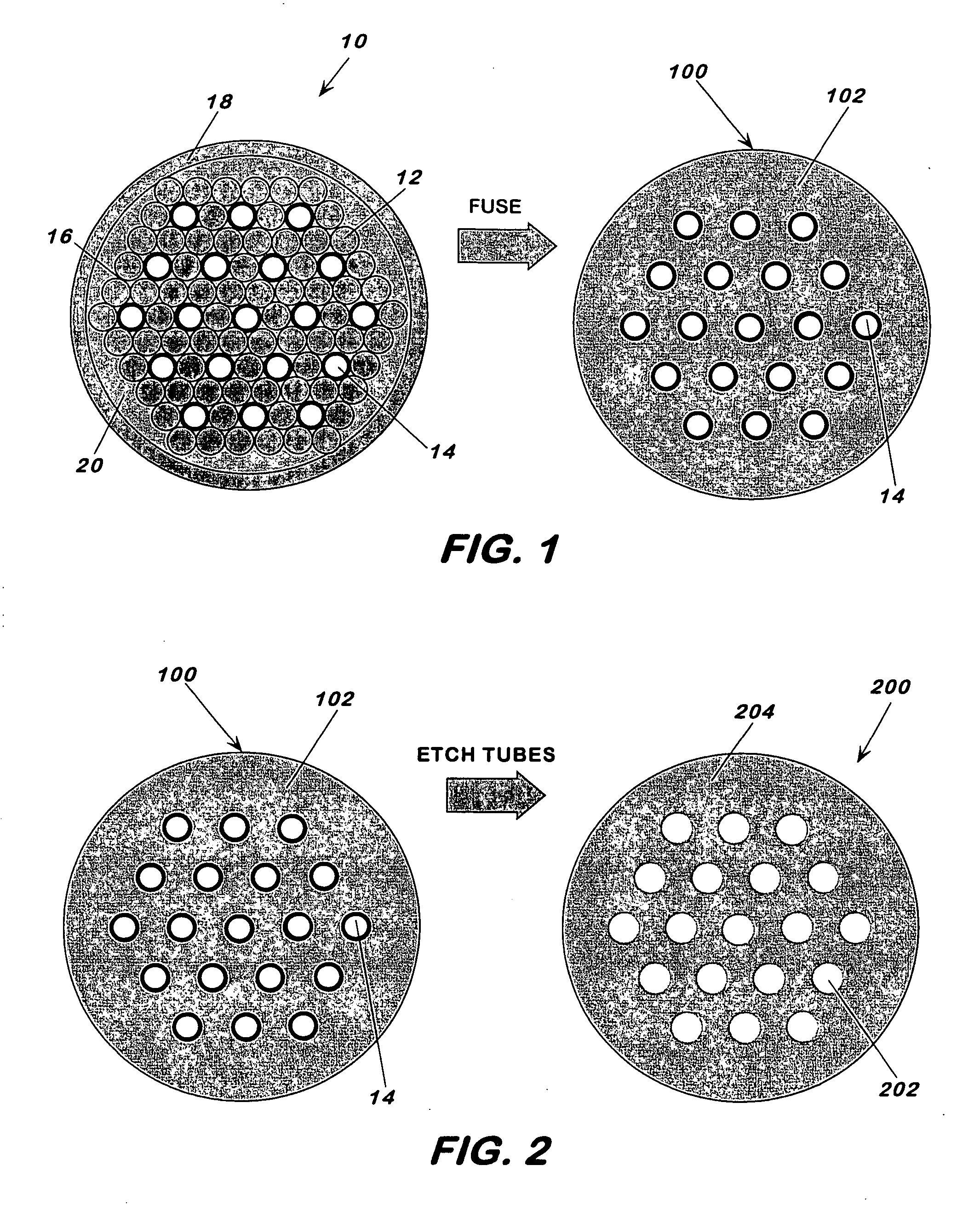
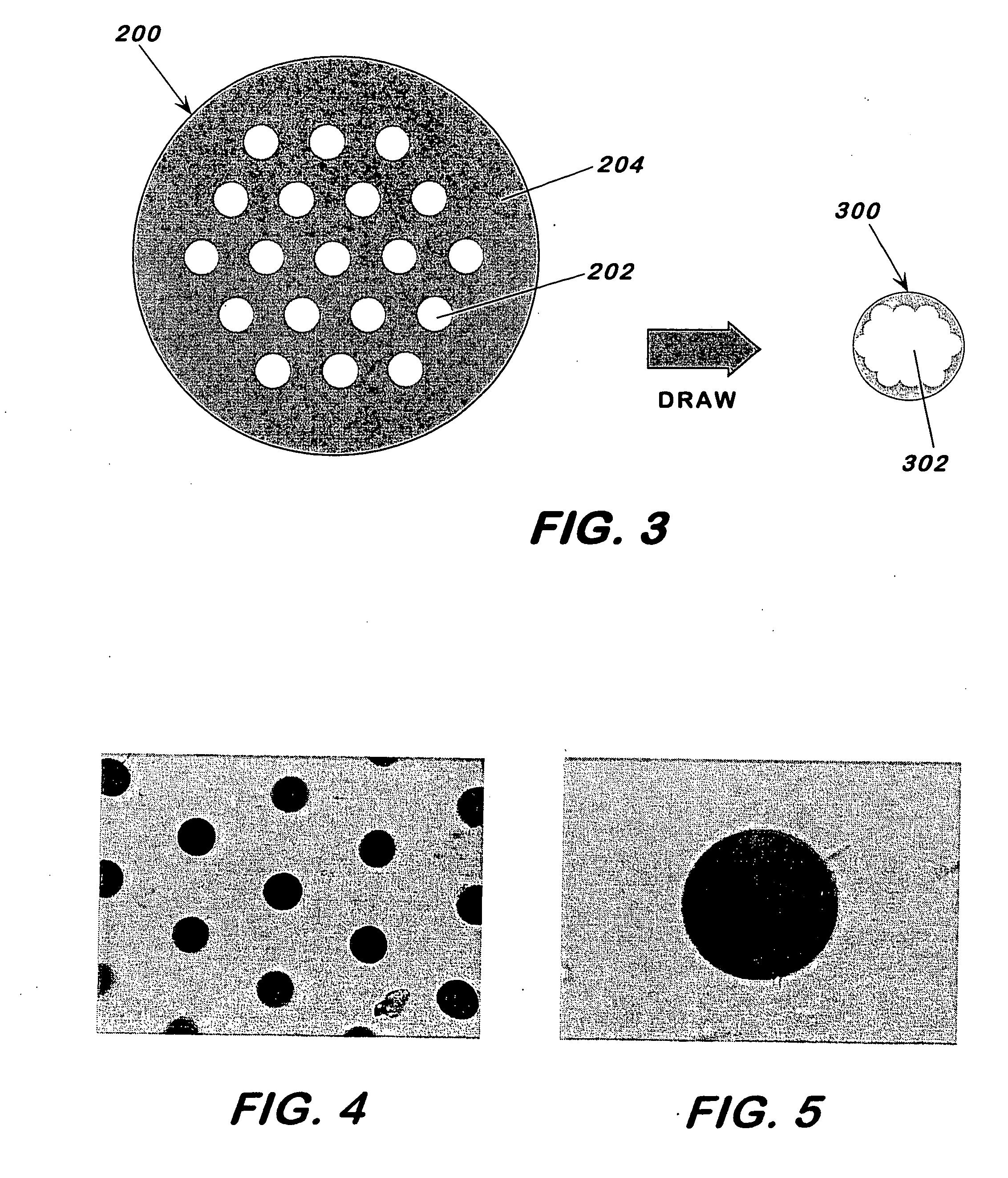
[0030] This invention pertains to a fabrication method for making holey fibers and to the holey fibers made thereby. The method generally includes the steps of stacking into a bundle rods and tubes in an arrangement, with the tubes having a softening point that is higher than that of the rods; heating the bundle to a temperature to fuse the rods but not the tubes and form a fused element characterized by a continuous phase around the tubes; removing the tubes to form a preform characterized by a continuous phase and channels, corresponding to the outline of the removed tubes, passing through the preform; and drawing the preform at a temperature below the softening temperature of the rods to form the holey fiber with solid or hollow core, having a periodic and highly uniform channel arrangement along the length of the fiber. For solid or hollow core holey fibers with or without photonic structure, no holes or holes of different sizes can be mixed and matched to obtain the desired eff...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com