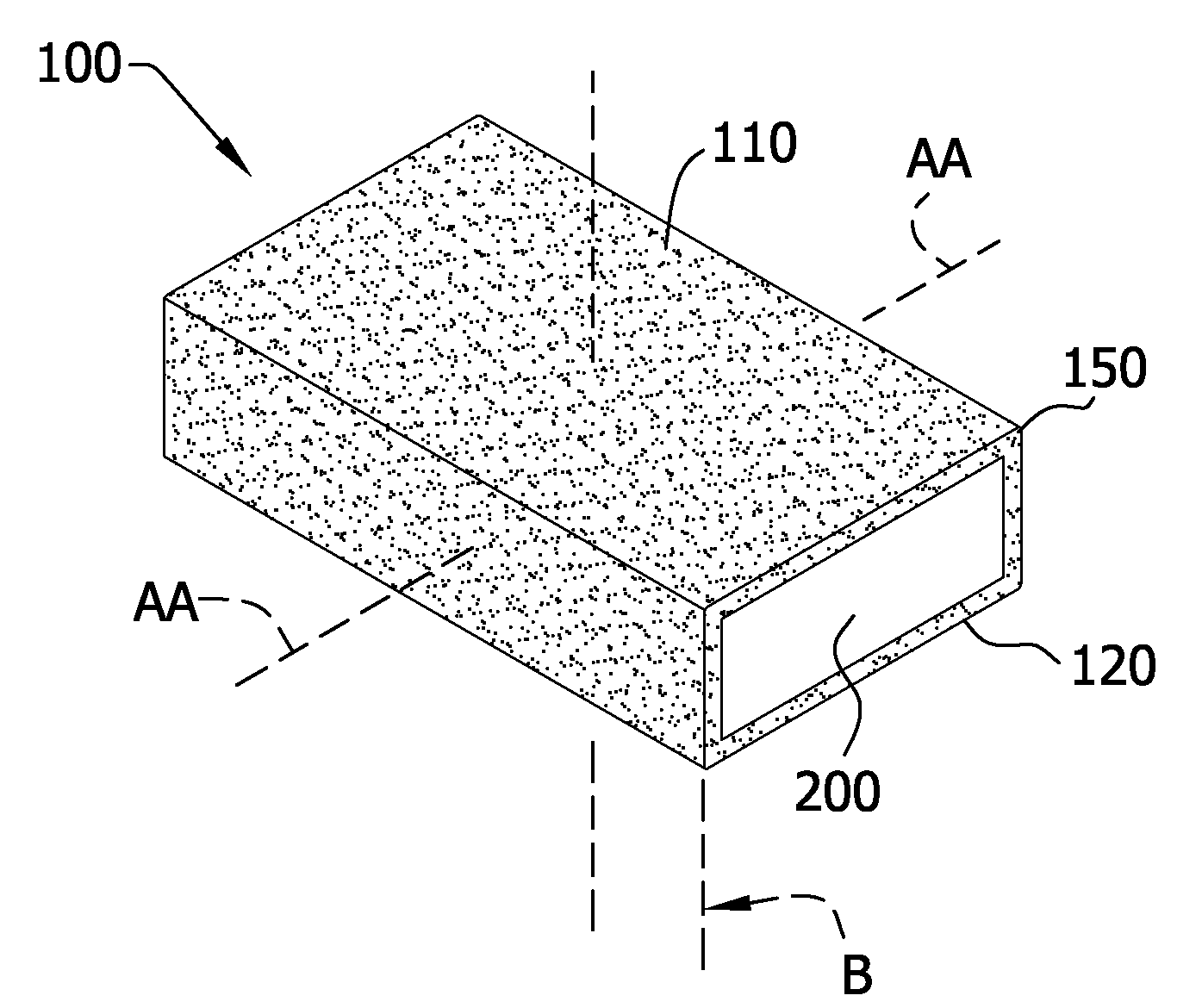
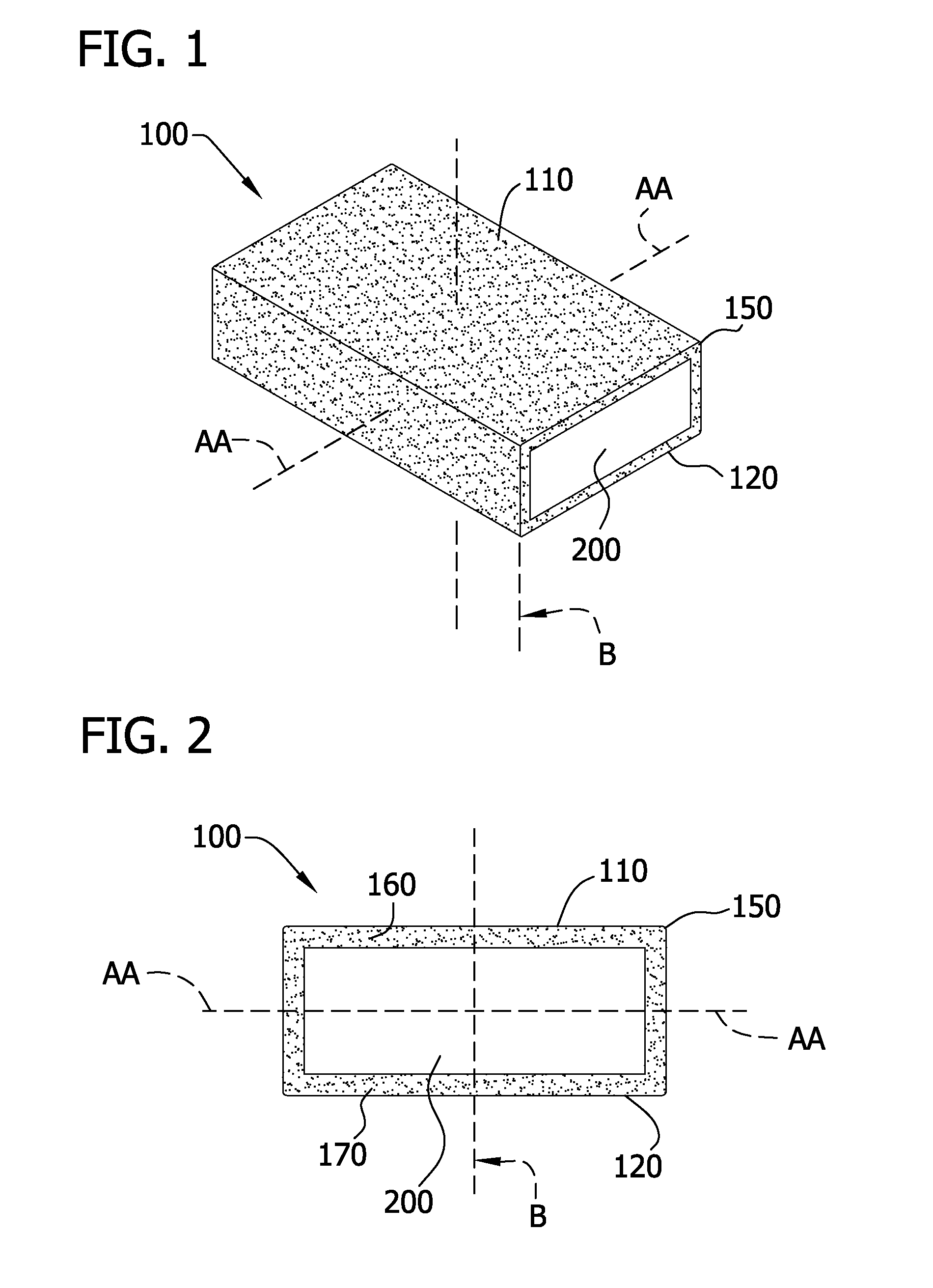
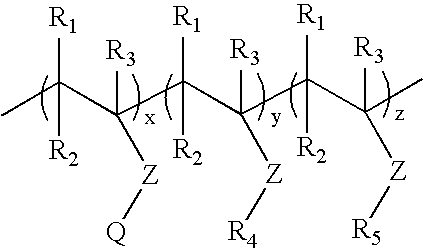
Wet wipe having a stratified wetting composition therein and process for preparing same
a wet wipe and composition technology, applied in weaving, lightening and heating apparatus, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of limited application of terpolymer as a dispersible binder in such wipes, inability to achieve hard water dispersibility, and limited solution-based systems in terms of ingredients or components. to achieve the effect of more economical or less expensive, maximizing skin us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0237]In this Example, a formulation was made with silicone phospholipids, and more specifically has the following composition:
Water =89.7 wt %; Monasil PCA (PCA dimethicone) = 5 wt %;Cetiol HE (PEG-7 glyceryl cocoate) =1.5 wt %;Propylene Glycol =1.5 wt %;Glydant Plus =0.3 wt %;Sodium Chloride = 2 wt %.
[0238]This formulation is known to be unstable, and thus phase separate, over time. Water-disintegratable or dispersible wipes were made with this formulation and allowed to age at room temperature for 1 week. At the end of the 1 week period, another batch of the same formulation was made, and another set of wipes was prepared therefrom. Both set of these wipes were then immediately