Semiconductor memory device having selective activation circuit for selectively activating circuit areas
a memory device and selective activation technology, applied in the direction of information storage, static storage, digital storage, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to control only a part of the internal circuit, the sub-threshold current of the transistor is increased in a non-conductive state, and the power consumption cannot be reduced to a satisfactory extent, so as to achieve the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
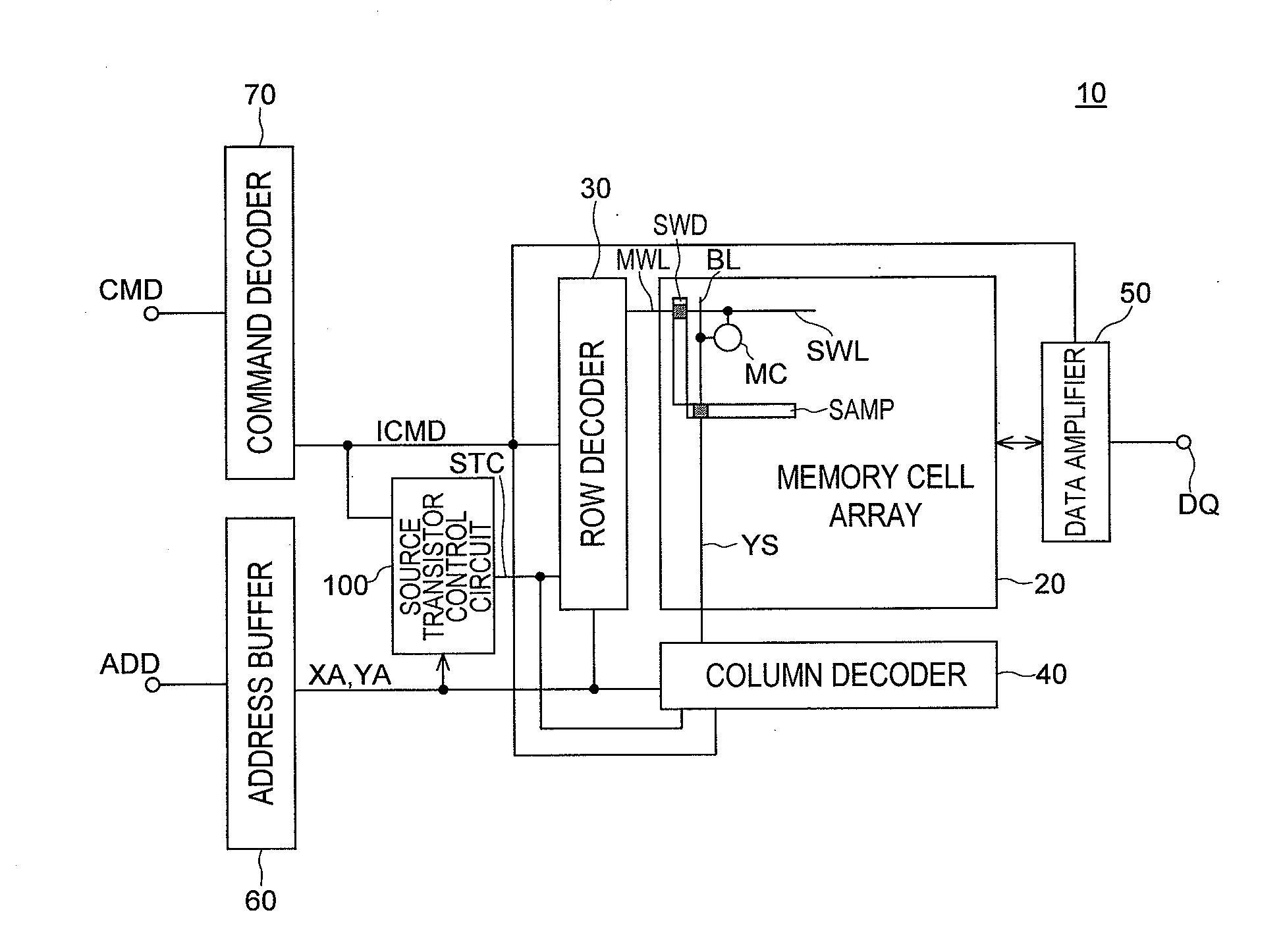
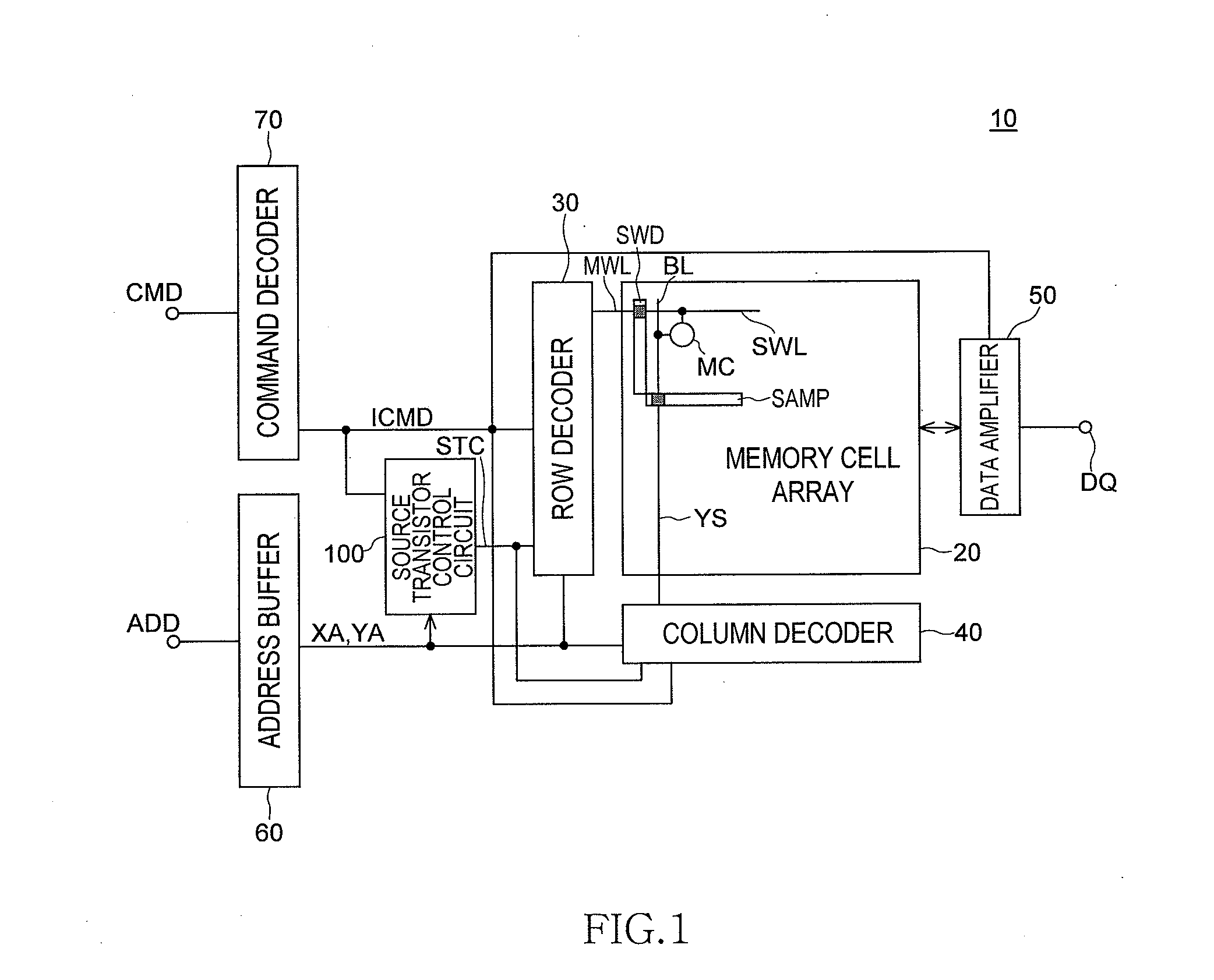
[0030]FIG. 1 is an overall block diagram of a semiconductor memory device 10 according to the present invention.
[0031]As shown in FIG. 1, the semiconductor memory device 10 includes a memory cell array 20 that includes a plurality of memory cells, a row decoder 30 that performs a row access to the memory cell array 20, and a column decoder 40 that performs a column access to the memory cell array 20. The memory cell array 20 includes a sub-word line SWL, a bit line BL, and a memory cell MC that is connected to the sub-word line SWL and the bit line BL. The sub-word line SWL is connected to a sub-word driver SWD that is controlled by a main-word signal on a main-word line MWL. The bit line BL is connected to a sense amplifier SAMP that is selected by a column selection signal on a column selection line YS. Selection of the main-word line MWL and the sub-word line SWL is performed by the row decoder 30 based on a row address signal XA. Selection of the column selection line YS and the...
second embodiment
[0075]the present invention is explained next.
