Wound cleansing apparatus in-situ
a wound cleansing and in-situ technology, applied in the field of wound cleansing apparatus, can solve the problem that relevant devices tend to be not portable, and achieve the effect of promoting wound healing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cleansing Fe(II) from Aqueous Solution with the Apparatus of FIG. 1: Single-Phase Hand-Syringe Pumped Dressing Containing Solid Sequestrant (Cadexomer—Desferrioxamine)
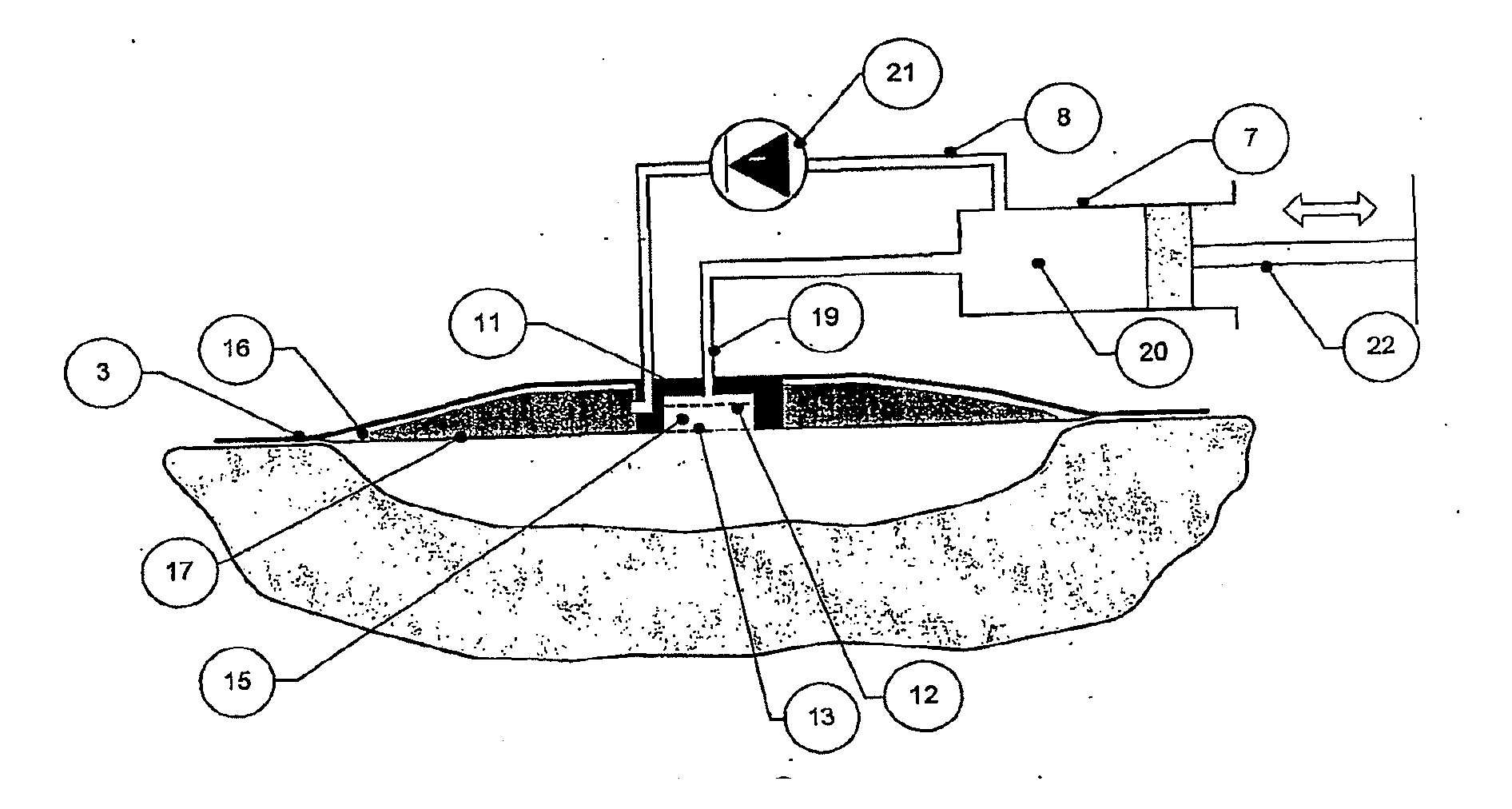
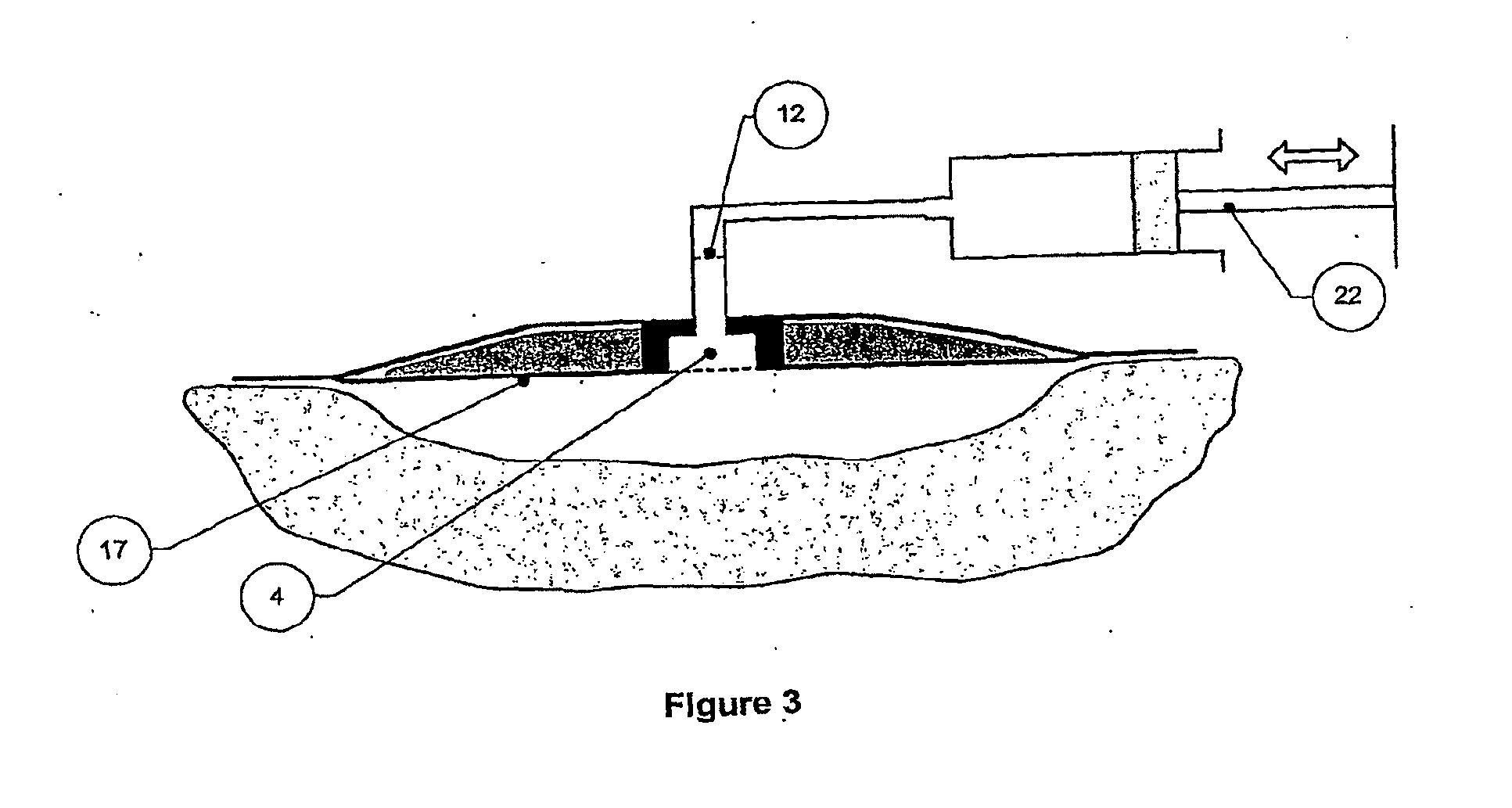
[0386] A hand-syringe pumped dressing as shown in FIG. 14 was made up. The cleansing chamber (15) contains a solid particulate (not shown) desferrioxamine supported on Cadexomer (50 mg) to sequester and remove deleterious Fe(II) ions from surrogate exudate.
[0387] The porous film (12) and a permeable membrane (13), both made of Porvair permeable membrane, are chosen to allow perfusion and flow under syringe pumping through the cleanser but to contain the solid reagent.
[0388] In triplicate, the dressing as shown in FIG. 1 was applied to a 9.60 ml capacity circular wound cavity (cast in Perspex) containing an aqueous solution of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate (Aldrich) (9.60 ml, 200 μmolar).
[0389] The solution was repeatedly completely withdrawn and completely reinjected using the device syringe. At each withdrawal, a ...
