Avalanche photodiode detector
a photodiode detector and photodiode technology, applied in the field of photodiode detectors, can solve the problems of reducing the overall quantum efficiency and after pulsing performance of an apd, affecting the selection of materials, and affecting the quality of the photodiod
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
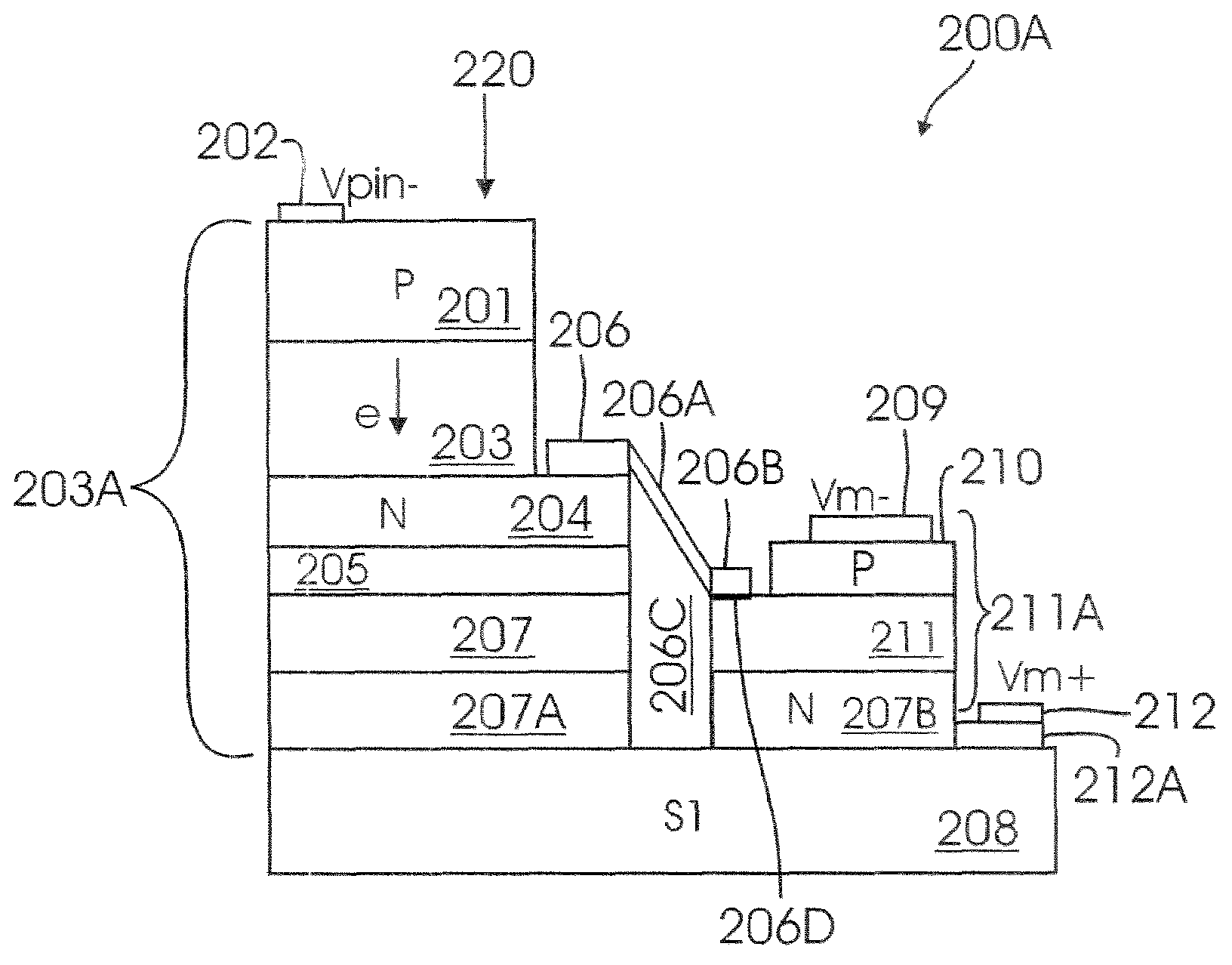
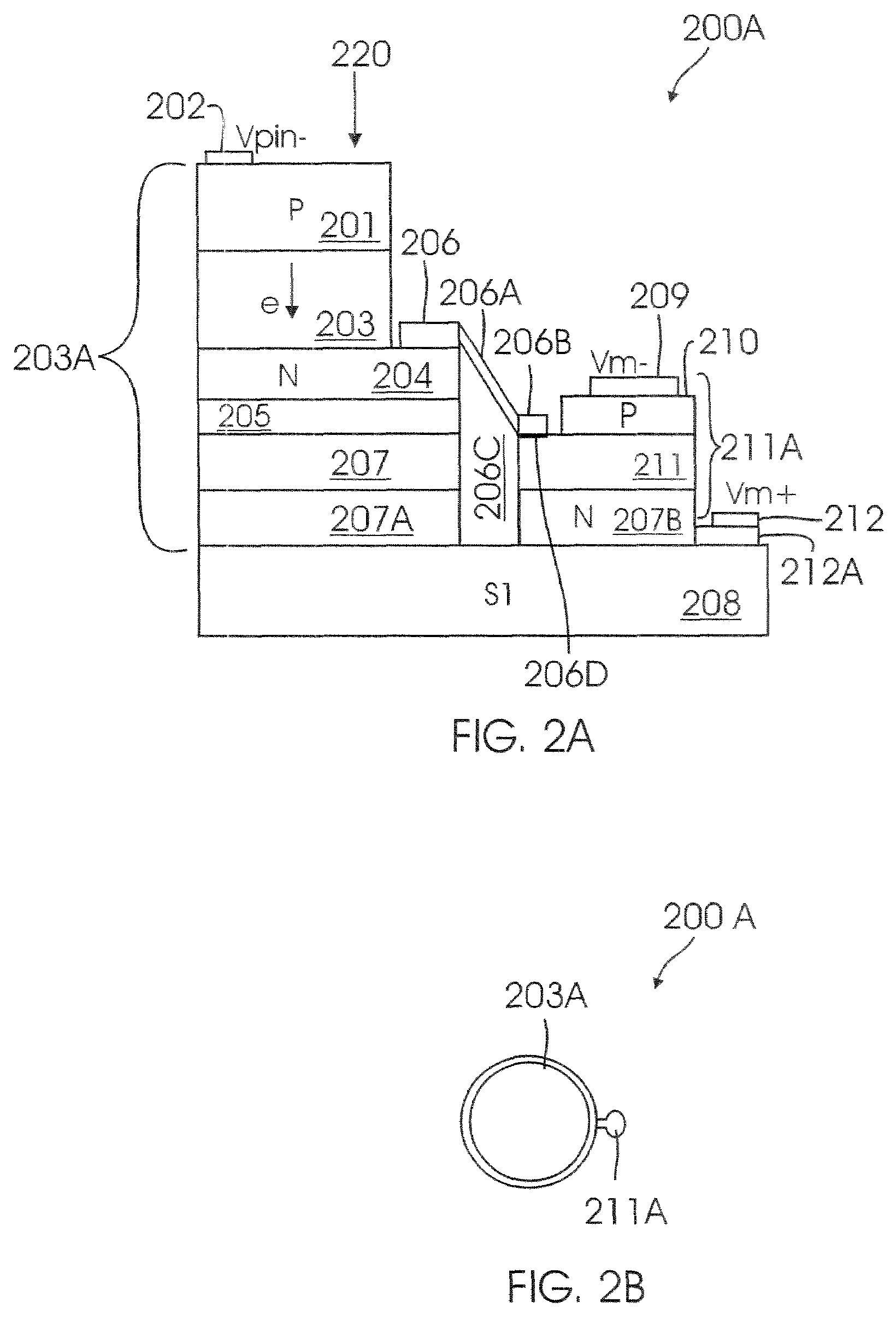
[0018]In one aspect of the present invention, a three terminal APD structure with separate absorption and multiplication layer (also referred to as “TT-SAM APD or APD”) is provided. The absorption layer and multiplication layer may be grown separately and hence are controlled independently. This allows one to select different materials for the absorption and multiplication layer. The APD of the present invention also provides an additional terminal. The additional terminal enables individual control of bias across an absorption (Absorber”) region and a multiplication (“Multiplier”) region.
