Containerless mixing of metals and polymers with fullerenes and nanofibers to produce reinforced advanced materials
a technology of nanofibers and nanofibers, which is applied in the field of material science, can solve the problems of high potential, and achieve the effects of increasing strength, shear strength, and strengthening metal systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
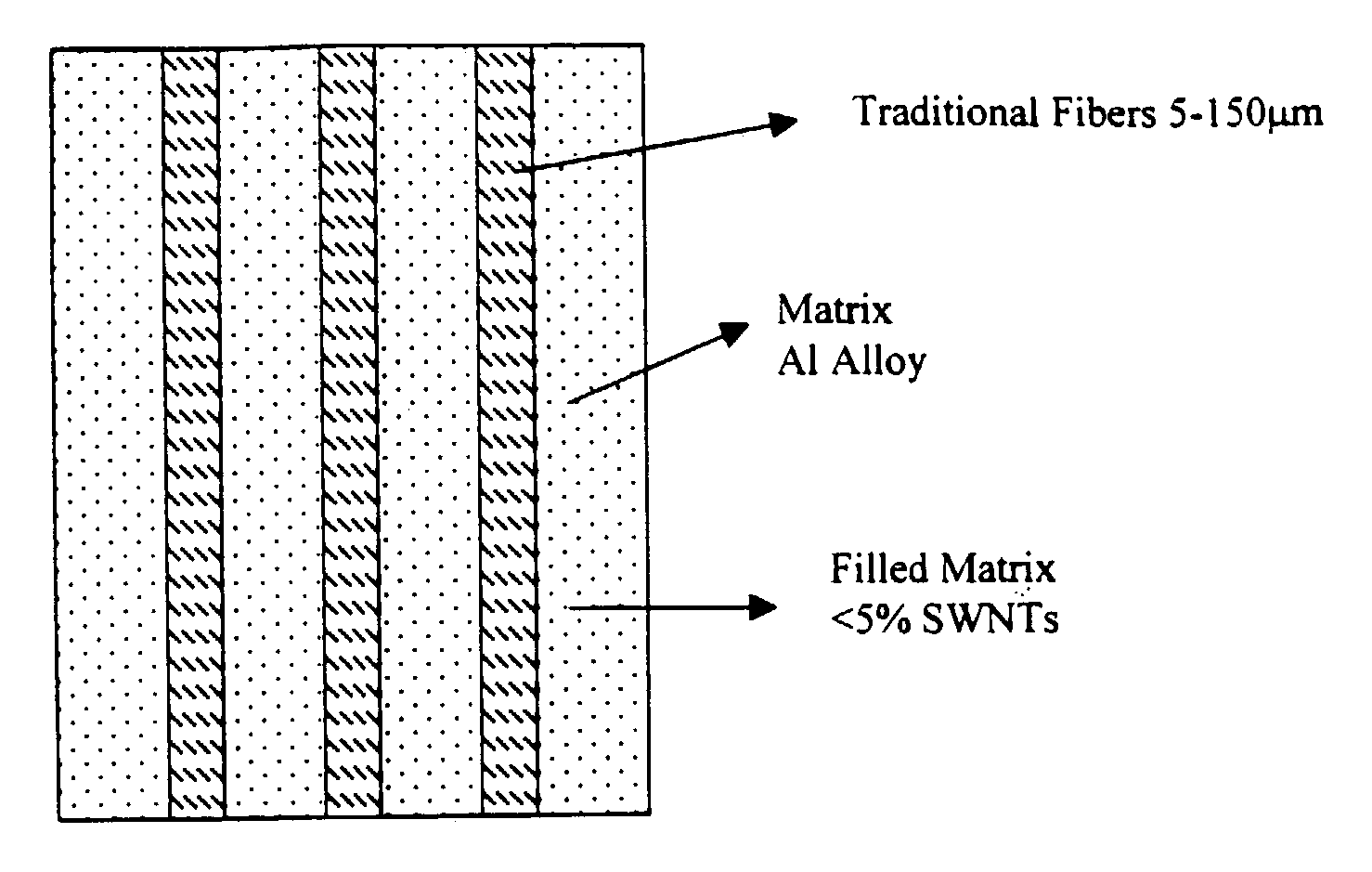
[0030]The present invention allows for the development of composite materials reinforced with single- and multi-walled nanotubes in order to produce materials that are lightweight, possess high strength and stiffness, and show improved composite toughness. A complementing aspect of the invention allows for tailoring the thermal and electrical properties of these nanotube derived materials, and processing and manufacturing parts using them.
