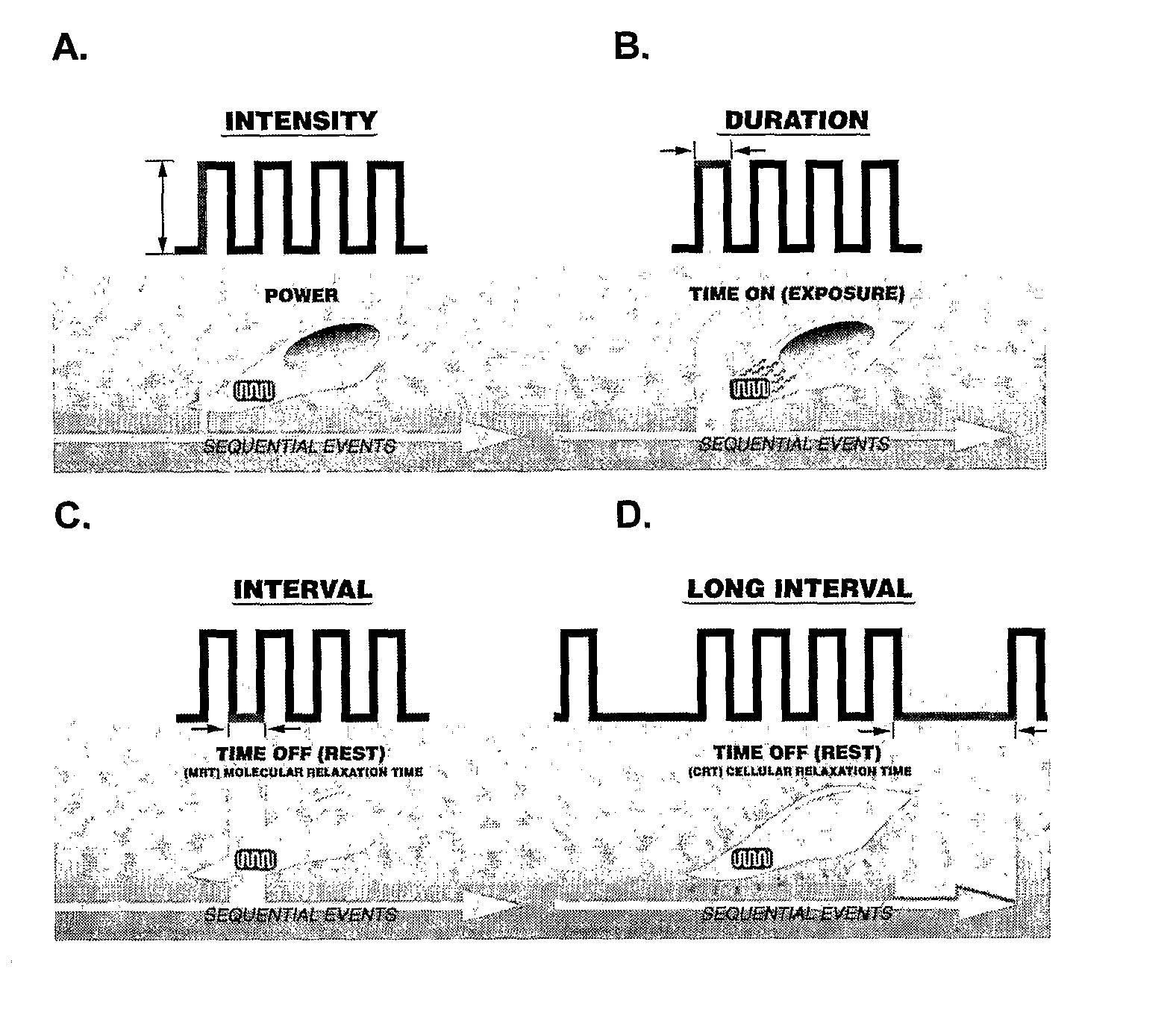
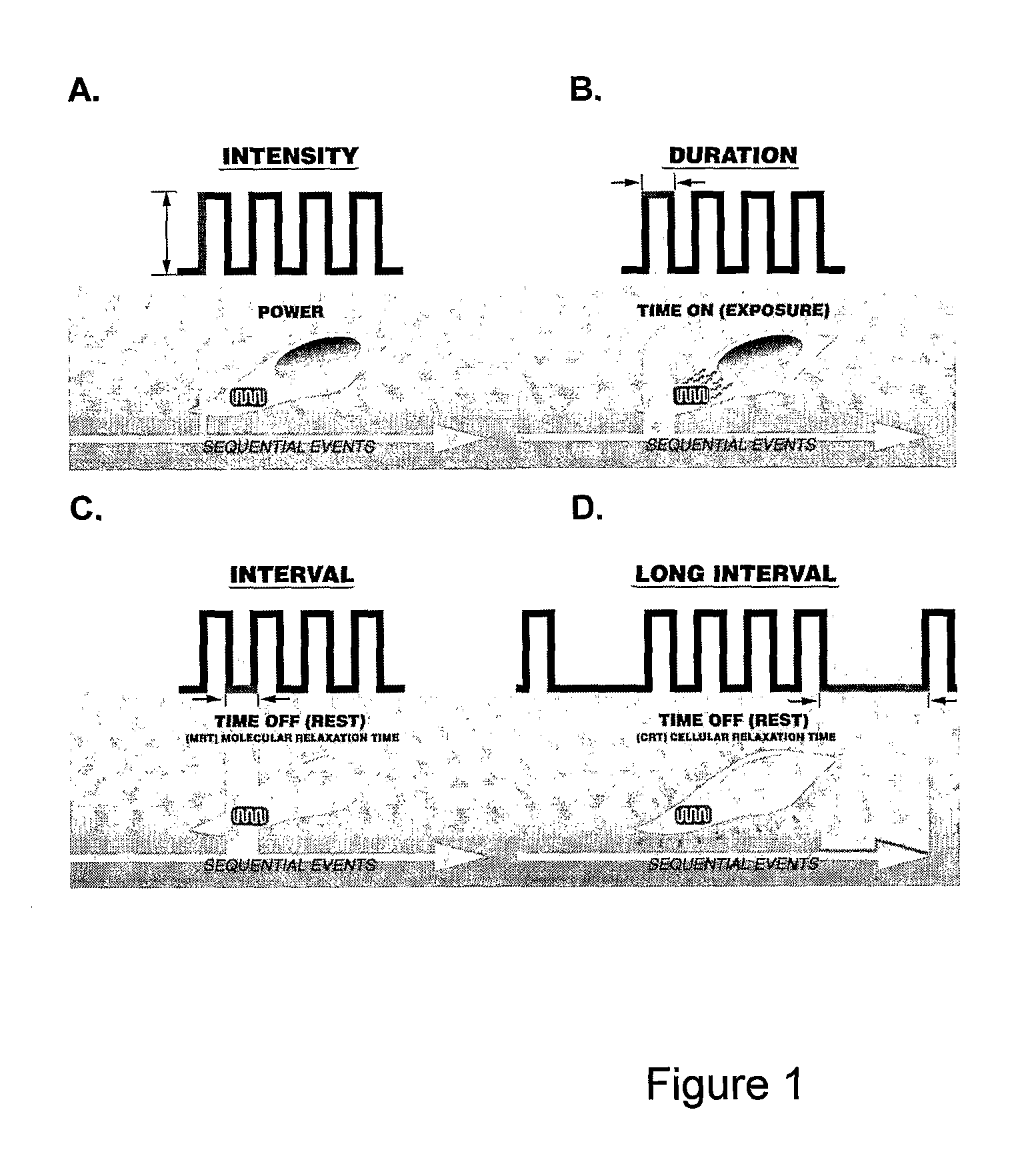
Method for the Treatment of Mammalian Skin Tissues Via Pulse Irradiation in the Presence of a Photoactive Compound
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
In vitro Experiments:
In vitro Experiments: Human Reconstructed Skin Model
[0083] Cell culture media. Keratinocytes were grown in complete DME-HAM medium: a combination of Dulbecco-Vogt modification of Eagle's medium (DME) with Ham's F12 in a 3:1 proportion (Gibco), supplemented with 5% Fetal Clone II serum (FCSII) (HyClone, Logan, United States), 10 ng / mL epidermal growth factor (Austral biologicals, San Ramon, United States), 24.3 μg / mL adenin (Sigma), 5 μg / mL insulin (Sigma), 5 μg / mL transferrin (Roche), 2×10−9 M 3,3′5′ triiodo-L-thyronin (Sigma), 0.4 μg / mL hydrocortisone (Calbiochem, La Jolla, United States), 100 IU / mL penicillin G (Sigma), and 25 μg / mL gentamycin (Schering, Pointe-Claire, Canada). Fibroblasts were cultured in DME containing 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) (HyClone), 100 IU / mL penicillin G, and 25 μg / mL gentamycin.
[0084] Cell isolation. Human epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts were isolated from normal skin specimens; keratinocytes are mainly found in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com