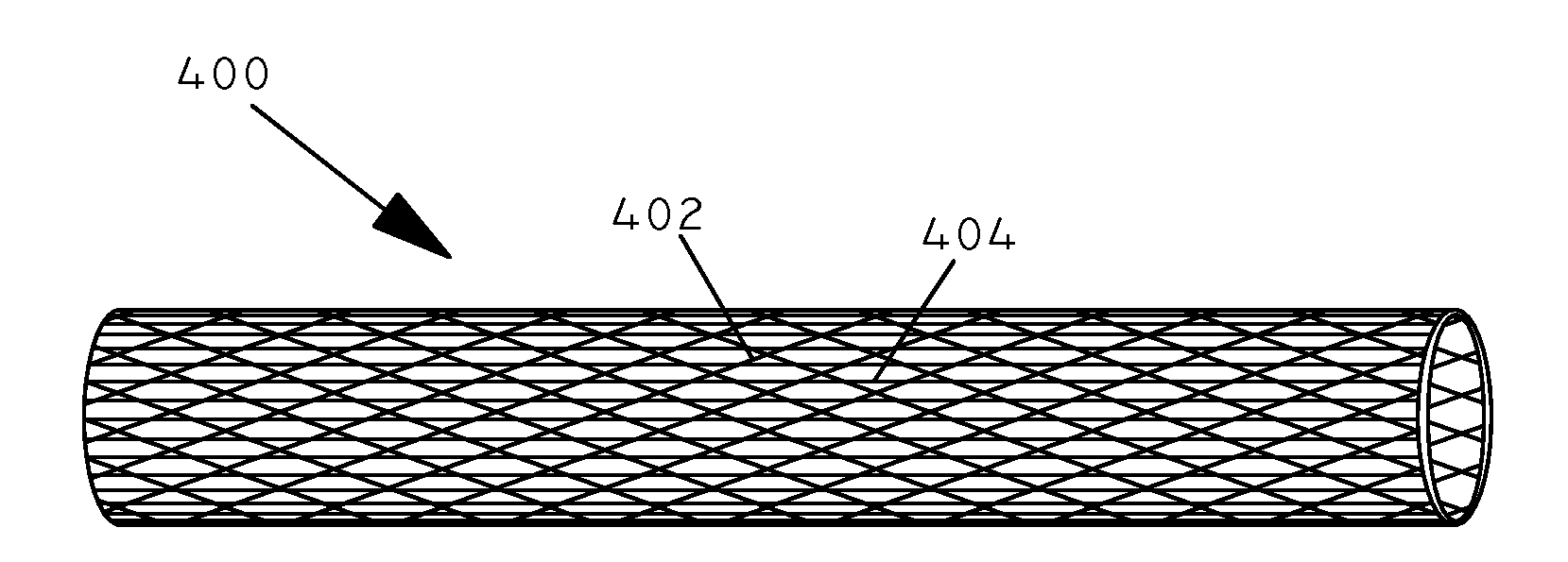
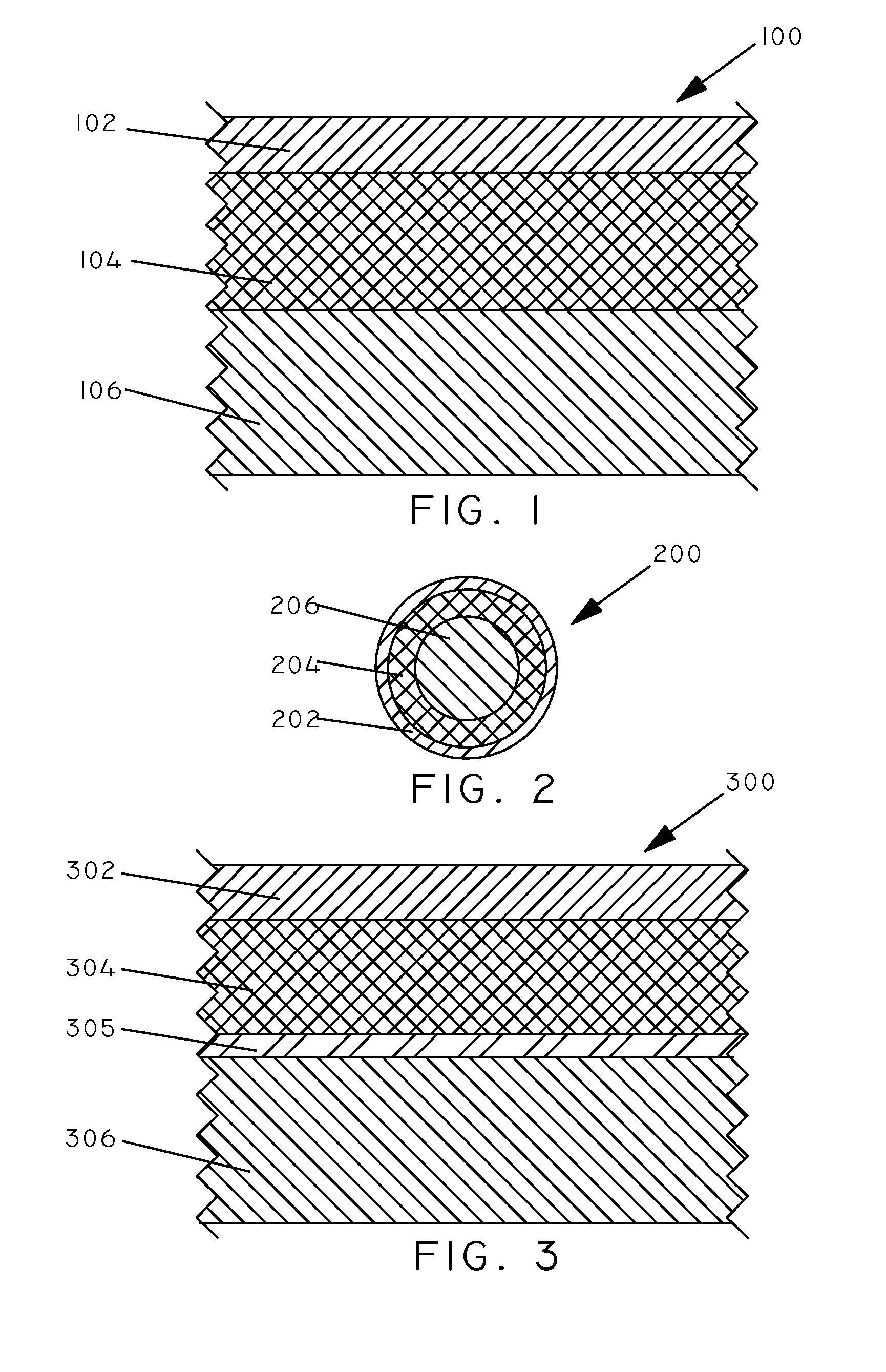
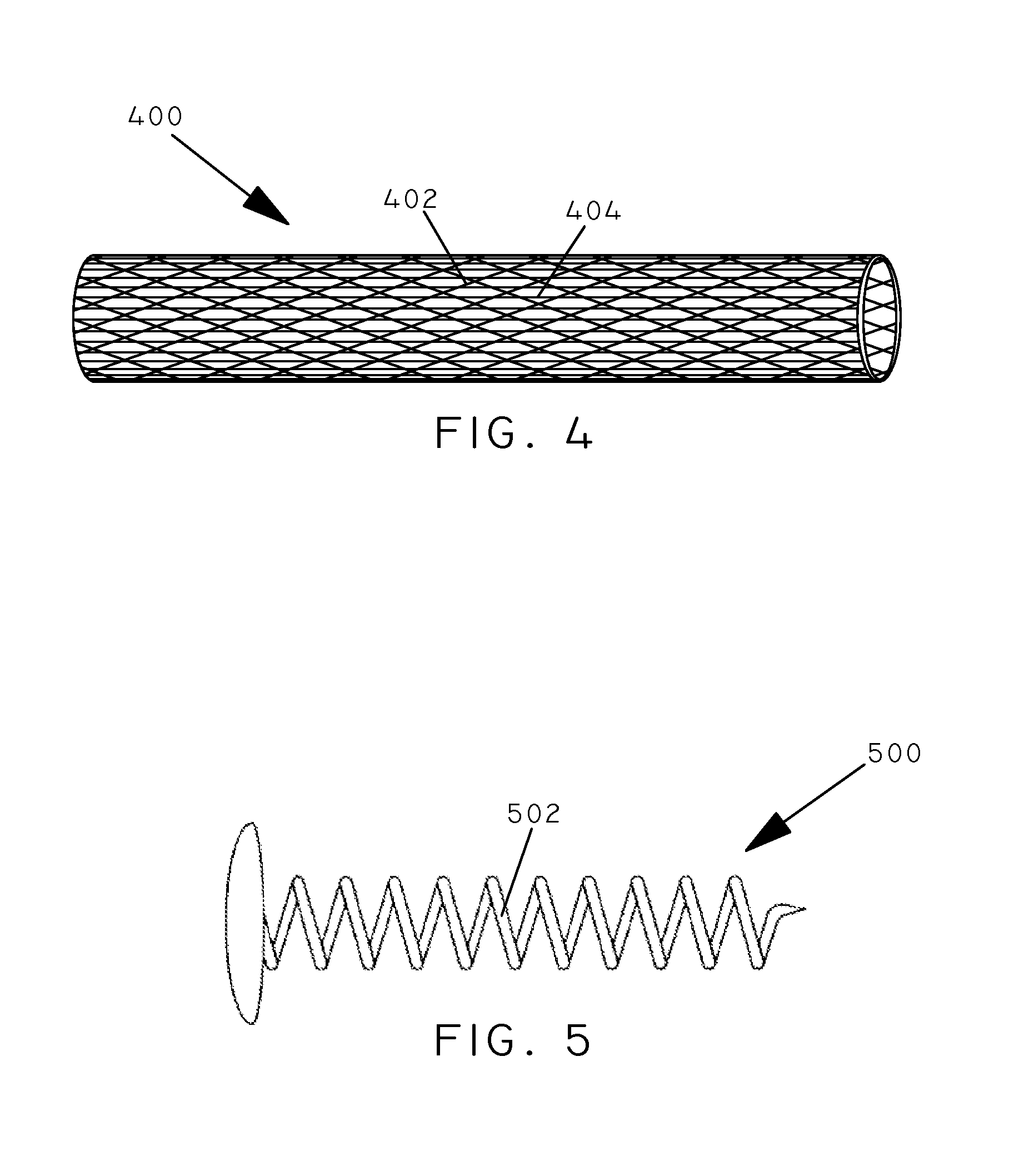
Multi-layered coatings and methods for controlling elution of active agents
a technology of active agents and coatings, applied in the direction of packaging foodstuffs, prostheses, packaged goods, etc., can solve the problems of peptides and proteins being delivered either more quickly or more slowly, and posing a challeng
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Parylene Coat Over Non-Degradable Hydrophobic Matrix
[0089]Poly-n-butylmethacrylate (PBMA) and polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate (PEVA) were combined in a solvent of chloroform to form a non-degradable polymer solution having 10 mg / ml PBMA and 10 mg / ml PEVA (total solids concentration of 20 mg / ml).