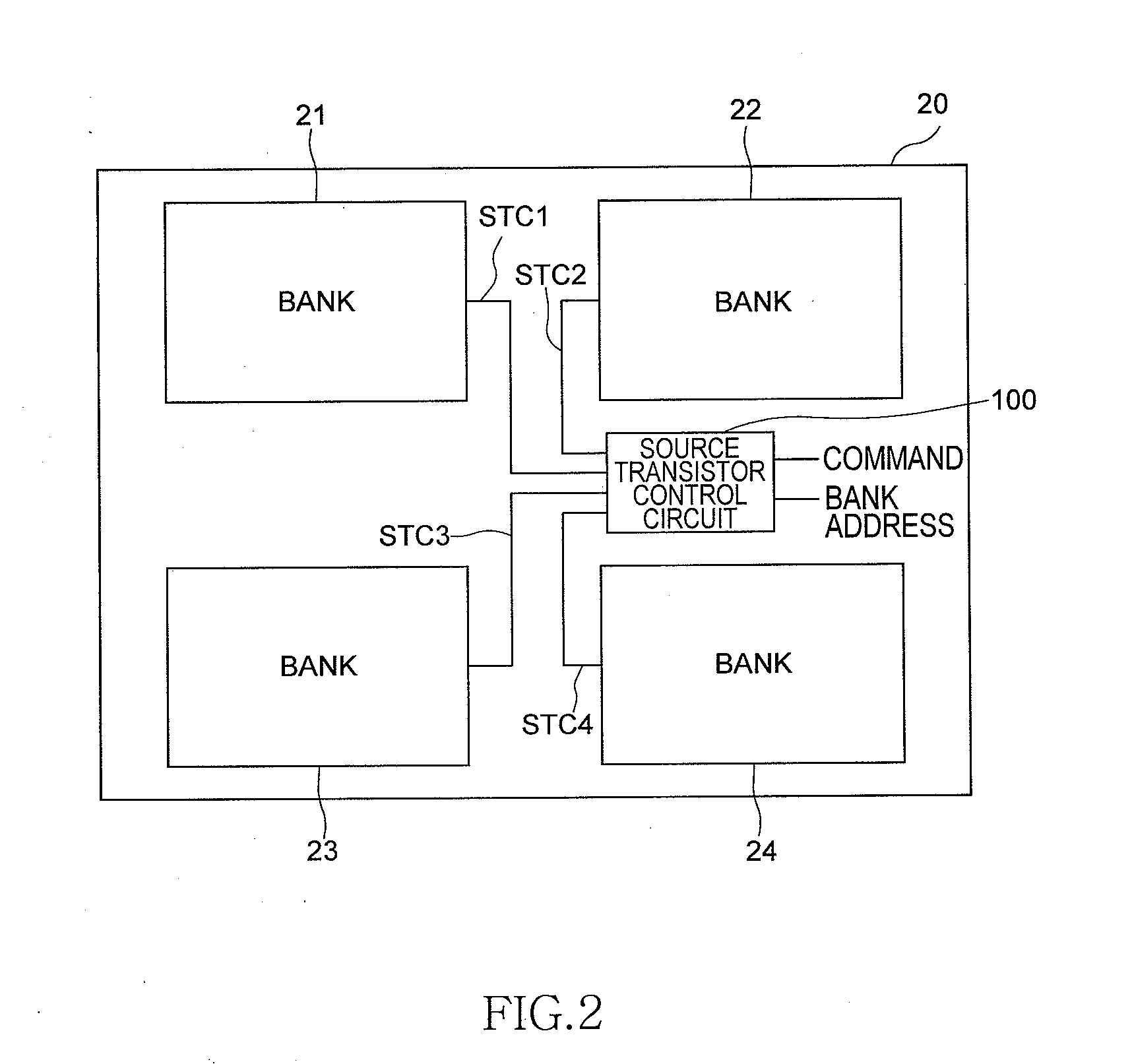
[0076]FIG. 11 is an enlarged block diagram of a memory bank 21 according to the second embodiment showing its main parts, and FIG. 11 corresponds to FIG. 3 for explaining the first embodiment.
[0077]As shown in FIG. 11, the second embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that the source transistor control circuit 100 includes an SR latch circuit 110 and an output of the SR latch circuit 110 is the source transistor control signal STC1. Other features of the second embodiment are identical to those of the first embedment, and thus explanations thereof will be omitted.
[0078]An internal signal RASB is supplied to a set-side input terminal S of the SR latch circuit 110 via a pulse generating circuit 120. The internal signal RASB is a signal that becomes a Low level in response to issuance of an active command. Therefore, when the active command is issued, the SR latch circuit 110 is set, by which the source transistor control sign...
third embodiment
[0086]FIG. 14 is a block diagram of a semiconductor memory device according to the present invention.
[0087]In the third embodiment, as shown in FIG. 14, a source transistor control signal STC1 is supplied to a column select circuit group 41 that constitutes the column decoder 40. The column select circuit group 41 includes a plurality of column select circuits 400, 401, . . . , which are selected based on their corresponding pre-decode signals PY0, PY1, . . . . The pre-decode signals PY0, PY1, . . . are signals generated by pre-decoding a part of the column address YA by a column pre-decoder 42. The column select circuit group 41 and the column pre-decoder 42 form the column decoder 40 shown in FIG. 1.
[0088]In the above configuration, the column select circuits 400, 401, . . . are selectively activated based on the source transistor control signal STC1 and the pre-decode signals PY0, PY1, . . . , as it is in the first and second embodiments. Therefore, only a column select circuit t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com