Method for constructing a chair-type, self-supported earth retaining wall
a self-supporting, earth-supported technology, applied in the direction of artificial islands, excavations, constructions, etc., can solve the problems of durability and waterproof properties of the completed underground structure, large quantity of steel sheets, and large construction costs, so as to save construction costs, shorten construction period, and reduce the quantity of steel sheets used
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034]Now, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described hereinafter in detail with reference to FIGS. 1 to 9.
[0035]In the meantime, the illustration and detailed description of the constitution, operation, and effects that can be easily understood from a general earth retaining construction technique and a related technique applied to the present invention in the drawings will be omitted or only portions related with the present invention will be shown and described.
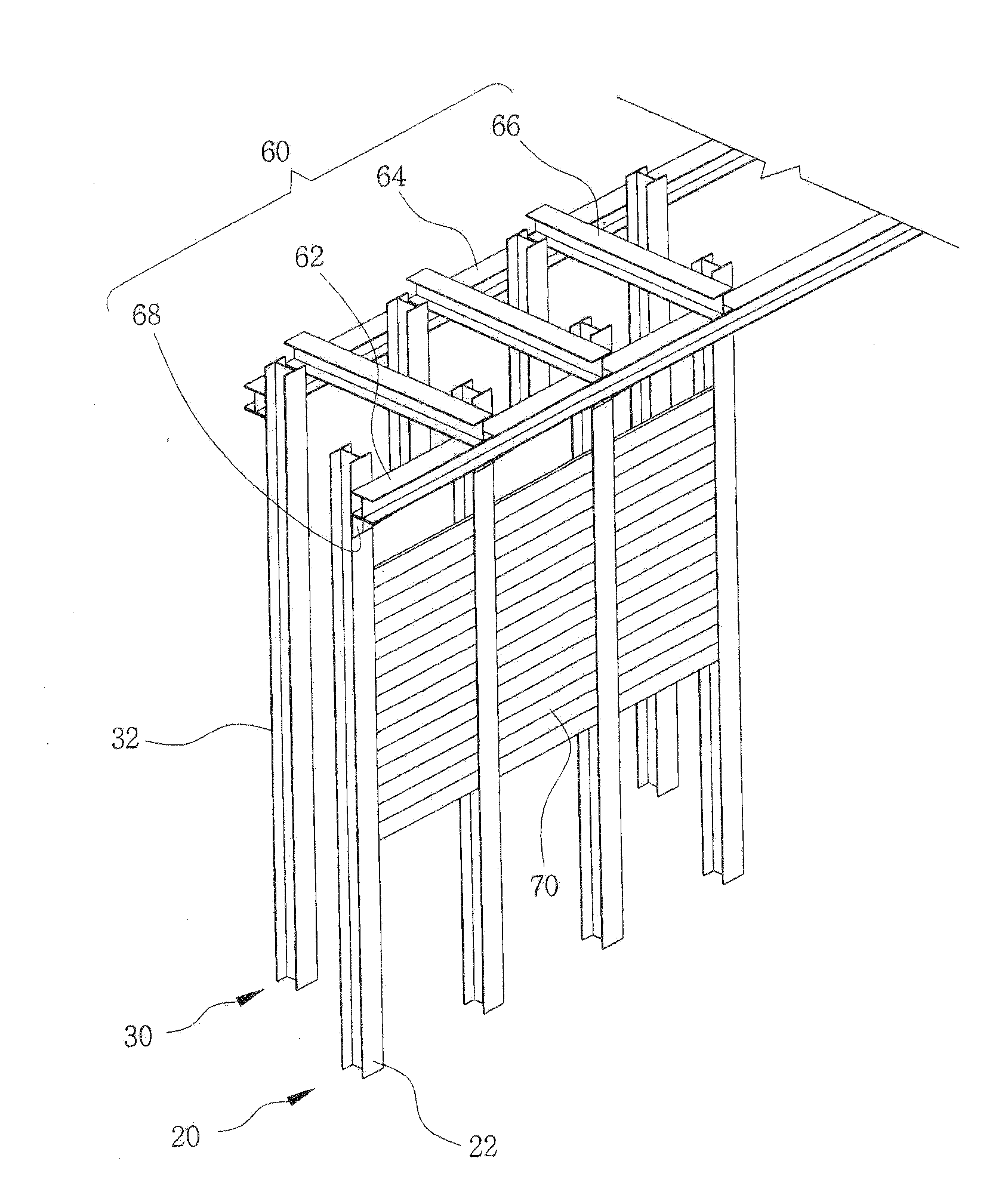
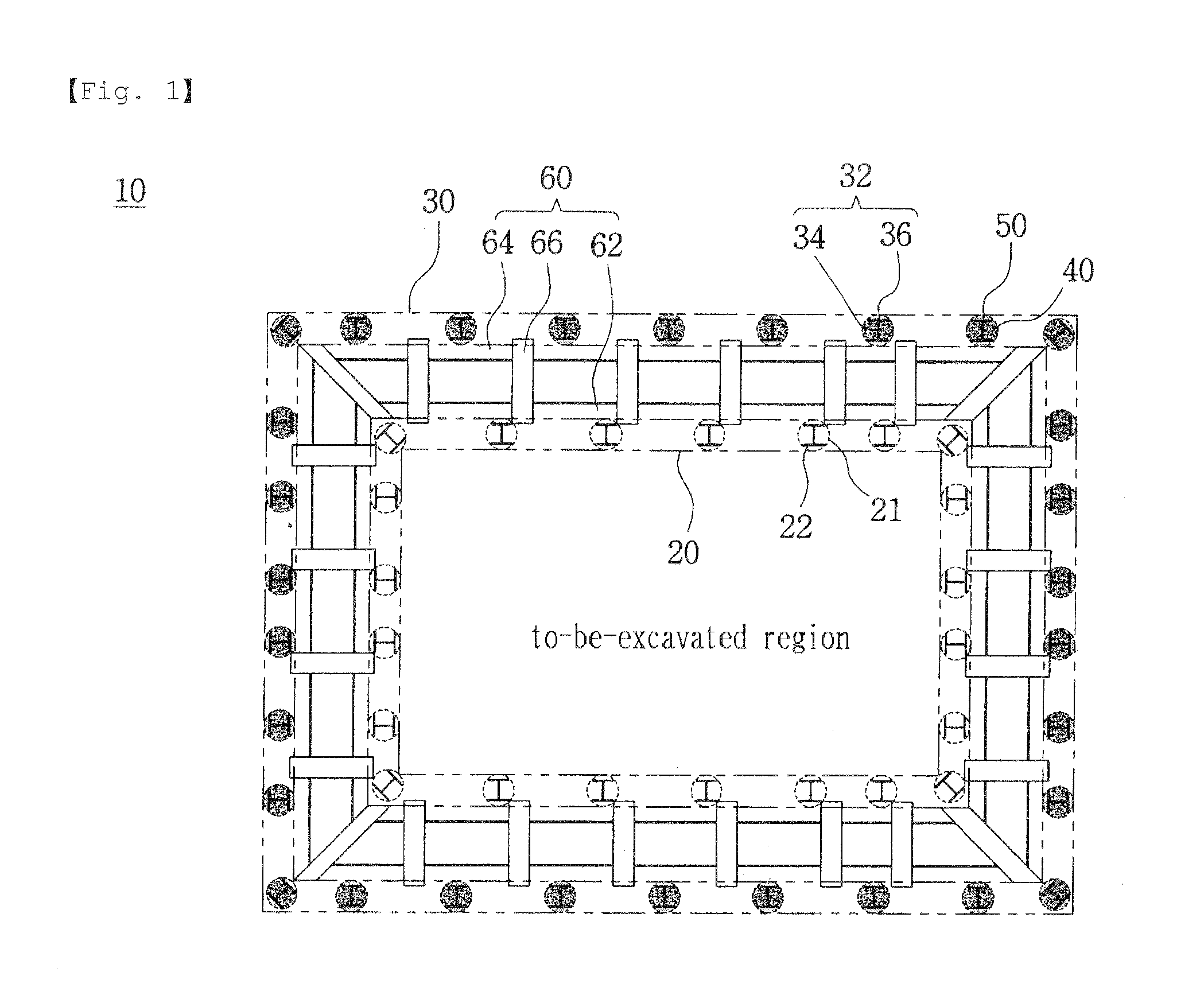
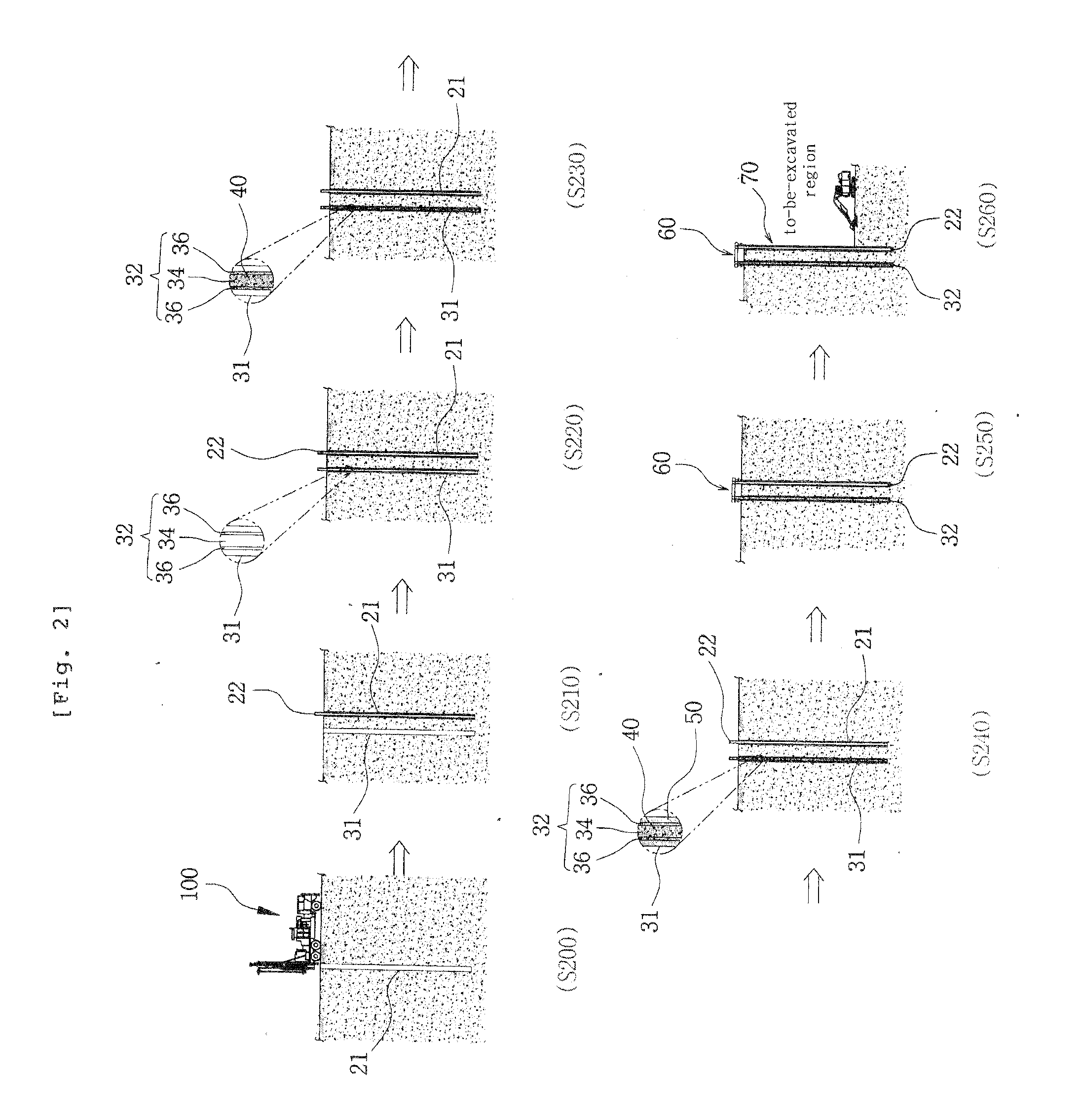
[0036]FIG. 1 is a schematic top plan view illustrating an earth retaining wall constructed by a method for constructing a chair-type, self-supported earth retaining wall according to the present invention, FIG. 2 is a view for explaining a method for constructing a chair-type, self-supported earth retaining wall according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 3 is a perspective view illustrating a constitution of an earth retaining wall constructed by the method for constructing the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com