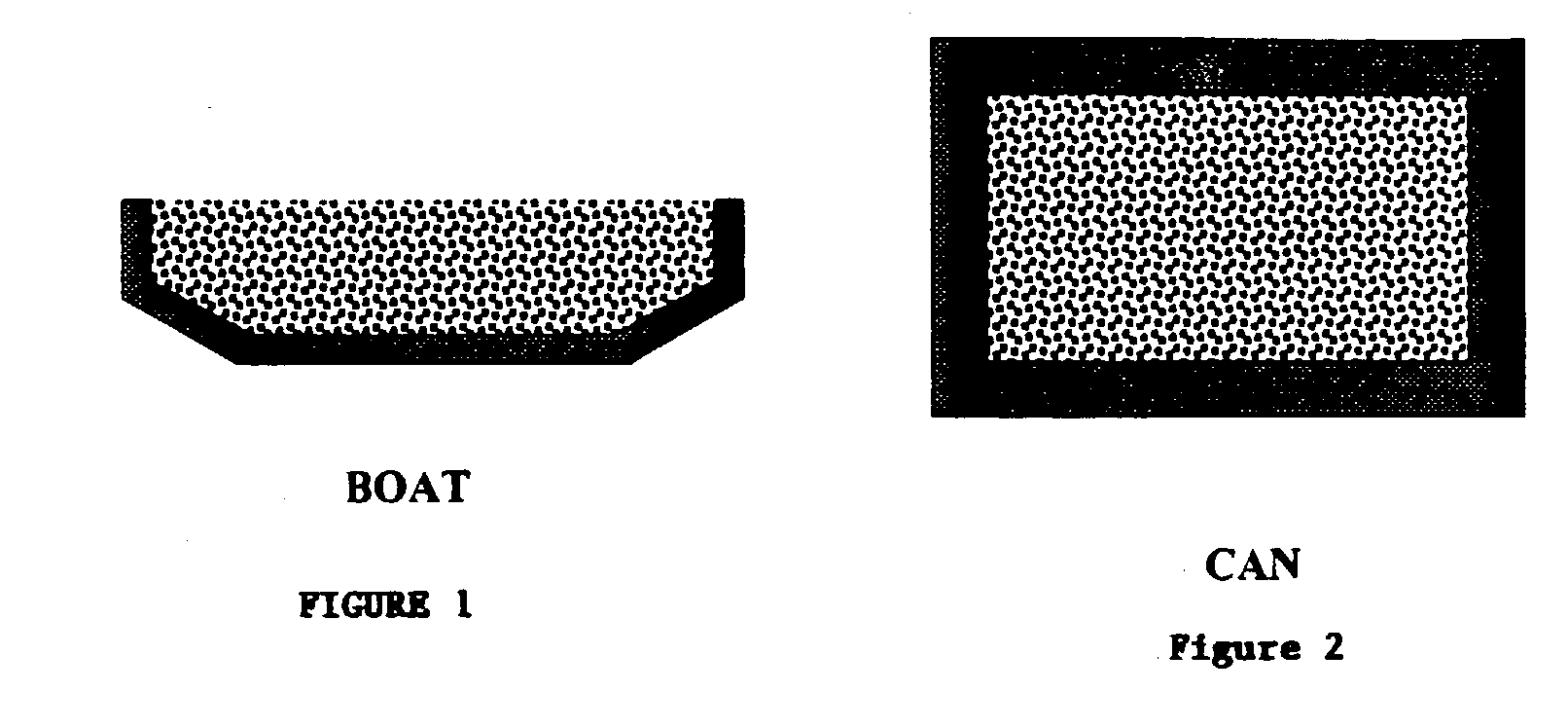
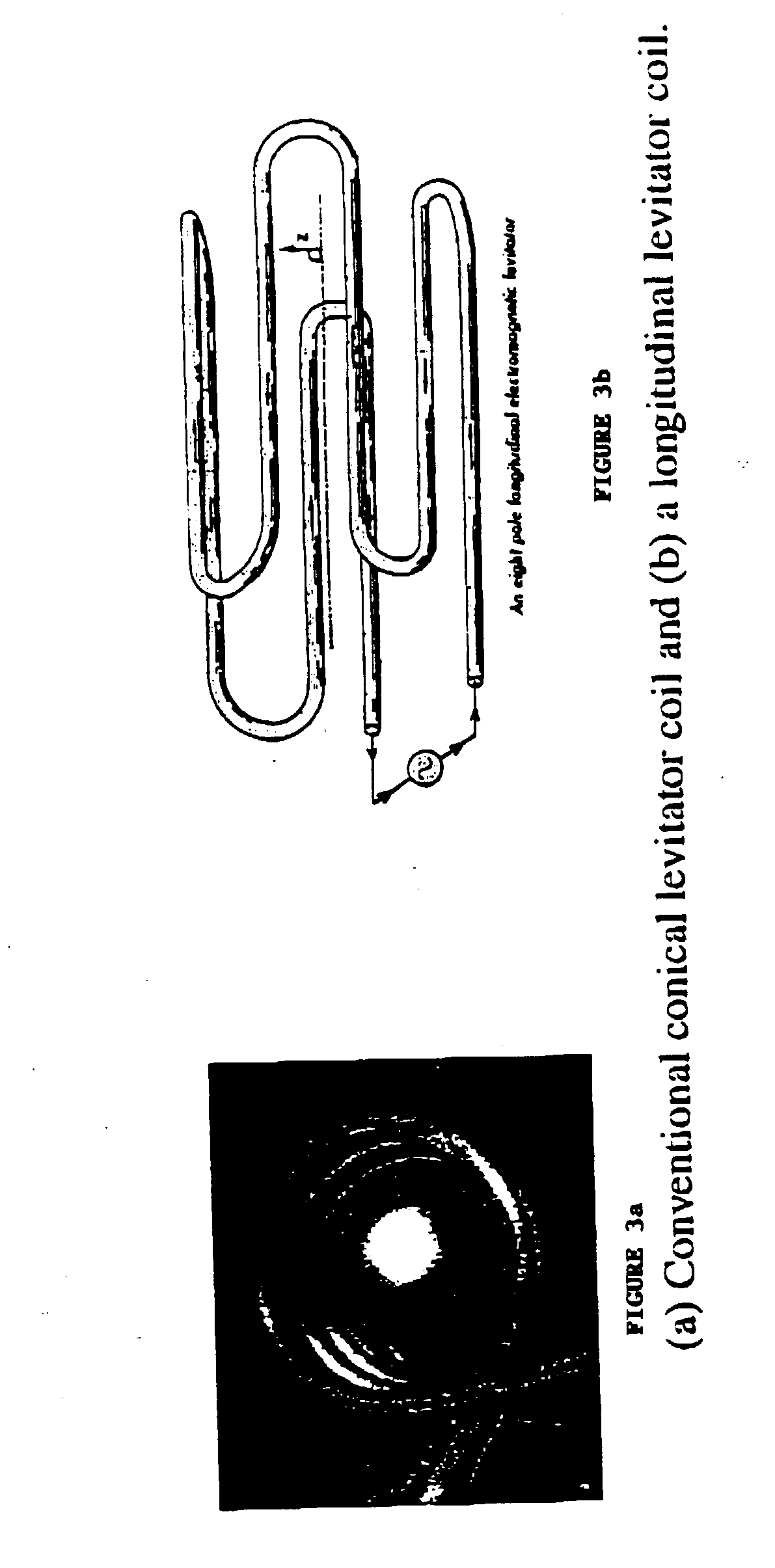
[0031]The problems with infiltration of a metal with the nanotubes can be solved by fluid mixing that occurs in the electromagnetic levitation process. The invention addresses embedded nanotube dispersion, wettability, adhesion, and alignment issues in a matrix of metals. Functionalizing of the metallic and semiconducting nanotubes along the tube wall can be used to ensure wetting. A series of metals and alloy matrices including aluminum, copper, and tin have been processed with nanotubes to investigate the thermophysical properties of the melt mix...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| band gap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electromagnetic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrically conducting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com