Enhanced Slurrification Method
a technology of enhanced slurrification and oily materials, which is applied in the direction of mixing methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, drilling compositions, etc., can solve the problems of large quantities of this kind of equipment, large health and safety risks, and large quantities of oil contaminated drilling materials removed from wells. achieve the effect of enhancing the slurrification and pumpability of oily materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
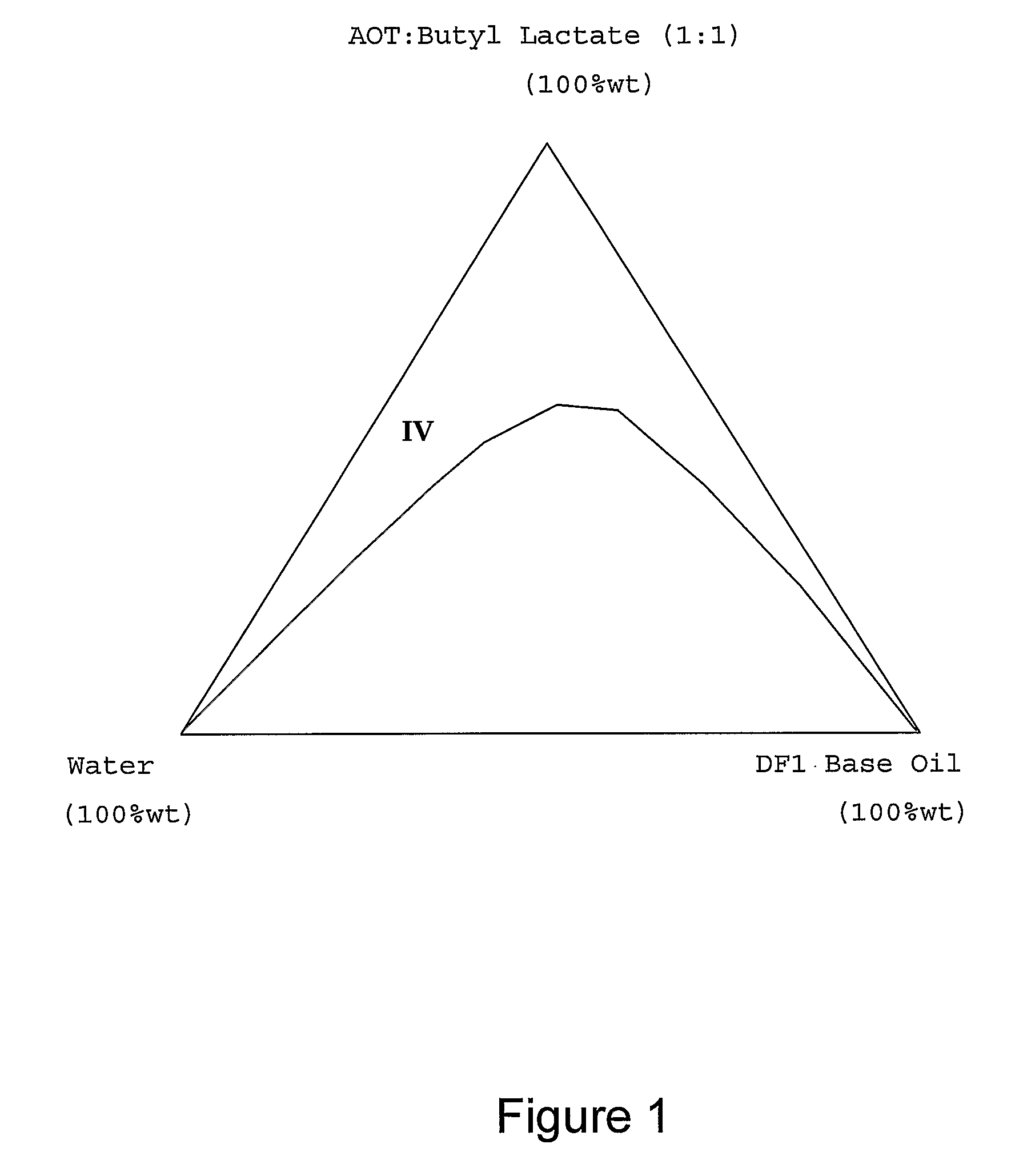