[0019]To facilitate an understanding of APD structure, a general overview of a conventional APD structure will be described. The specific structural components and layers of APD of the present invention, will then be described with reference to general structure of APD.
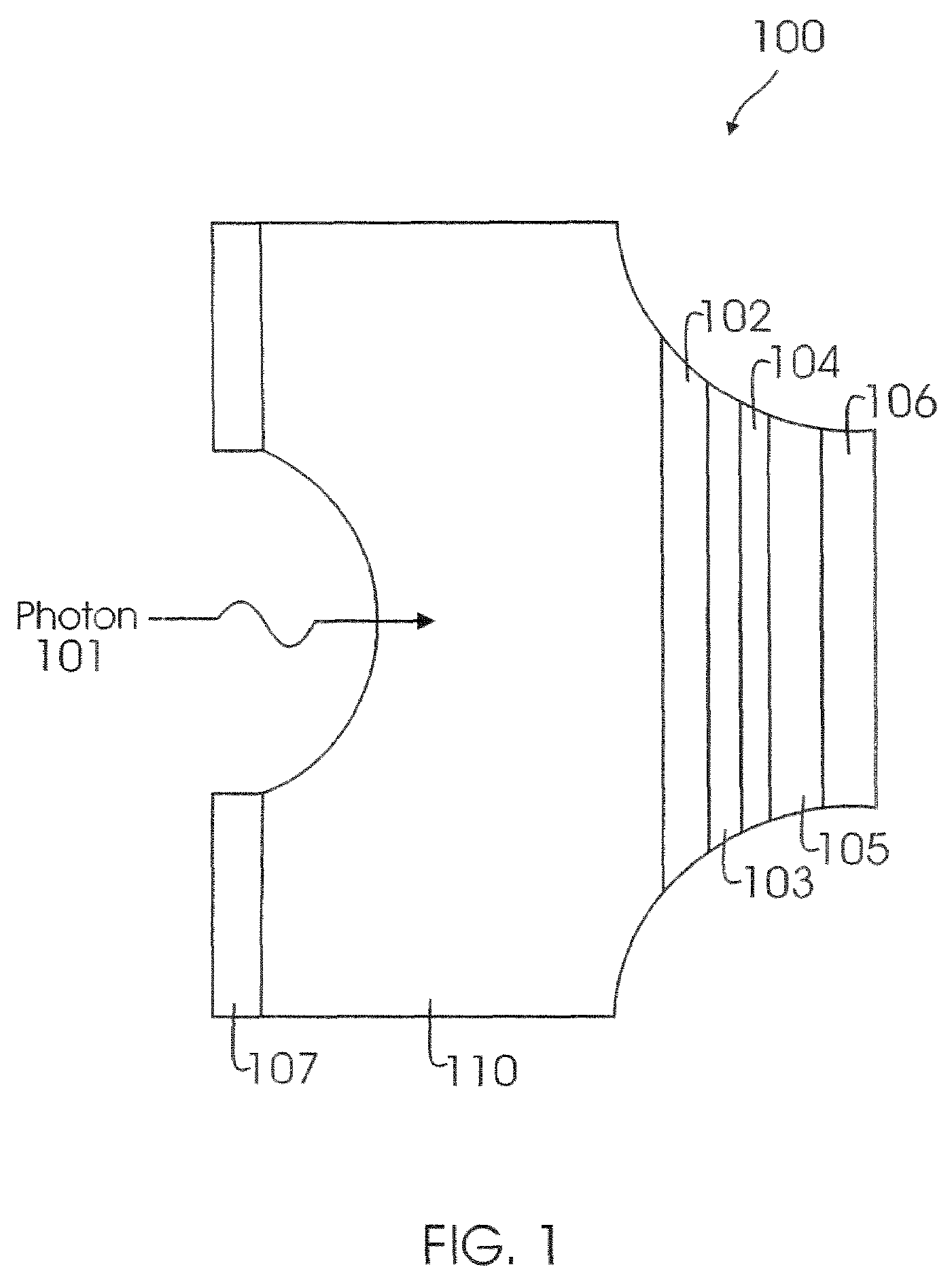
[0020]FIG. 1 shows a top level block diagram of a conventional APD structure. APD 100 includes a P-InP substrate layer 110; a P-InP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com