Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
a technology of semiconductors and semiconductors, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, basic electric elements, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of power consumption affecting the continuous operation time, and achieve the effects of low power consumption, low power consumption, and low parasitic capacitan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
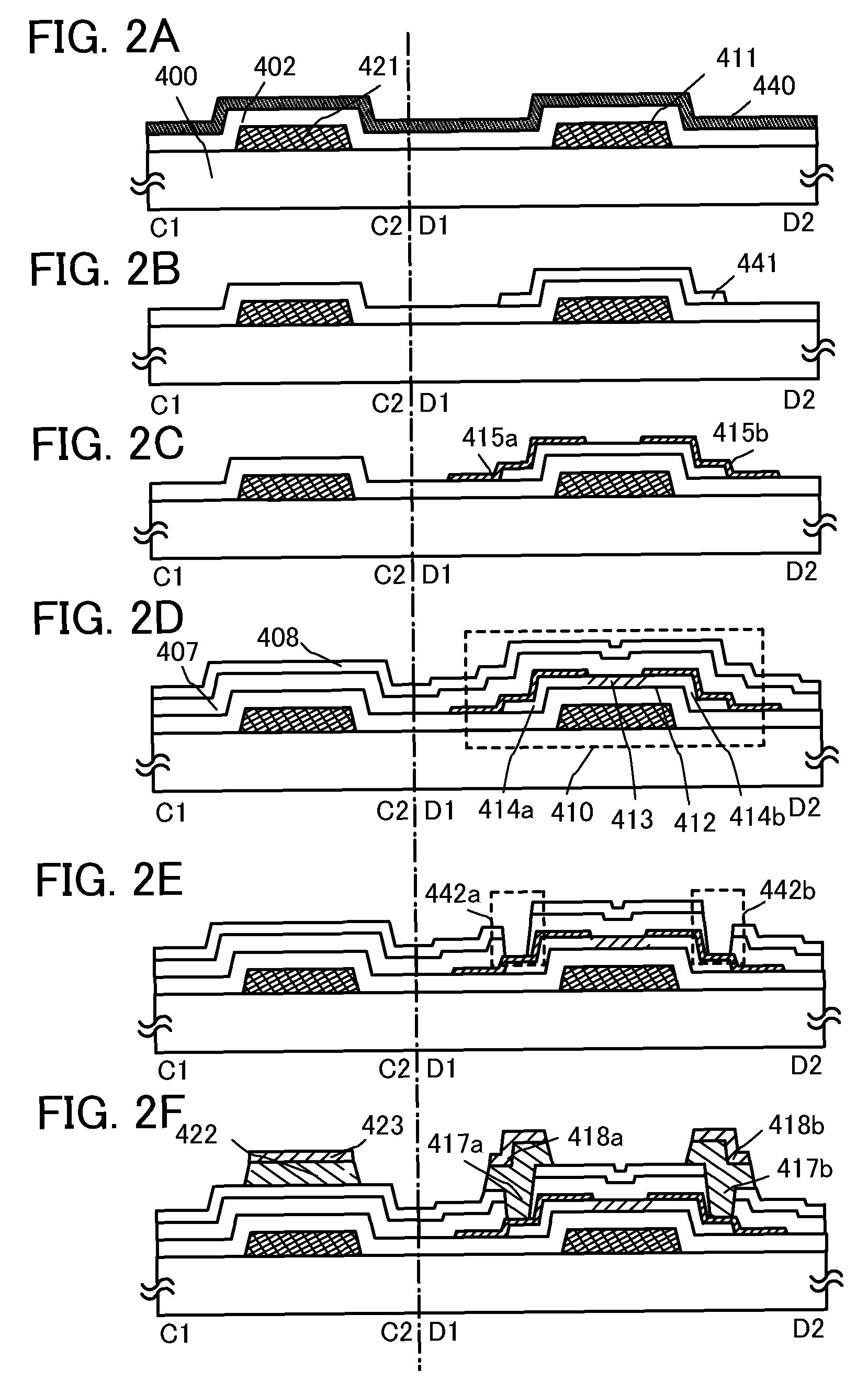
[0080]In Embodiment 1, one embodiment of a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method of the semiconductor device will be described with reference to FIGS. 1A1 and 1A2 and FIG. 1B, FIGS. 2A to 2F, and FIGS. 6A and 6B.
