Method of direct plating of copper on a substrate structure
a substrate structure and copper technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient support of future interconnect technology, void-free filling of interconnect features via conventional metallization techniques, and difficult to have adequate seed step coverage with pvd techniques,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
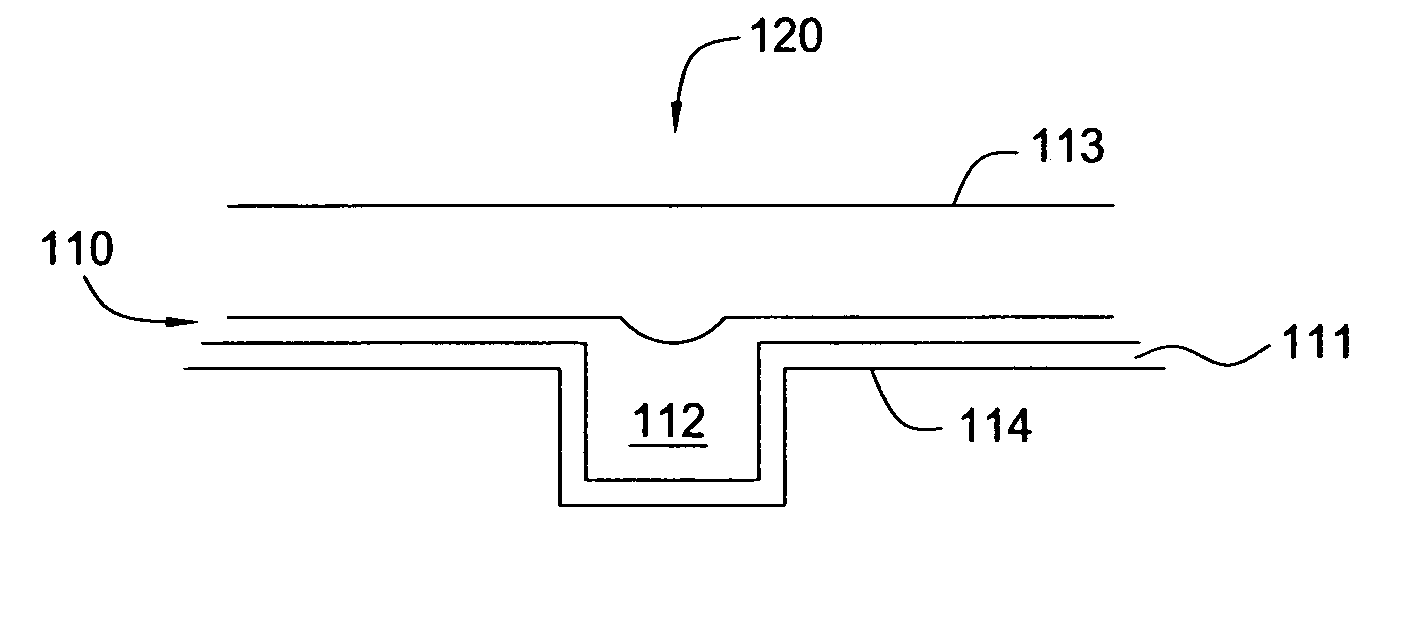
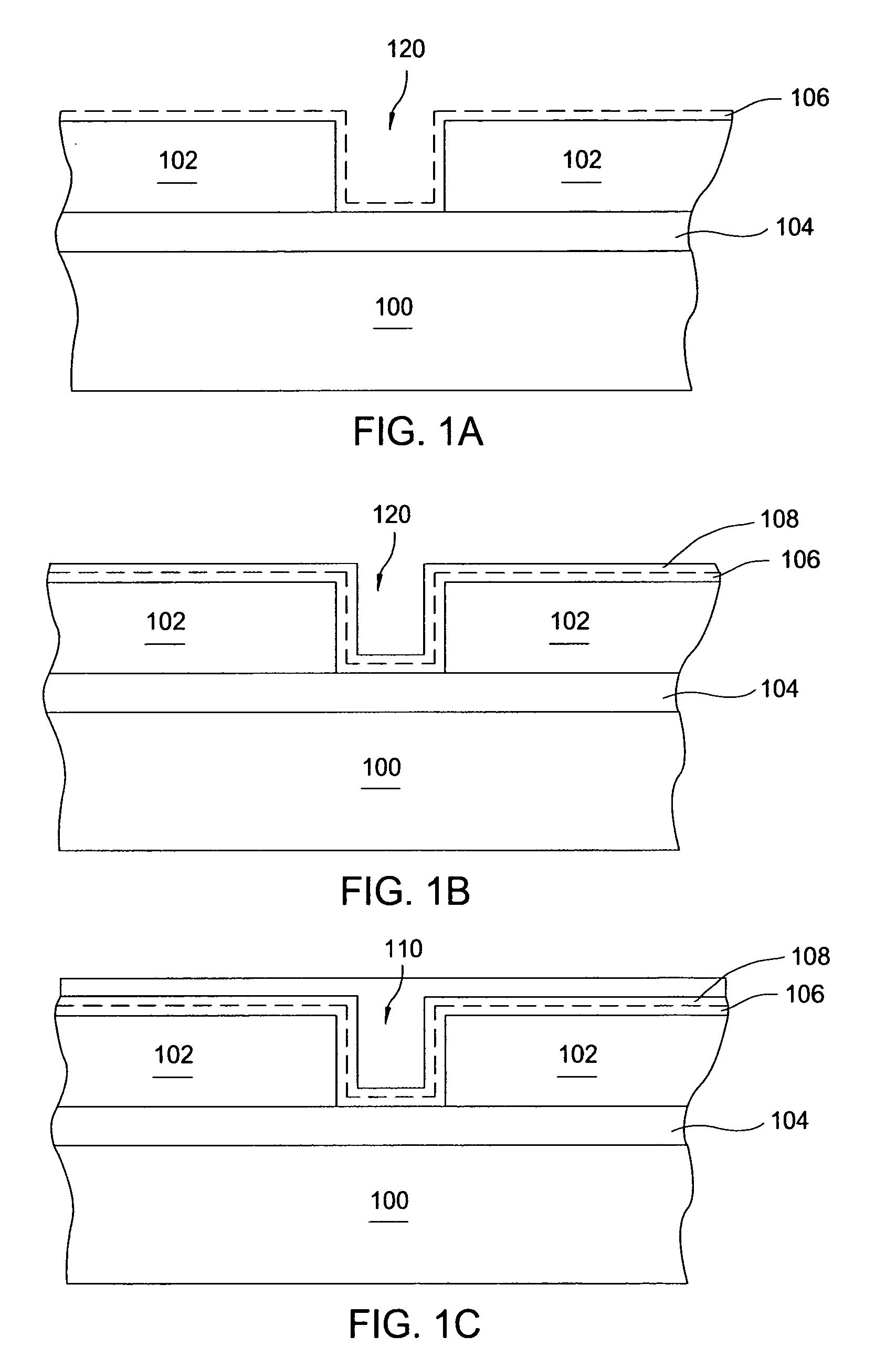
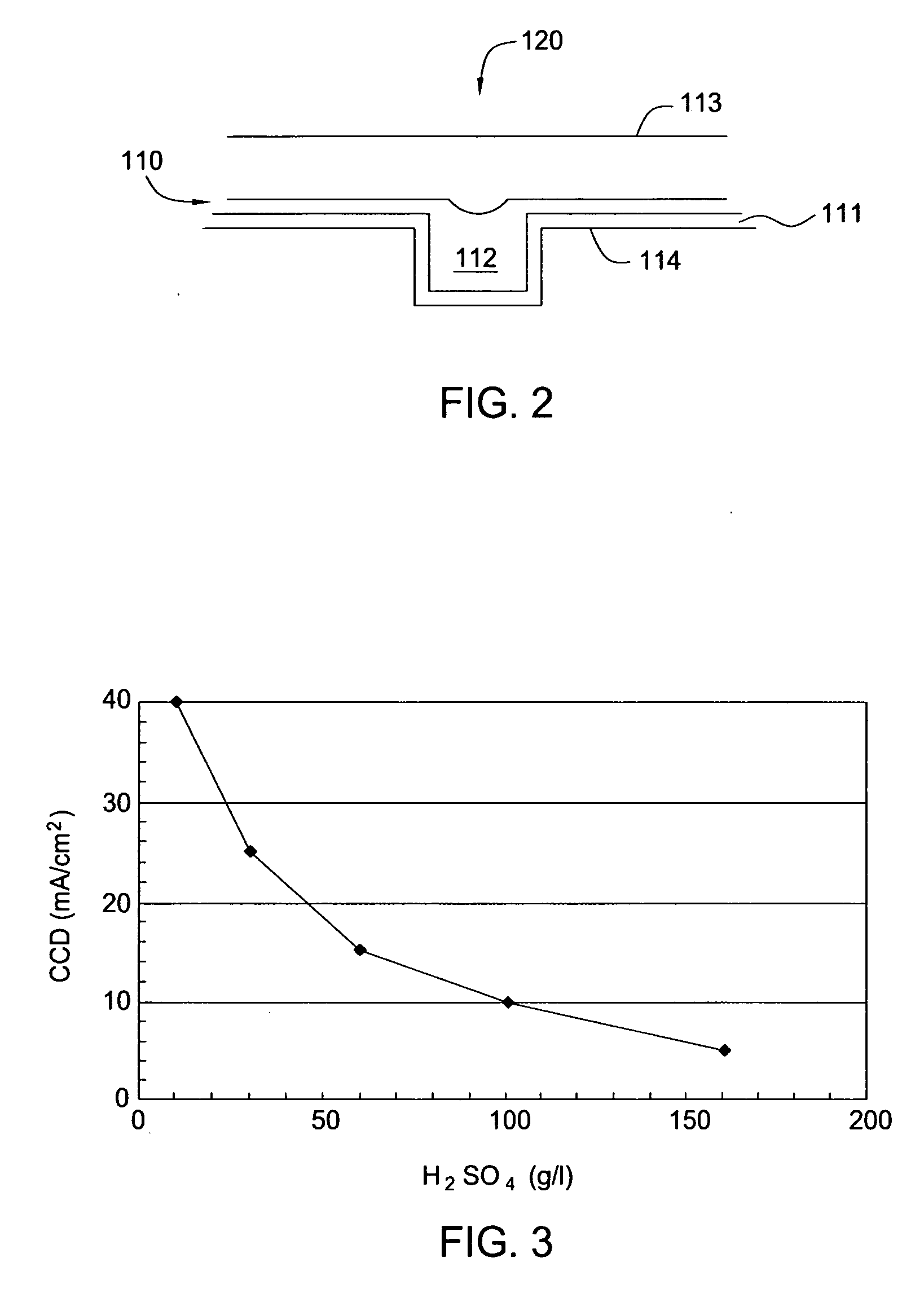
[0021] The present invention teaches a method for depositing a copper layer onto a substrate surface, generally onto a barrier or adhesion layer. The barrier layer may include a refractory metal and / or a group VIII metal. The term group VIII metals (e.g., old CAS system notation) is generally intended to describe group 8, 9 and 10 elements, such as ruthenium (Ru), rhodium (Rh), palladium (Pd), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), osmium (Os), iridium (Ir), and platinum (Pt). The method includes cathodically pre-treating the substrate surface in an acid-containing solution that is free of copper ions. This pre-treatment reduces the critical current density (CCD) required for forming a continuous and void-free seed layer on the barrier or adhesion layer via an ECP process. The substrate is then placed into a neutral or alkaline (pH≧7.0) complex copper solution that includes complexed copper ions and a current or bias is applied across the substrate surface. A “complex bath” or “complex solution”...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by atom | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com