Computing long term orbit and clock models with variable time-horizons
a clock model and long-term orbit technology, applied in the field of global navigation satellite system (gnss) receivers, can solve the problems of less accurate, the accuracy of the worst-case satellite clock model is much more than the orbit accuracy, and the accuracy of the worst-case clock model of ultra-rapid orbits is many times worse than the quoted accuracy. to achieve the effect of improving the accuracy of the orbit and clock model
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
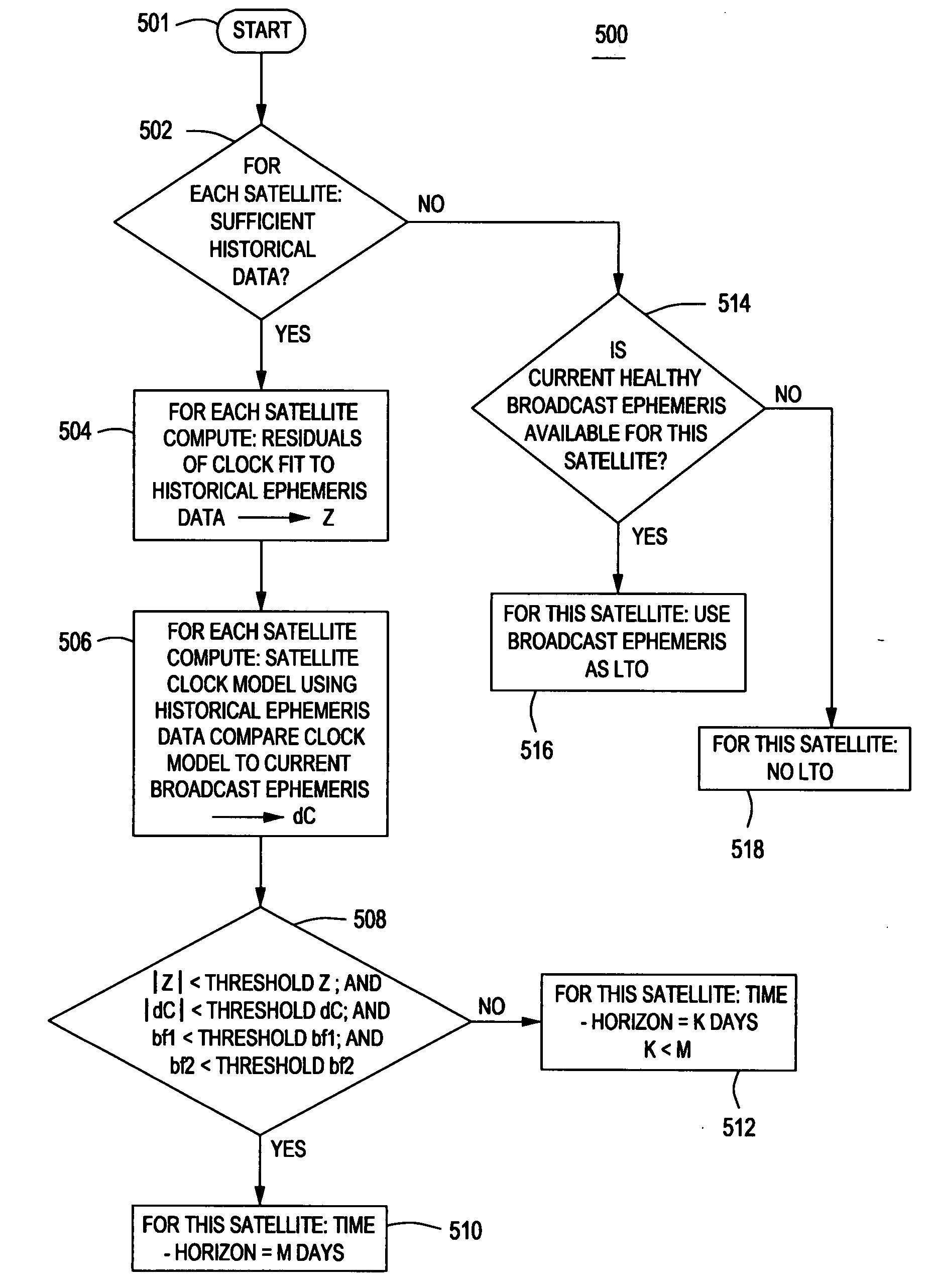
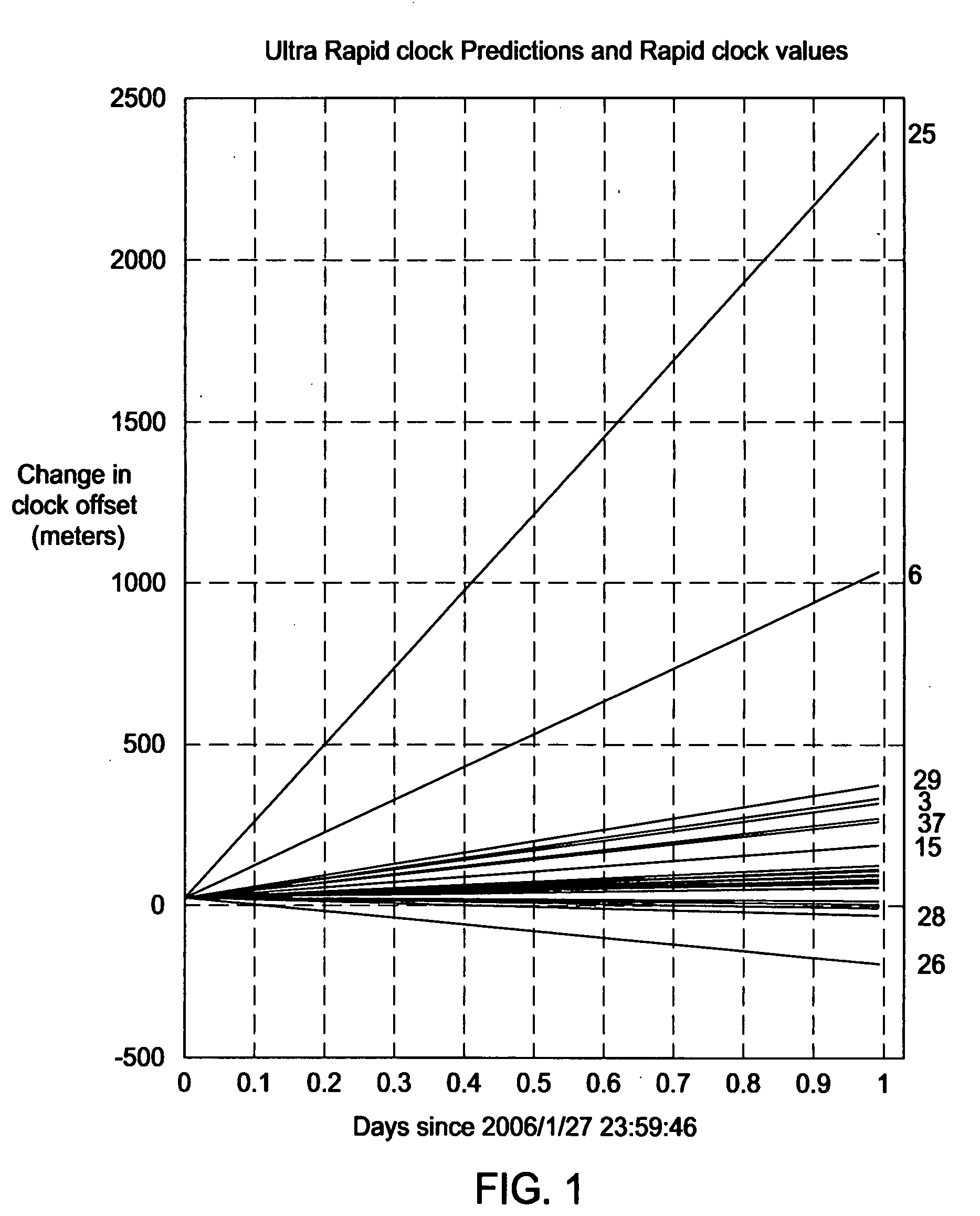
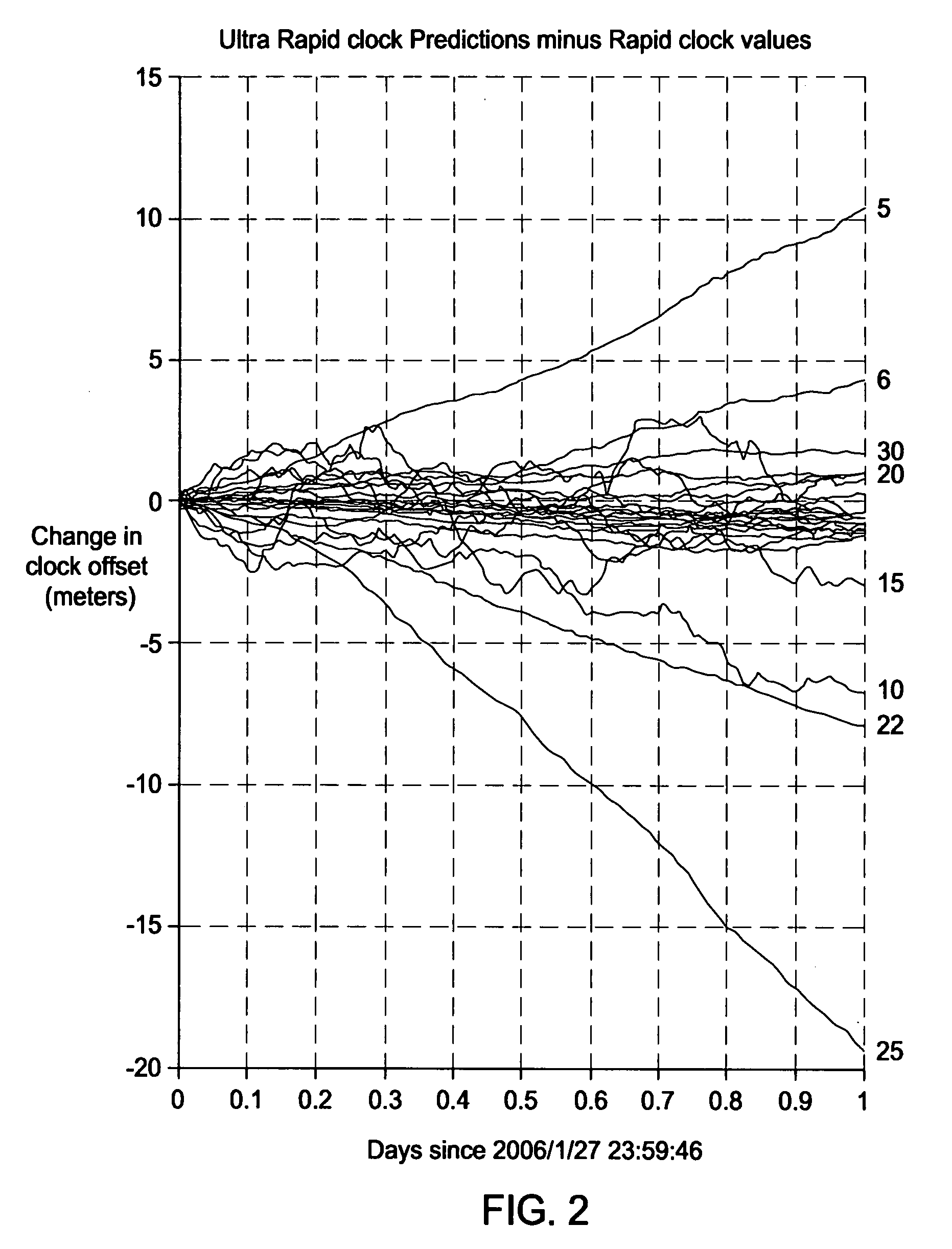
[0022]FIG. 3 depicts a computer system 300 used for creating long term orbit (LTO) models using variable time horizons in accordance with the present invention. The computer system 300 comprises a central processing unit (CPU) 302, support circuits 304 and memory 306. The processor 302 may be one or more commercially available microprocessors or microcontrollers. The support circuits 304 comprise well-known circuits used to facilitate operation of the CPU 302 including, but not limited to, cache, clock circuits, power supplies, input / output circuits, and the like. The memory 306 comprises one or more digital storage circuits or devices including, but not limited to, random access memory, read only memory, optical memory, disk drives, removable storage, and the like. The memory 306 stores LTO software 308 that, when executed by the CPU 302, causes the CPU 302 to perform a method of generating at least one LTO model in accordance with the present invention. The LTO software 308 compri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com