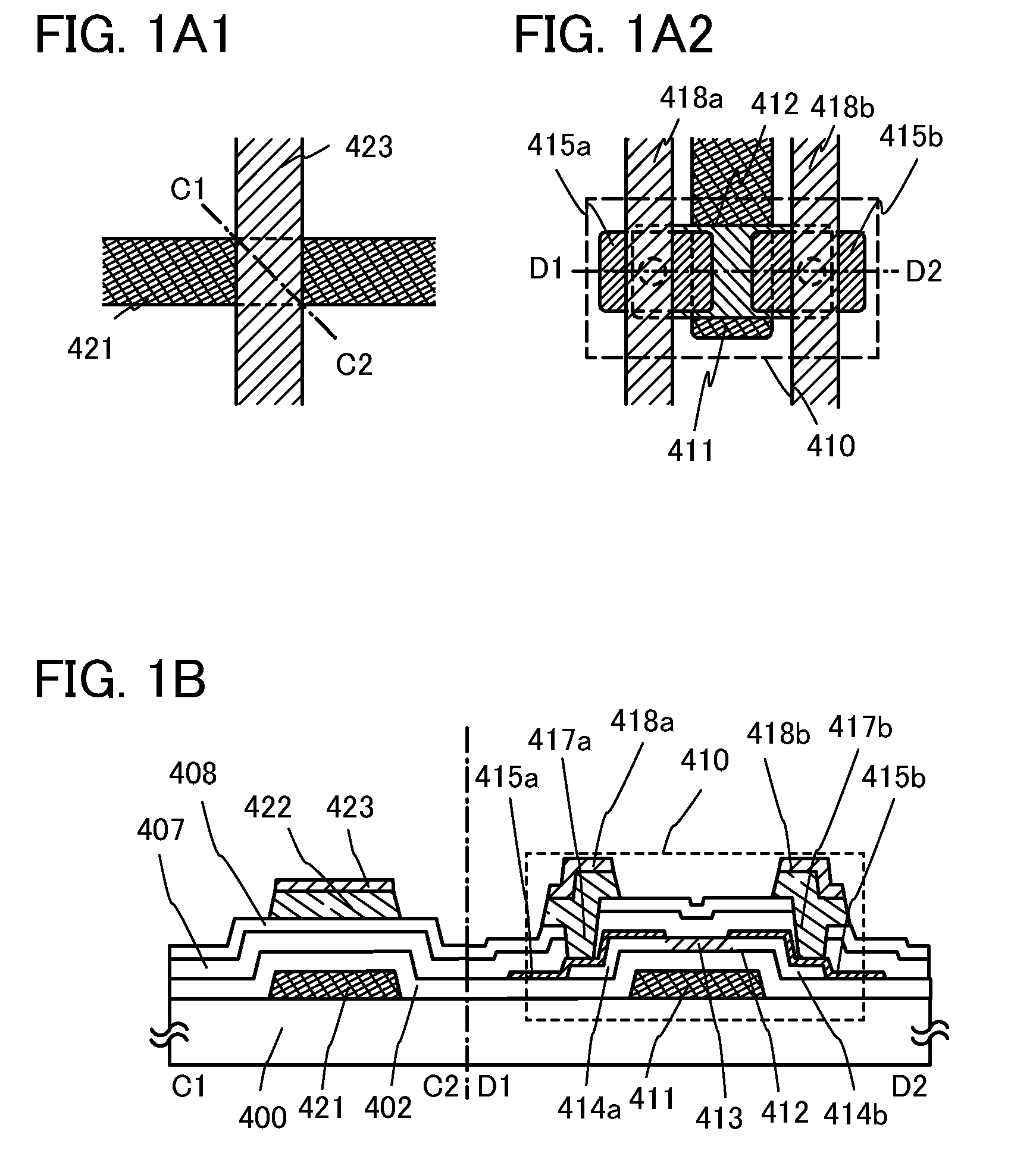
[0081]FIGS. 1A1 and 1A2 illustrate an example of a plane surface structure of a semiconductor device, and FIG. 1B illustrates an example of a cross-sectional structure of the same. A thin film transistor 410 shown in FIGS. 1A2 and 1B is a kind of bottom-gate structure called a channel-etched type and is also called an inverted staggered thin film transistor.
[0082]FIG. 1A1 is a plane view of an intersection between a gate wiring layer (formed by the same step as a gate electrode layer) and a source wiring layer (formed by the same step as a wiring layer); FIG. 1A2 is a plane view of the channel-etched thin film transistor 410; and FIG. 1B is a cross-sectional view along line C1-C2 and line D1-D2 in FIGS. 1A1 and 1A2.
[0083]The thin film transistor 410, which is a cha...
