Fluid coking unit stripper
a technology of coking unit and stripper, which is applied in the direction of oven details, thermal non-catalytic cracking, and incrustation prevention/removal of oven, etc., can solve the problems of uneven or too heavy coating of coke particles, insufficient fluidization of heavier coke particles, and the accumulation of deposits on strippers can become so severe, so as to achieve good interstitial performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
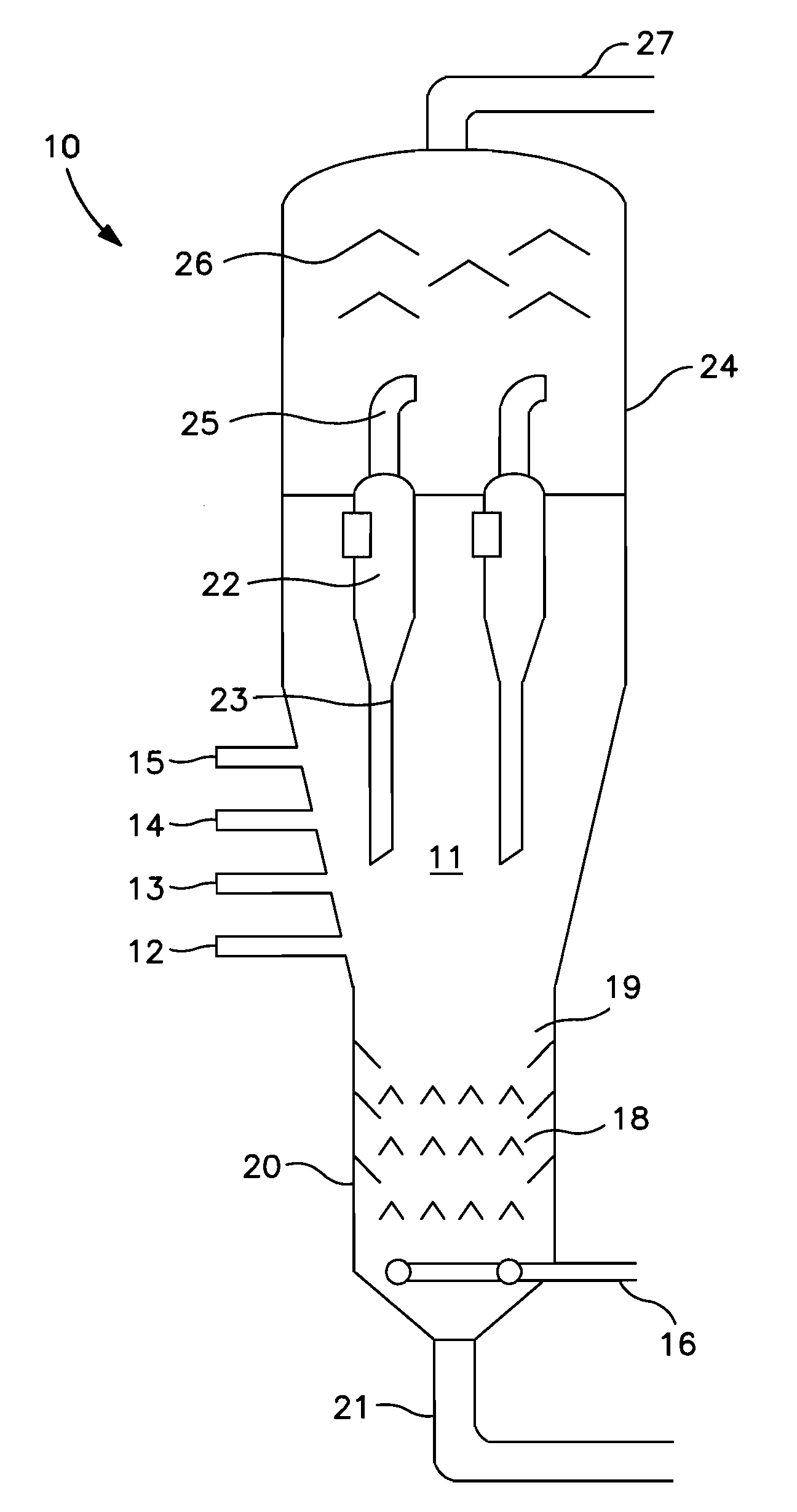
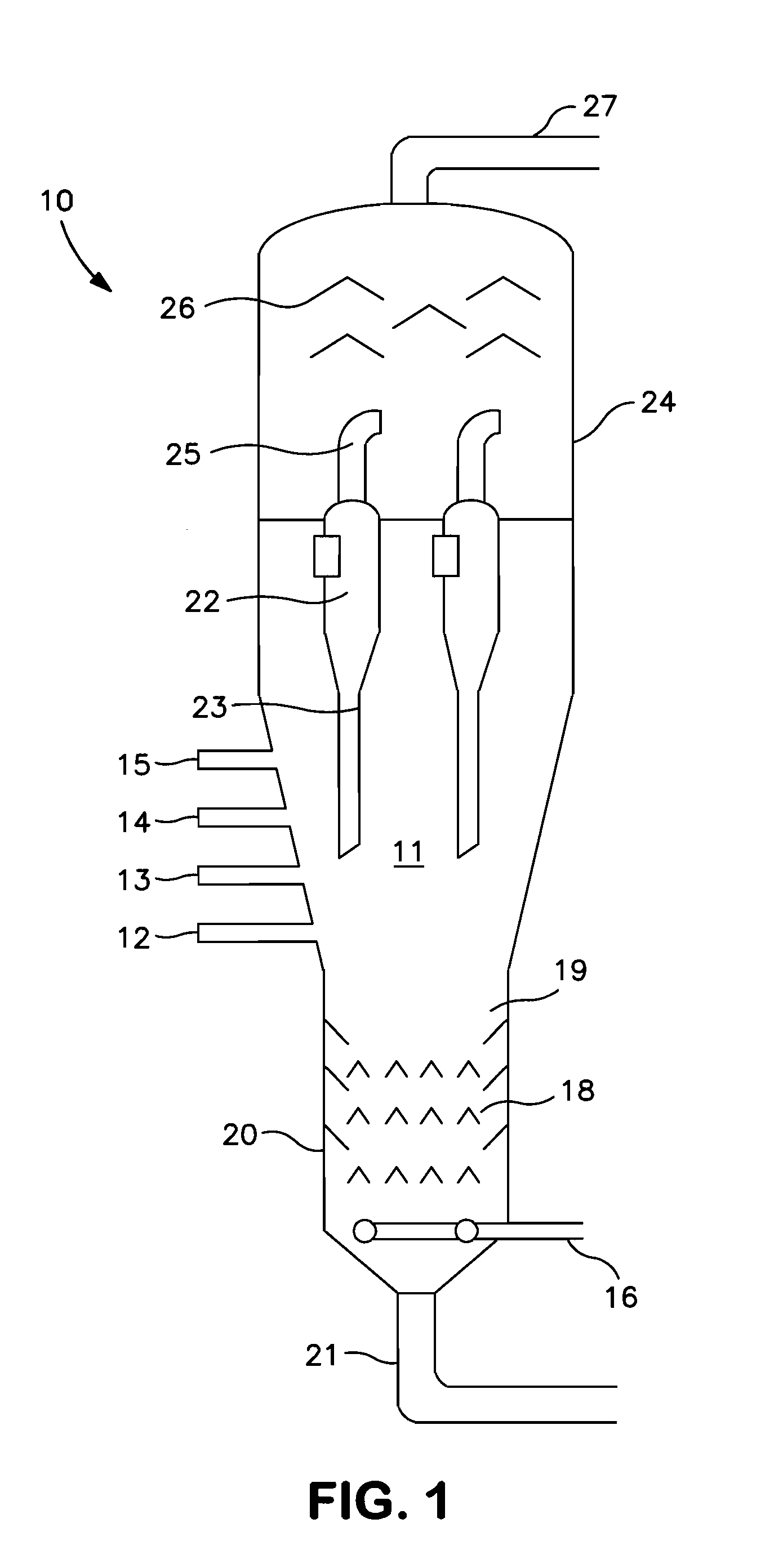
