Composite forming fabric
a technology of composite fabric and fabric, applied in the field of fabric, can solve the problems of undesired variations in sheet absorption properties, undesired wire marks, wire marks, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the potential water carrying potential of the fabric, enhancing the binding of the paper side layer, and reducing the overall height and void volume of the fabri
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
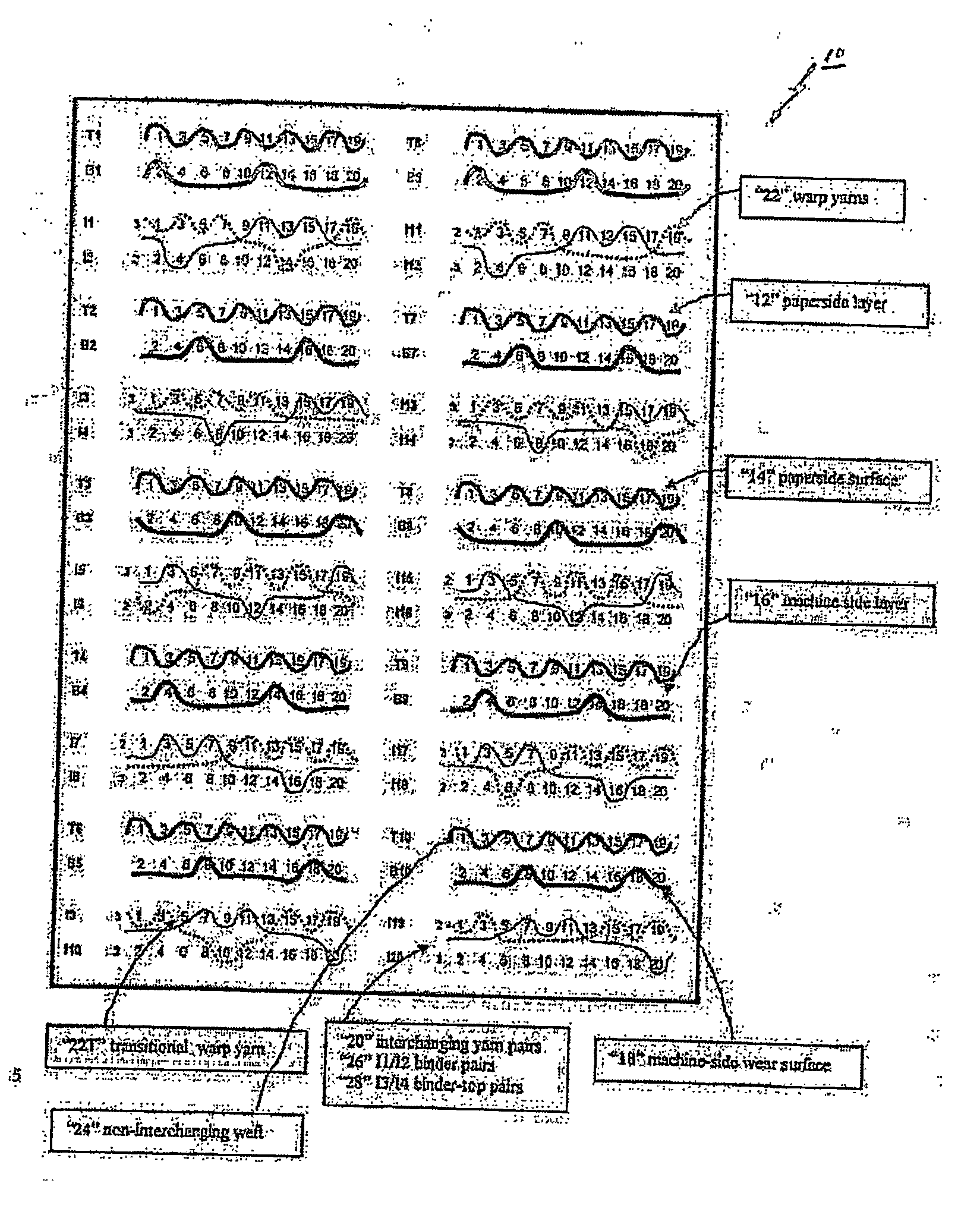
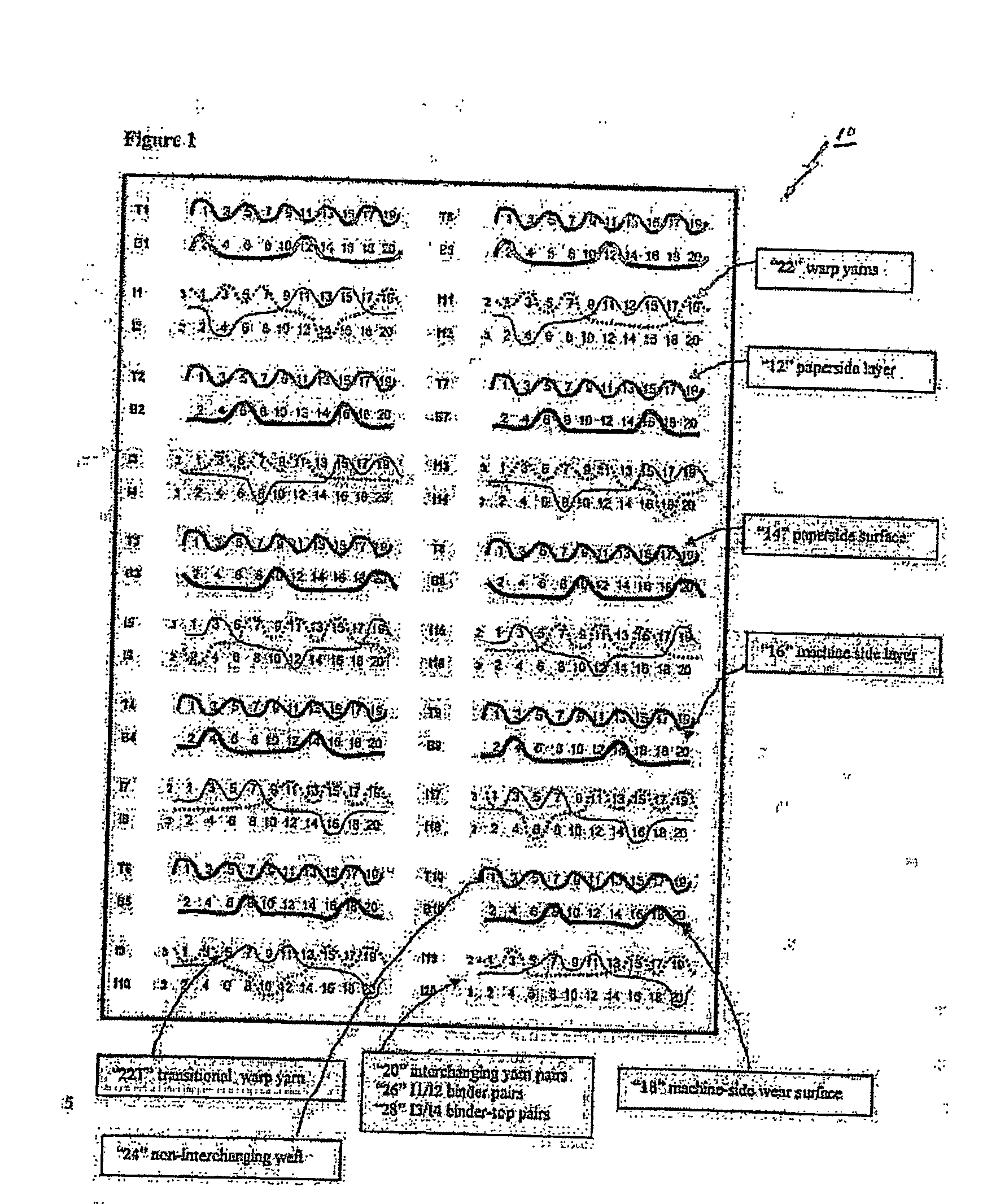
[0042] The weft paths of the paper side, wear side and interchanging yarn pairs for one preferred embodiment of a composite forming fabric 10 in accordance with this invention are shown in FIG. 1. In accordance with this embodiment, the composite forming fabric has a 20 shaft-40 pick repeat and includes a paper side layer 12 having a paper side surface 14, a machine side layer 16 having a bottom wear side surface 18 and a plurality of first and second interchanging yarns pairs, e.g., 20.
[0043] The paper side layer 12 and the machine side layer 16 each comprise a plurality of warp yarns 22 in the machine direction and plurality of non-interchanging weft yarns 24 woven together with the warp yarns. The paper side layer 12 and the machine side layer 16 each have a predetermined repeat of the weave pattern in the cross-machine direction. As illustrated, but not by a way of limitation, the illustrated composite fabric 10 is a twenty (20) shed-forty (40) pick fabric including ten (10) ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com