[0090]IgG rabbit anti-goat antibodies were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo. The IgG rabbit anti-goat antibodies were combined with non-specific IgG rabbit antibodies at a ration of 10:1 non-specific to specific in PBS (phosphate buffered saline) to form an IgG solution.
[0091]MP-35N alloy coils (N=7) were simultaneously coated with both the non-degradable polymer solution and the IgG solution. The non-degradable polymer solution was applied onto the exterior surface of a first ultrasonic nozzle (60 KHz ultrasonic nozzle from Sono-Tek, Milton, N.Y., operating at about 0.5 to 1.5 watts) at a rate of 0.025 mL / minute. Simultaneously, the IgG solution was applied onto the exterior surface ...
example 2
Effects of Vacuum Drying on Elution Rate
[0095]Poly-n-butylmethacrylate (PBMA) and polyethylene-co-vinyl acetate (PEVA) were combined in a solvent of chloroform to form a non-degradable polymer solution having 12.5 mg / ml PBMA and 12.5 mg / ml PEVA (total solids concentration of 25 mg / ml).
[0096]IgG rabbit anti-goat antibodies were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo. The IgG rabbit anti-goat antibodies were combined with non-specific IgG rabbit antibodies at a ration of 10:1 non-specific to specific in PBS (phosphate buffered saline) to form an IgG solution with a concentration of 20 mg / ml of IgG.
[0097]MP-35N alloy coils (N=4) were segregated into two experimental groups (Group 1 (N=2) and Group 2 (N=4)). The non-degradable polymer solution and the IgG solution were simultaneously deposited onto the coils. Specifically, the non-degradable polymer solution was applied onto the exterior surface of a first ultrasonic nozzle (60 KHz ultrasonic nozzle from Sono-Tek, Milton, N.Y., oper...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| period of time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com