embodiment 2
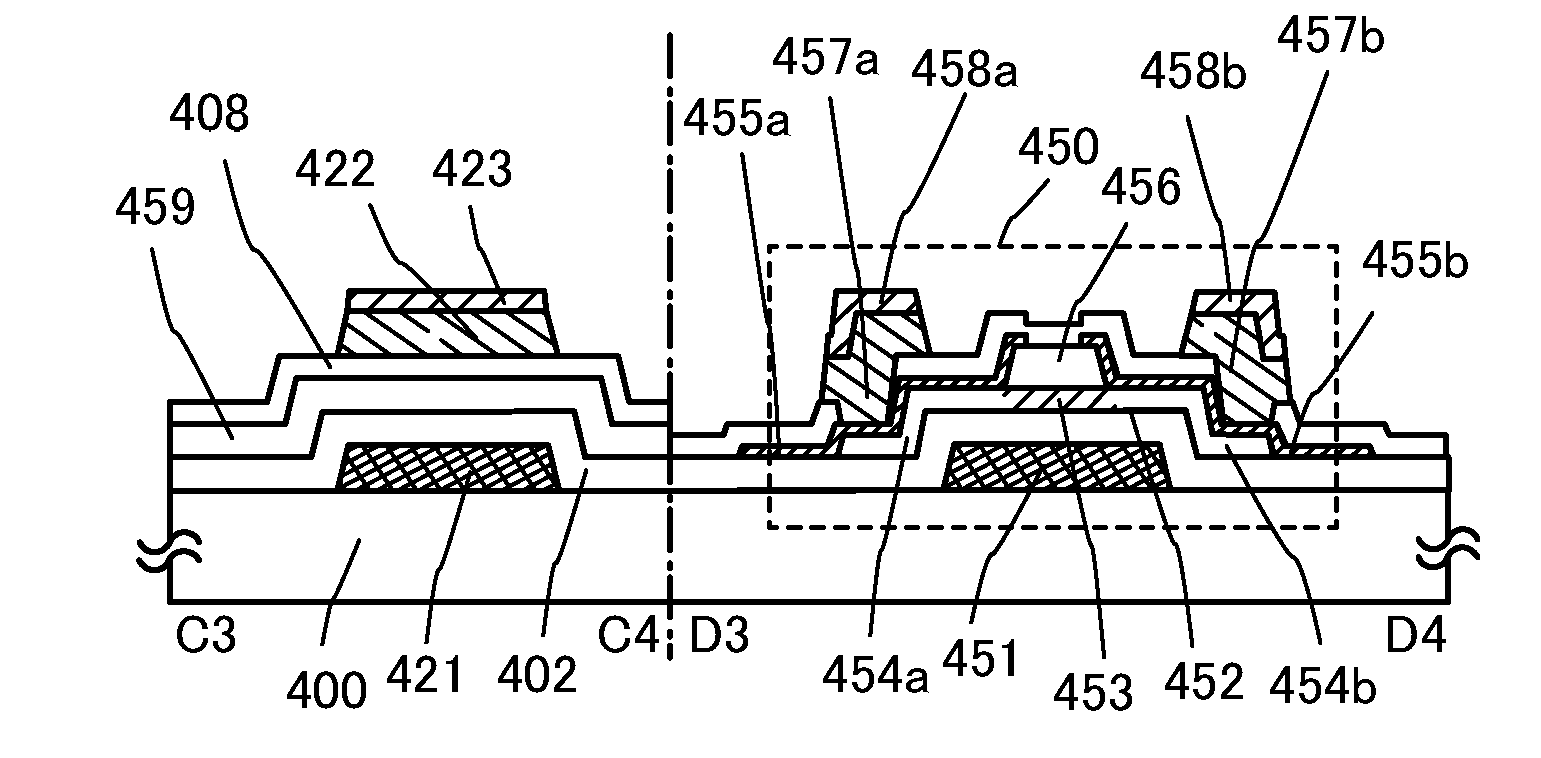
[0167]In Embodiment 2, an example of a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor having a structure different from that of Embodiment 1 will be described below.
[0168]FIGS. 3A1 and 3A2 illustrate an example of a plane surface structure of a semiconductor device, and FIG. 3B illustrates an example of a cross-sectional structure of the same. A thin film transistor 450 shown in FIGS. 3A2 and 3B is a kind of bottom-gate structure called a channel-protective type (channel-stop type) and is also called an inverted staggered thin film transistor.
[0169]FIG. 3A1 is a plane view of an intersection between a gate wiring layer (formed by the same step as a gate electrode layer) and a source wiring layer (formed by the same step as a wiring layer); FIG. 3A2 is a plane view of the channel-protective type thin film transistor 450; and FIG. 3B is a cross-sectional view along line C3-C4 and line D3-D4 in FIGS. 3A1 and 3A2.
[0170]The thin film transistor 450, which is a channel-protective t...
embodiment 3
[0208]In Embodiment 3, another example which is different from Embodiment 1 in the manufacturing process of a semiconductor device including a thin film transistor will be described with reference to FIGS. 5A to 5F. FIGS. 5A to 5F are the same as FIGS. 1A1, 1A2, and FIG. 1B and FIGS. 2A to 2F except that there is a difference in part of the process; therefore, the same portions are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description of the same portions is omitted. In this embodiment, a mask layer formed using a multi-tone mask is used in a photolithography step.
[0209]Since a mask layer formed with the use of a multi-tone mask has a plurality of film thicknesses and further can be changed in shape by performing etching on the mask layer, the mask layer can be used in a plurality of etching steps for processing into different patterns. Therefore, a mask layer corresponding at least two kinds of different patterns can be formed by one multi-tone mask. Thus, the number of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com