Cooling device of thin plate type for preventing dry-out
a cooling device and thin plate technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device details, lighting and heating apparatus, laminated elements, etc., can solve the problems of deteriorating the performance of semiconductor devices, reducing life expectancy, and increasing the heat emission rate of semiconductor devices per unit area, so as to improve the flow of coolant and improve the cooling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
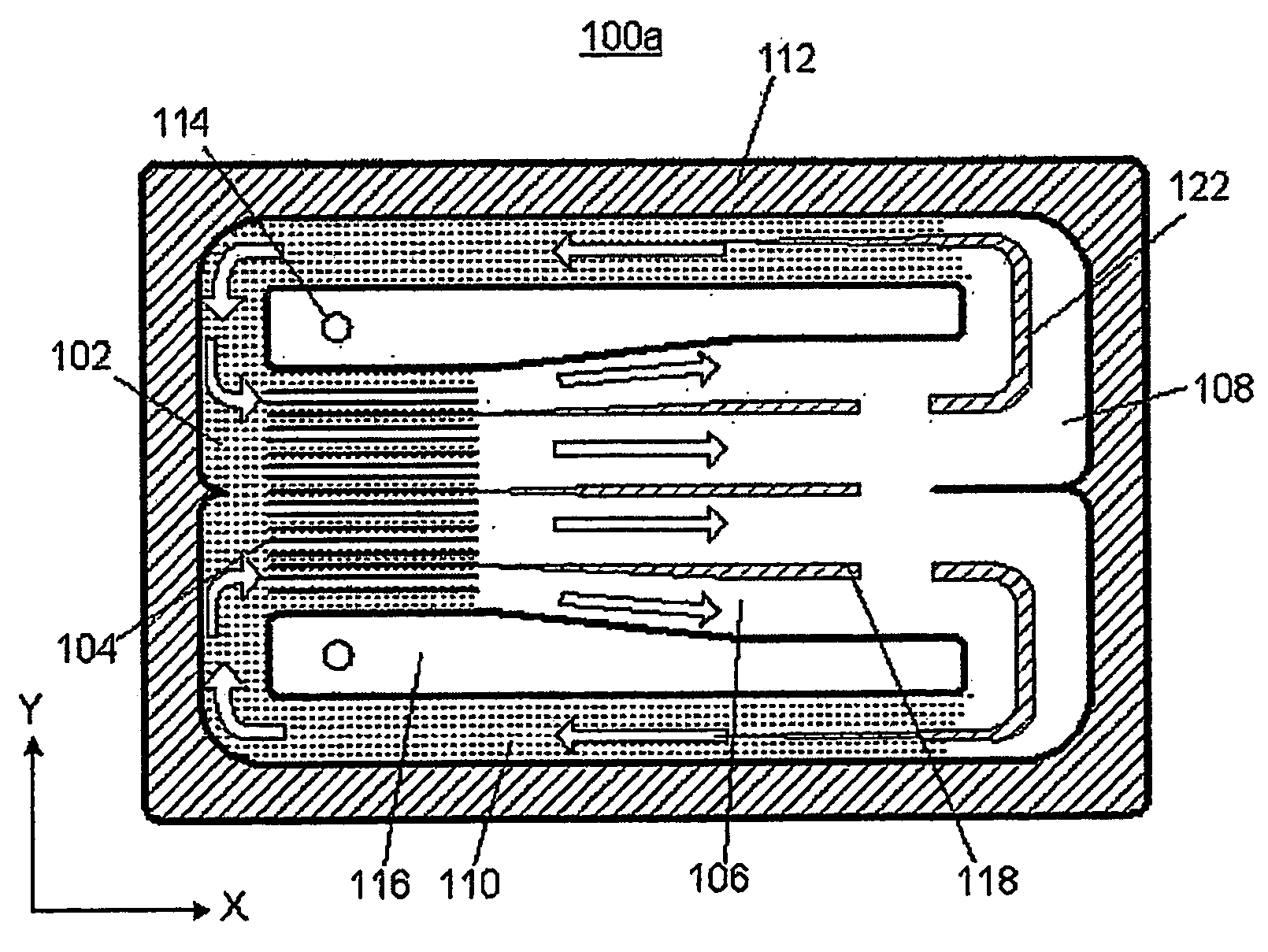
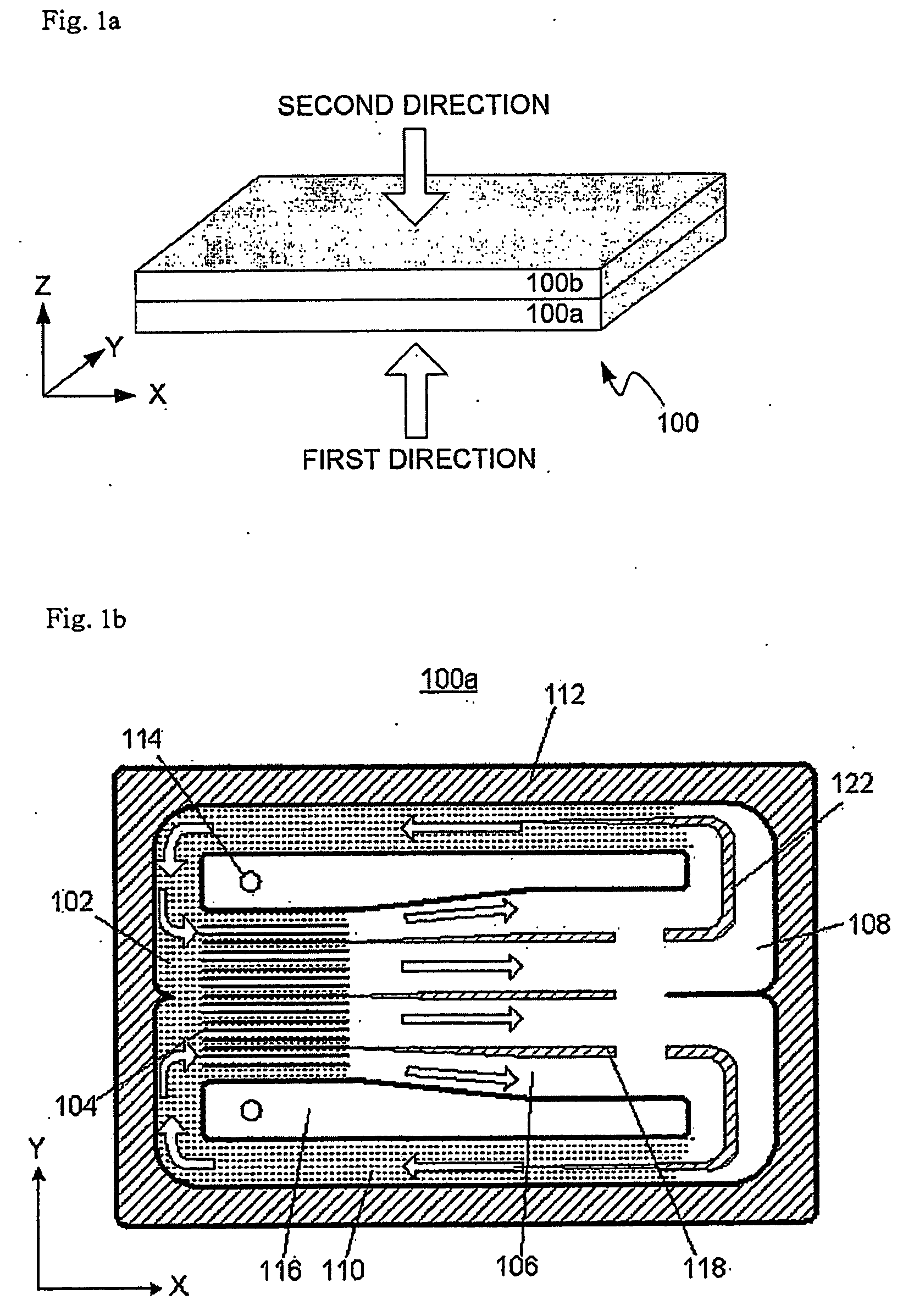
[0029] Referring to FIG. 1a, first, FIG. 1a shows the external appearance of a thin plate-type cooling device 100 according to this invention. It is preferable that the external appearance of the thin plate-type cooling device 100 of this invention is approximately rectangular, and the thin plate-type cooling device 100 is formed by bonding a lower plate 100a and an upper plate 100b in each of which internal elements have been formed.