evaluated in a blind test by 10 panelists. All but one panelist detected a difference between the feel of these wipes. The aged wipes were generally described as “silkier,” or “softer,” or “less sticky,” and sometimes perceived as thicker than the freshly prepared wipes. These results suggest that phase ...
example 2
[0239]A stratified wipe may be prepared by preparing a concentrated wipe emulsion according to formulation in the following table. The batching procedure would be as follows:[0240]1) Phase 1: Add ingredients with mixing and while heating to 40° C. until homogeneous.[0241]2) Disperse PEMULEN™ in PHA while heating to 40° C. Add to Phase 1 with high agitation and allow to hydrate 30 minutes.[0242]3) Combine the rest of the organic phase and heat to 40° C. Add to water phase with mixing for 10 minutes.[0243]4) Neutralize with KOH 10% to an approximate pH of between 6.5 and 7. Begin cooling to room temperature.[0244]5) Add preservative and mix until room temperature is reached.
Stratified Wipe ConcentrateTrade NameINCI Name% wtPhase 1WaterWater91.65Butylene GlycolButylene Glycol1.25Versene Na2 (Dow)Disodium EDTA0.05Phase 2Hetester PHAPropylene Glycol2.50(Bernel / Alzo)Isoceteth-3 AcetatePEMULEN ™ TR-1Acrylates / C10–30 Alkyl0.20(Noveon)Acrylate CrosspolymerPhase 3Safflower OilCarthamus Tincto...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com