Composite steel-wood floor structure
a floor structure and composite technology, applied in the direction of building components, constructions, building constructions, etc., can solve the problems of general incompatibility between the cement surface and the floor covering, the lack of workability, and the difficulty of use, so as to increase the strength performance of the floor structure, and increase the effect of the floor structur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Present Invention
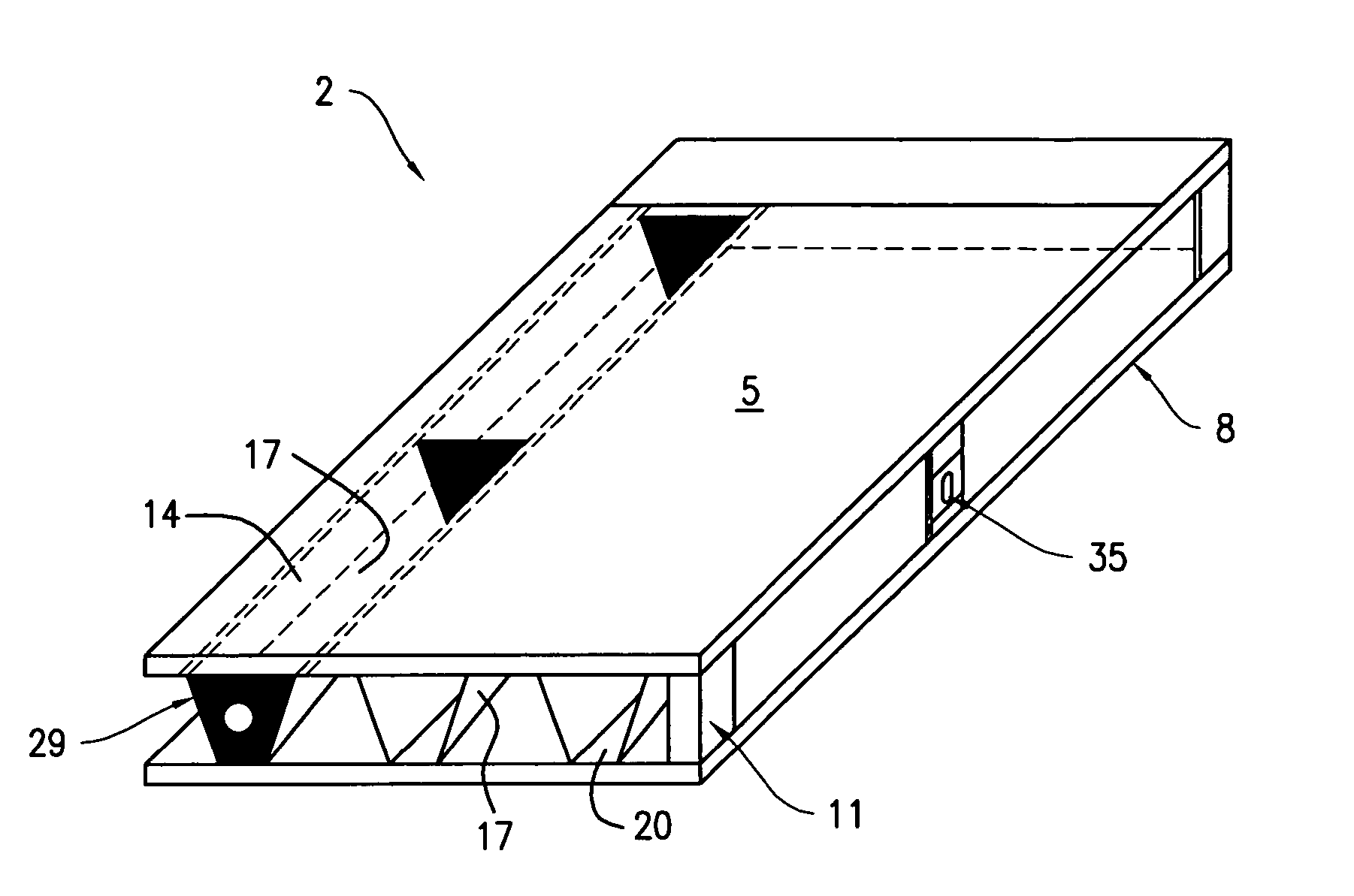
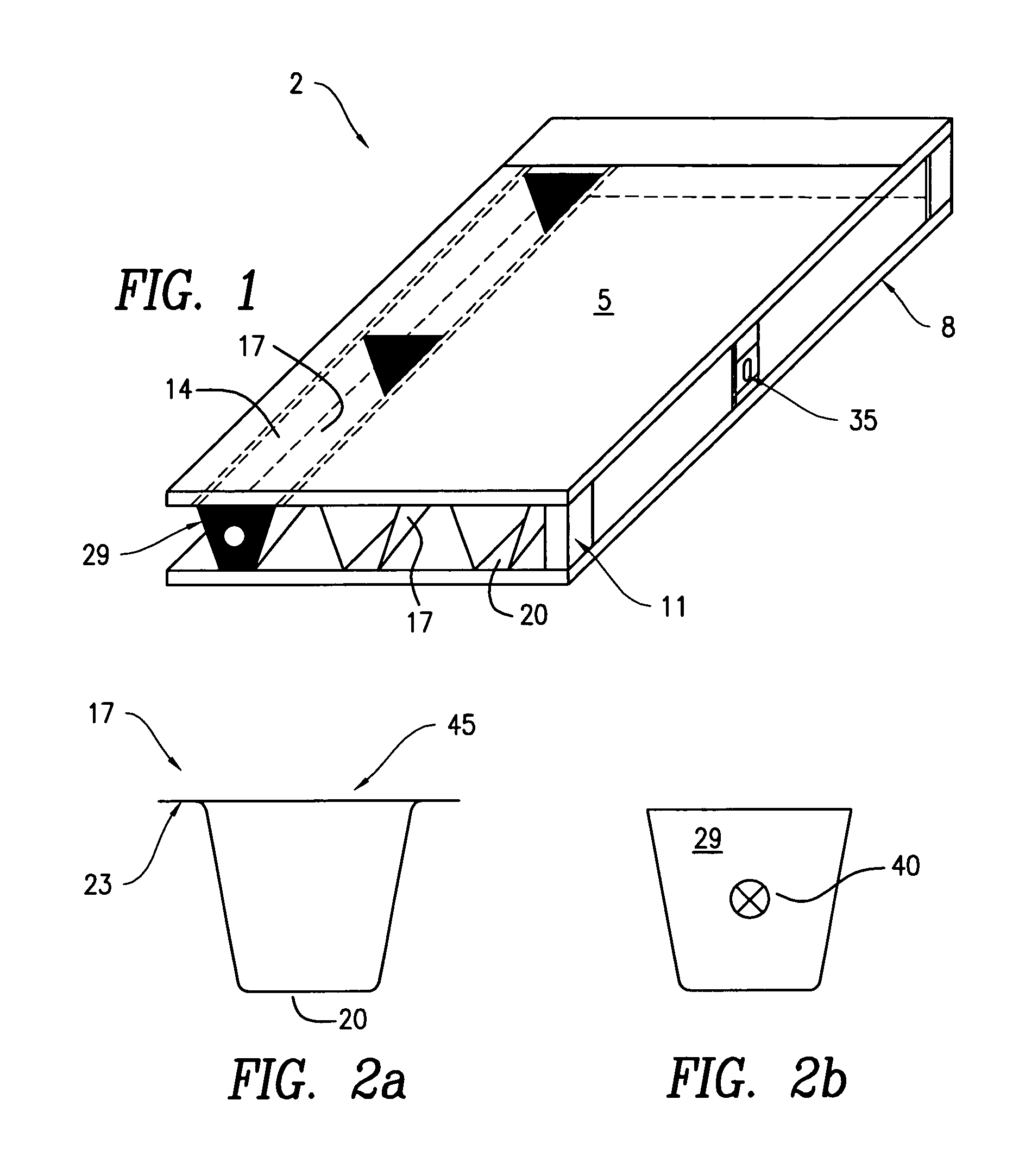
[0026] Floor structures were prepared according to the present invention as follows. The floor structures were four feet wide, 20 foot long, and 9.5 inches thick. The upper and lower composite wood boards were 23 / 32″ AdvanTech boards. Between the upper and lower composite wood boards were arranged three channels, cross sectional illustrations and dimensions of these channels are shown in FIG. 2. The channels themselves were 20 feet long, and stiffeners at each end and along the channels at a longitudinal spacing of one stiffener for every four feet.