[0030] For the sake of understanding and description, it is defined that, as shown in FIG. 1a, an “X-axis direction” is the longitudinal direction (from the left to the right of the drawing) of the thin plate-type cooling device 100 of this invention, a “Y-axis direction” is the lateral direction (into the drawing) of the thin plate-type cooling device 100, and a “Z-axis direction” is the vertical direction (from the bottom of the top of the drawing) of the thin plate-type cooling device 100. Moreover, it is also defined that a “section viewed in a firs...
third embodiment
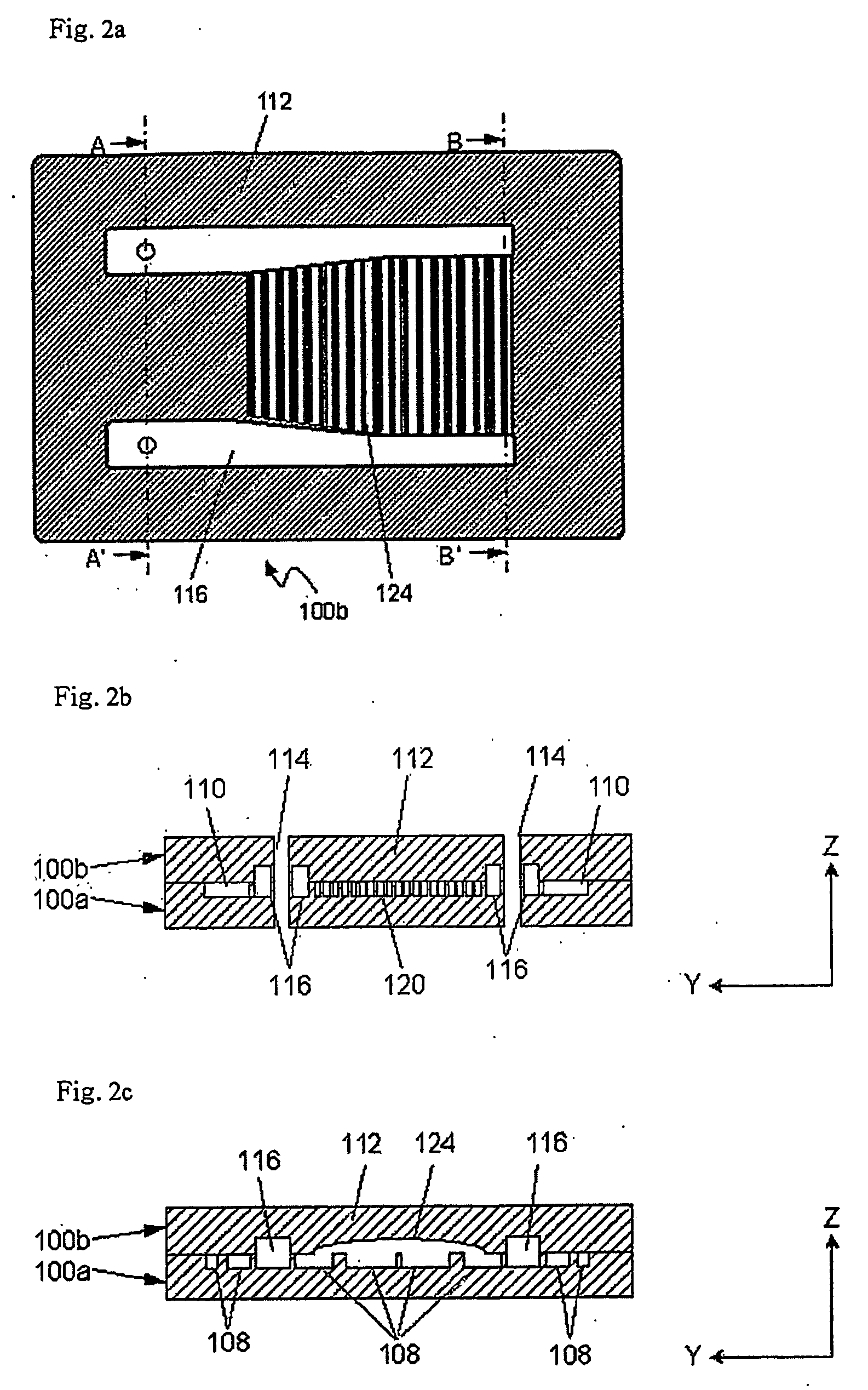
[0064] As shown in the drawings, the upper plate 100b of the thin plate-type cooling device 100 in the third embodiment further includes a plurality of second cavities 126 formed on areas corresponding to the condensation section 108 of the lower plate 100a. That is, the upper plate 100b includes the plurality of the first cavities 124 formed on areas corresponding to the gaseous coolant transfer section 106 of the lower plate 100a and the plurality of second cavities 126 formed on areas corresponding to the condensation section 108 of the lower plate 100a, where the first and second cavities 124 and 126 are respectively connected to each other.
[0065] Moreover, as shown in the drawing, it is preferable that the width of each of the second cavities 126 becomes narrow as it proceeds to the area corresponding to the liquefied coolant transfer section 110. Accordingly, when the lower plate 100a and the upper plate 100b are bound, the sections of the second cavities 126 become small as t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com