example 2
Neutralising the pH of an Acidic Solution with the Apparatus of FIG. 15: Single-Phase Recirculating Pumped Dressing Containing Solid Acid Scavenger, ScavengePore® Phenethyl Morpholine
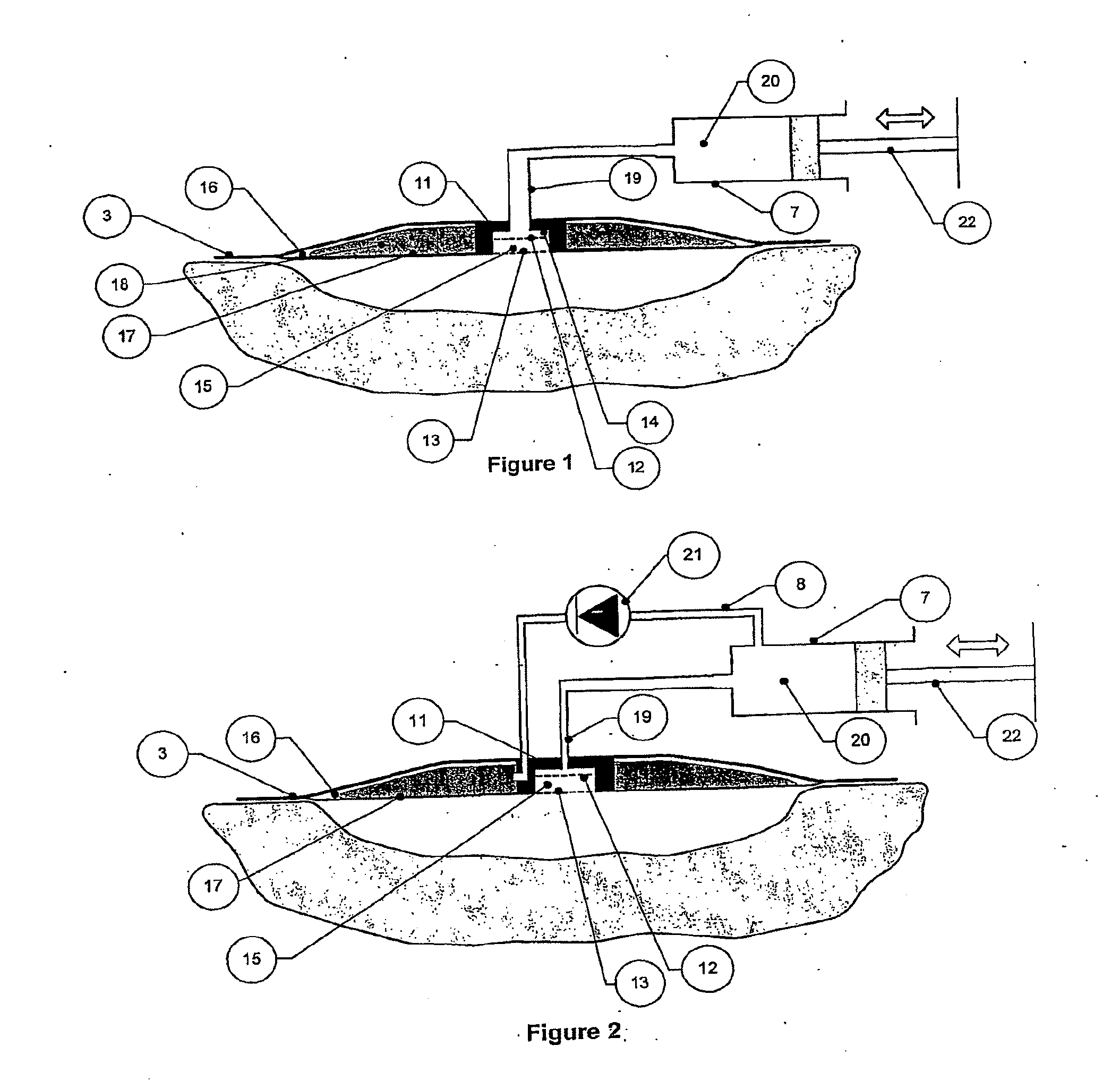
[0393] A recirculating pumped dressing as shown in FIG. 15 was made up. The cleansing chamber (15) contains a solid particulate (not shown) of ScavengePore® phenethyl morpholine (Aldrich) (50 mg), which is a low-swelling macroporous highly crosslinked polystyrene / divinylbenzene ion-exchanger resin matrix, with 200-400 micron particle size, to scavenge and remove protons, which are acidic species which adversely affect the pH in the wound exudate, from surrogate exudate.
[0394] The porous film (12) and a permeable membrane (13), both made of Porvair permeable membrane, are chosen to allow perfusion and flow under pumping through the cleanser but to contain the ion-exchange reagent.
[0395] In triplicate, 4.80 ml DMEM was In triplicate, Device 2 was applied to a 9.60 ml capacity circular wound cavity (cas...
example 3
Cleansing Elastase from Aqueous Solution by Diffusion Across a Dialysis Membrane with the Apparatus of FIG. 12: Two-Phase Recirculating Pumped Dressing Containing No Reagent
[0398] A recirculating pumped dressing as shown in FIG. 12 was made up. The cleansing chamber (5) is in the form of tubules made from a polymer membrane that is selectively permeable to a deleterious materials in wound exudate (elastase). These in an array under the backing layer (3) within the wound space between a first boss (71) and a second boss (72) both mounted in the backing layer (3). The tubules contain a dialysate fluid and are in a circuit with a pump (7).
[0399] In triplicate, the dressing as shown in FIG. 12 was applied to a 9.60 ml capacity circular wound cavity (cast in Perspex) containing elastase solution (porcine pancreatic elastase, Sigma) (4.80 ml, 0.5 mgml−1 in TRIS buffer, pH 8.2, 0.2 M). The remaining cavity volume was filled with glass beads. The inlet and outlet ports were connected to t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com