[0027] Screws were inserted every 8-inches as indicated by in FIG. 2 to fasten the metals channels to the upper and lower composite wood boards. The screws used were Primeguard Plus™ exterior screws. As can be seen the metal channel in FIG. 2b is in the shape of an isosceles trapezoid, with the top of the channel 14 having a length of seven inches, the height of the trapezoidal channel 14 being 8 inches, the non-paralle...
example 2
Prior Art
[0030] A conventional floor structure was built with concrete foundation walls made according to size and set at the proper spacing. The 2×4 plate was bolted down to the top of the concrete supports, and the rimboard was placed on the plate and attached thereto with nail fasteners, at an industry-wide standard spacing for nails of every 12″, I Joists were installed on the rimboard and AdvanTech floor sheathing was fastened to the I Joists with a continuous bead of polyurethane construction adhesive. The I joists were made from ⅜ inch OSB webstock and solid wood lumber flanges that were 1.5 inch by 2.5 inch.
[0031] Examples 1 and 2 were then tested to measure the stiffness of the flooring structures and assess whether they are sufficiently stiff as to avoid undesirable vibrations. A drop weight apparatus was used to apply a repeatable dynamic loading to the floor systems. Two accelerometers and two linear variable displacement transducers (LVDTs) were installed at the cente...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com