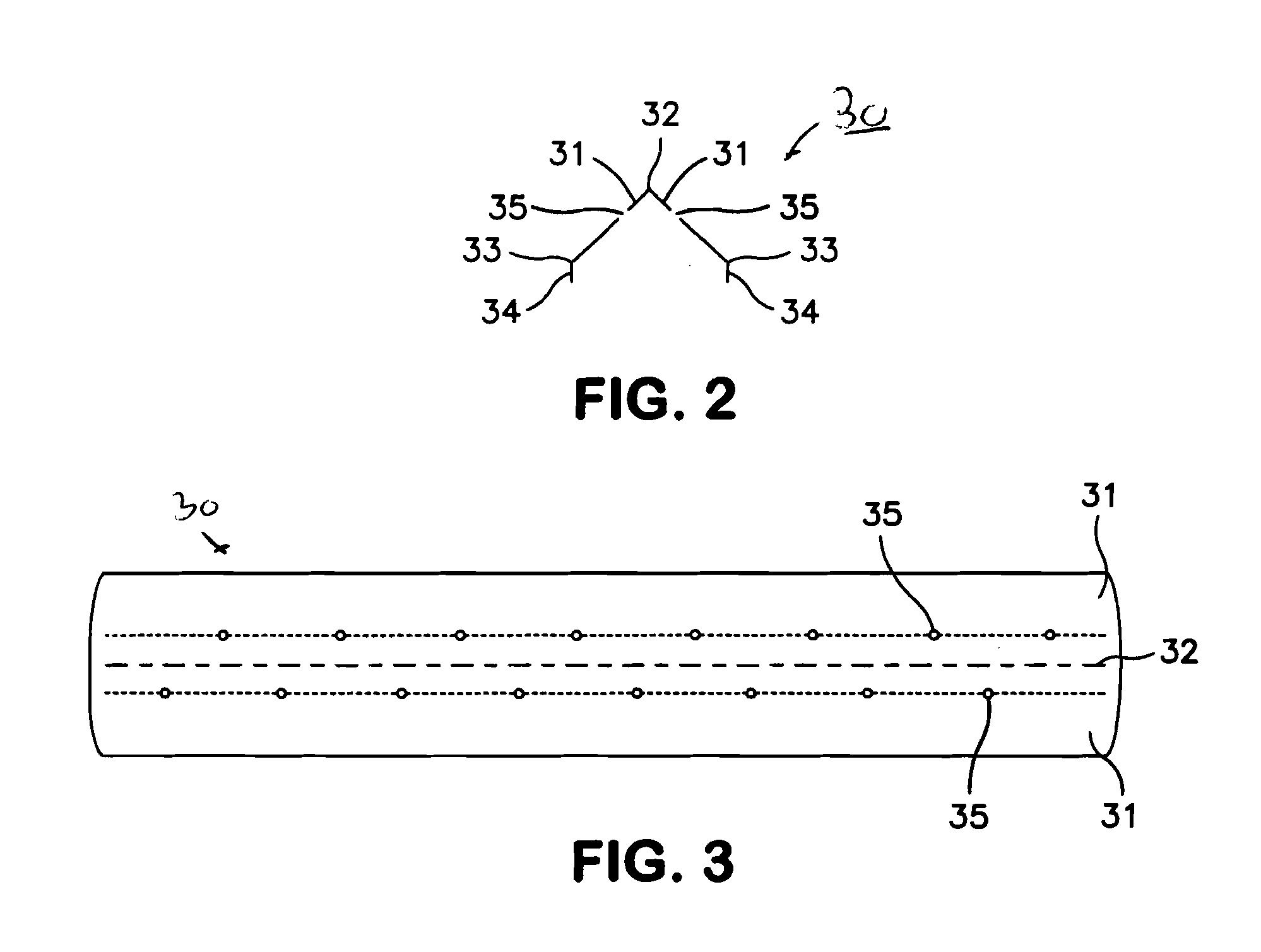
[0022]In FIG. 1 which is a highly simplified diagram of the reactor of a fluid coking unit, the reactor 10 contains a fluidized bed in coking zone 11 of heated seed coke particles into which the feedstock, heated to a temperature sufficient to initiate the coking (thermal cracking) reactions and deposit a fresh coke layer on the hot fluidized coke particles circulating in the bed. The feed is injected through a ring of feed injection ports 12, 13, 14, 15 which are positioned so that the feed with the atomizing steam enters directly into the fluidized bed 11 of hot coke particles. A fluidizing gas, usually steam, is admitted at the base of coker reactor 10, through conduit 16, into stripping zone 20 of the coking reactor in an amount sufficient to obtain a superficial fluidizing velocity in the coking zone, typically in the range of about 0.15 to 1.5 m / sec (about 0.5 to 5 ft / sec). The coking zone is typically maintained at temperatures in the range of 450 to 650° C. (about 840 to 120...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com