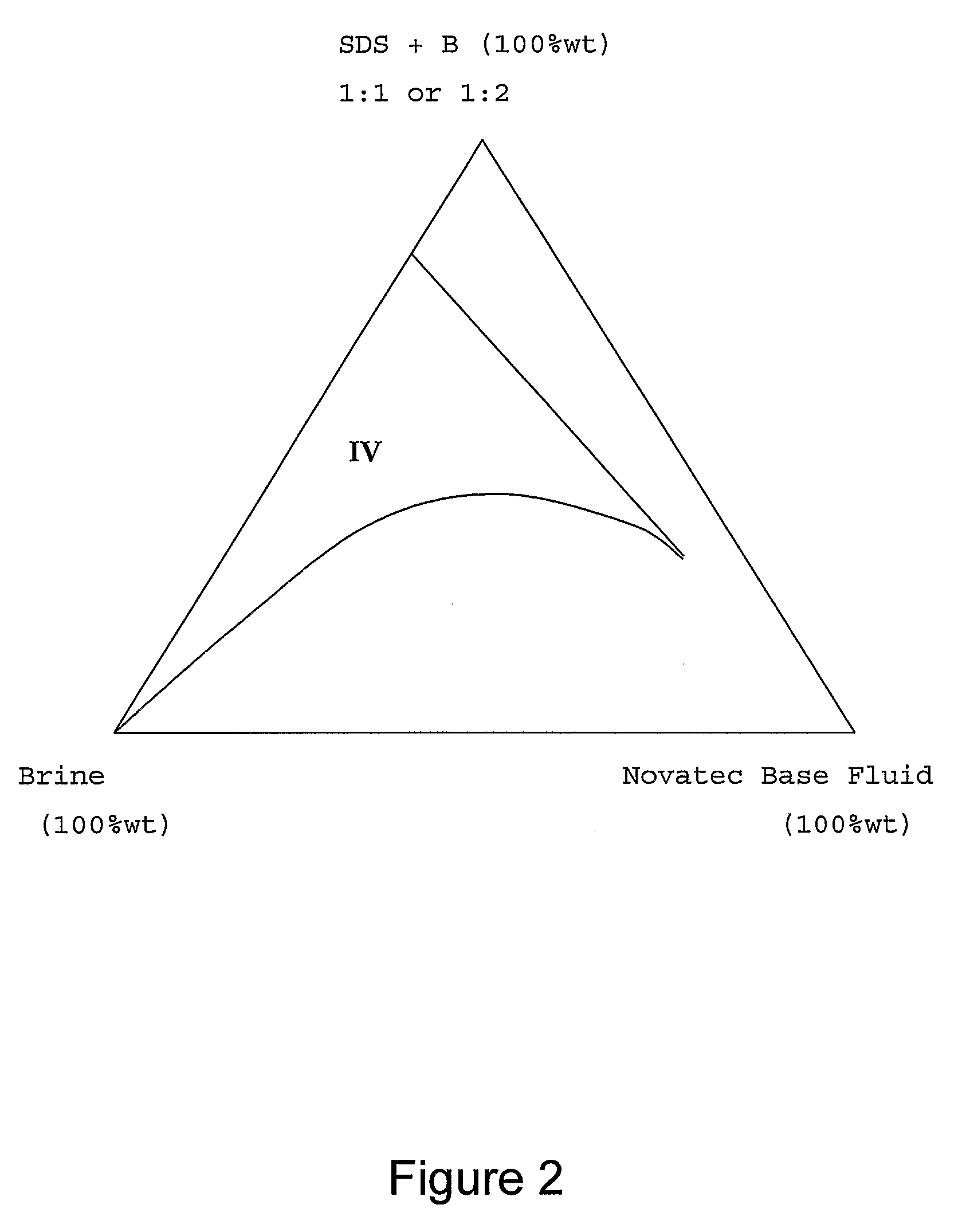
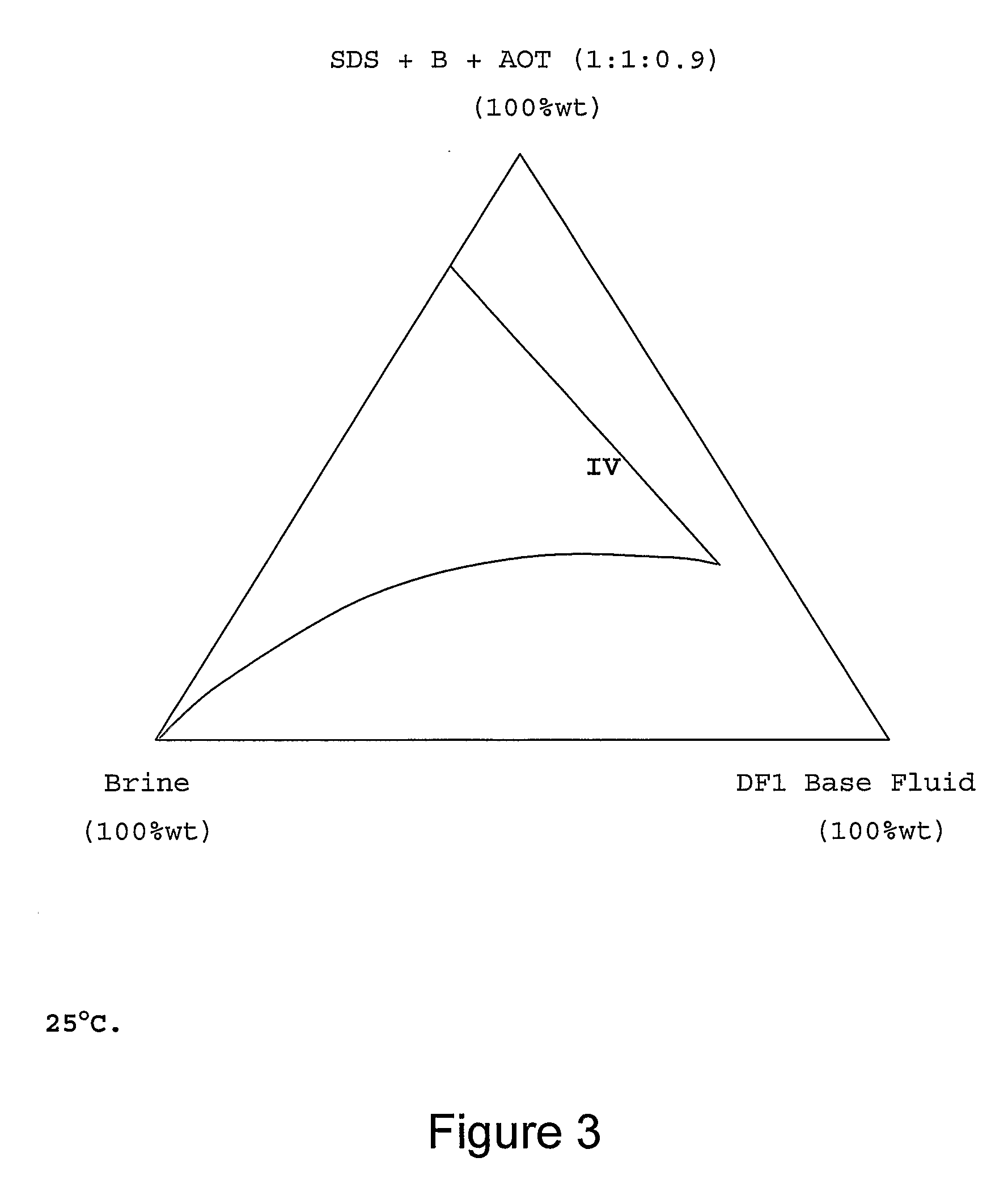
[0023]The term microemulsion was first referred to in the 1950's to describe specific surfactant stabilised immiscible fluid systems that exhibited extremely low interfacial surface tensions. At the time, it was thought that these mixtures were like conventional emulsion systems (macroemulsions), but with much smaller droplet (micelle) sizes, hence the use of the term. The terminology is still in use today but the modern understanding of these systems originally described show that microemulsions are fundamentally different from small droplet conventional emulsion type systems. Microemulsions are dynamic systems with structures, which may or may not be droplets that form, disintegrate, and reform in milliseconds. Several structures or domains are known to exist—the simplest being that of the micelle, with lamellae, spherulite and bi-continuous (sometimes referred to as a sponge phase) structures or domains being present, or existing as transitional stages between other structures. O...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mixing forces | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com