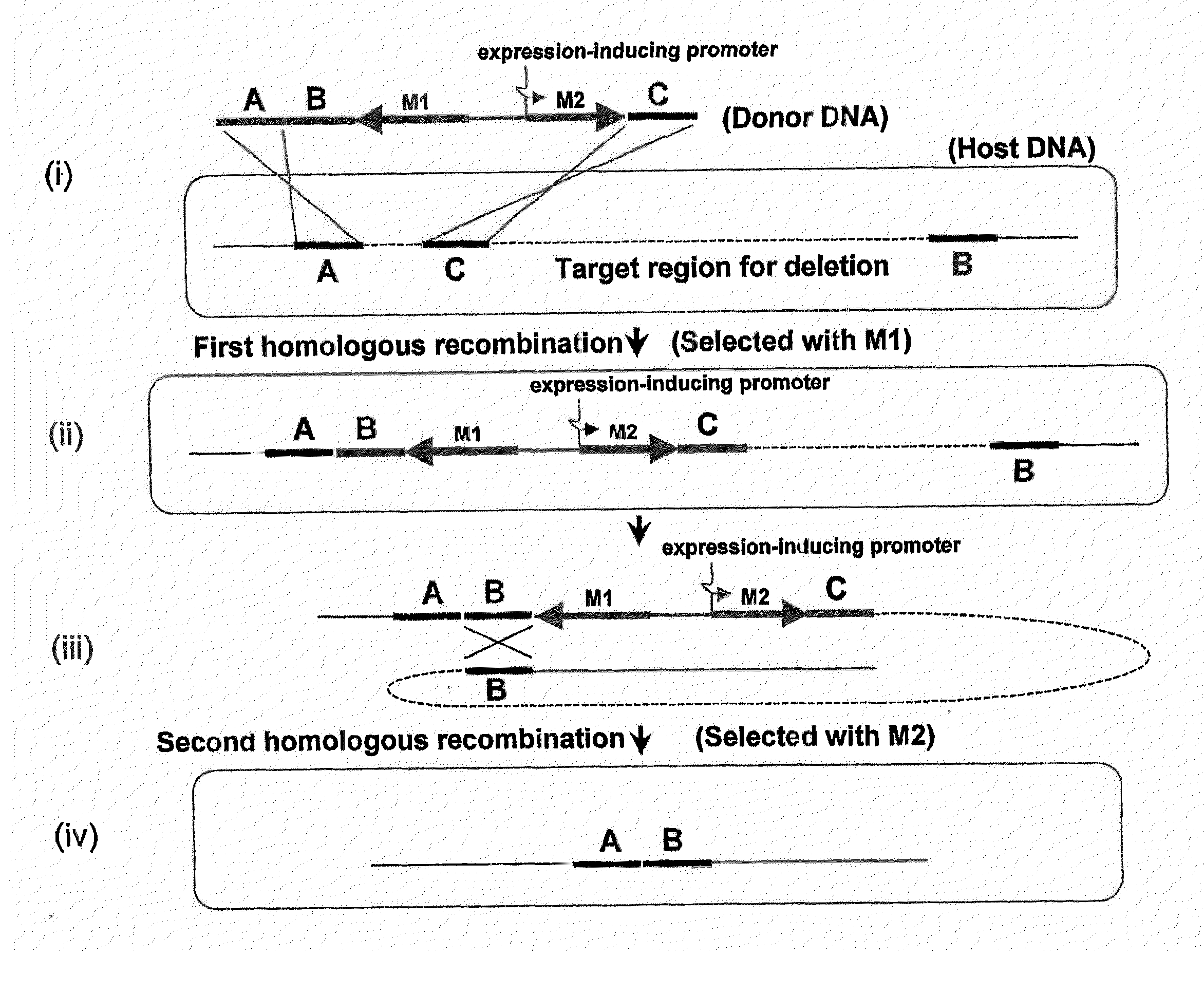
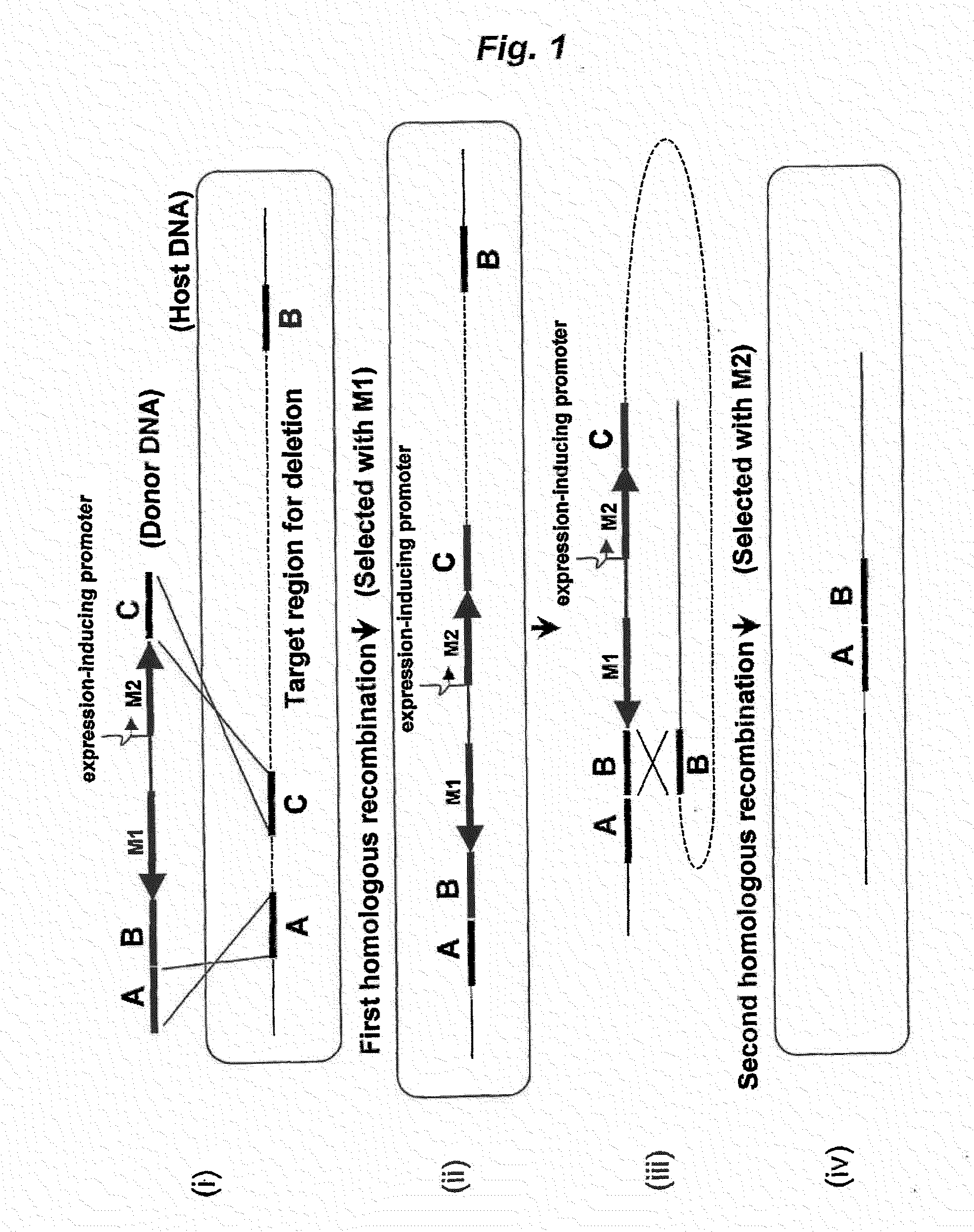
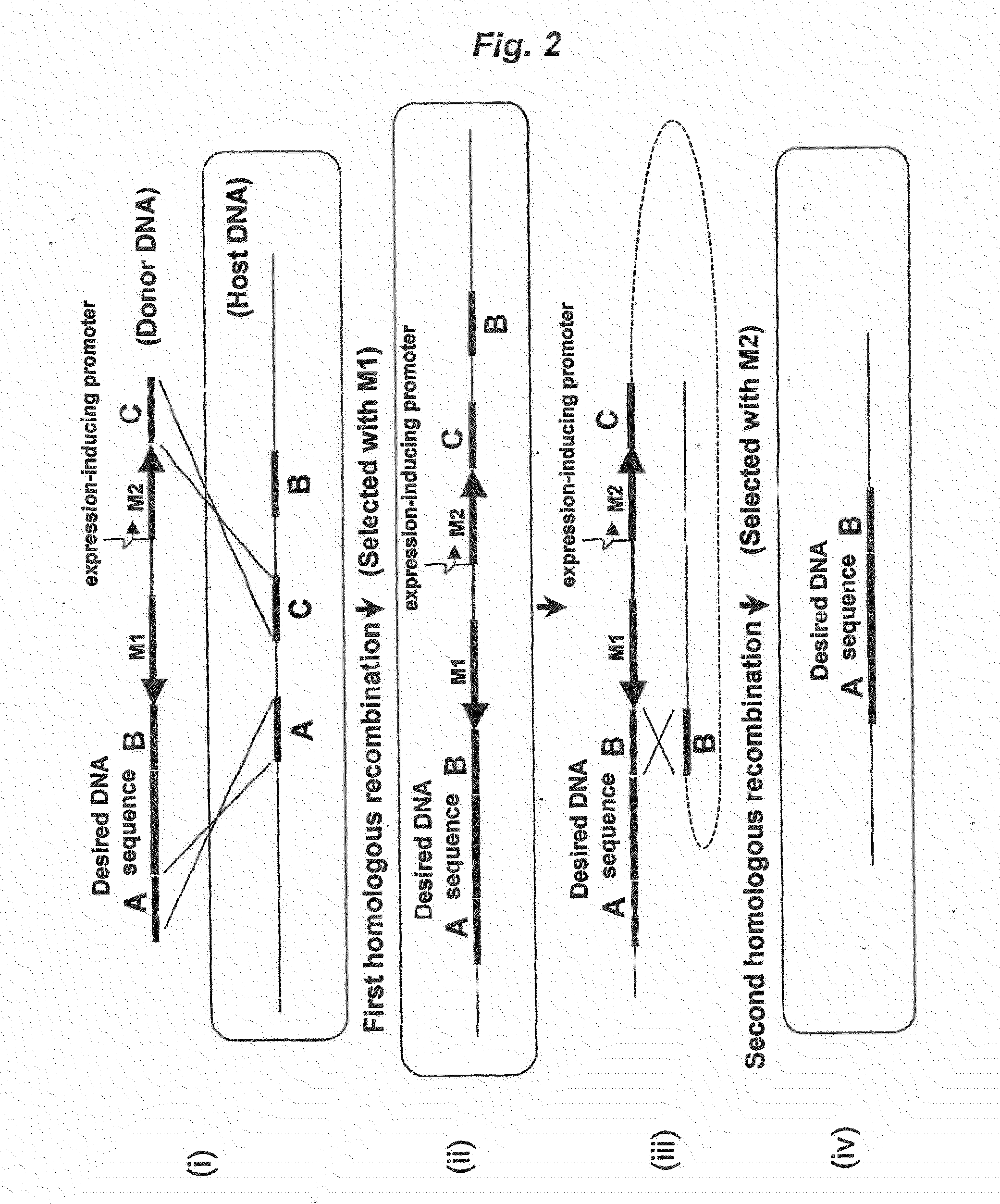
Method of Modifying Target Region in Host DNA and Selectable Marker Cassette
a technology of target region and host dna, which is applied in the field of modifying target region in host dna and relating to selectable marker cassette, can solve the problems of insufficient improvement of operational efficiency, difficult to introduce large-size dna segment or lethal gene into the desired region of host dna, and the method is not entirely satisfactory for improving operational efficiency. the effect of efficiency improvemen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0127] In the present Example, the pro5 region (20,485 bp), which is the region from 1,879,258 bp to 1,899,742 bp on the genome of Bacillus subtilis 168, was deleted as the target region for deletion. The sequences of the primers used in the present Example are shown in Table 1. The flow diagrams of the present Example are shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6.
TABLE 1Primer sequencesSEQ IDPrimerNucleotide sequenceNO:pO2HC-lacFCTCACATTAATTGCGTTGCG 3pO2HC-lacRCTTACCATAGTTAATTTCTCCTCTTTAATG 4chpA-FGAAATTAACTATGGTAAGCCGATACGTACC 5chpA-RCGCGGATCCTACCCAATCAGTACGTTAATTTTG 6APNC-FCGACAGCGGAATTGACTCAAGC 7pro5-DF1GAGCAAAGAAGAGCGCATGG 8pro5-DR1CAGCATGGAGAAGATTTCAACGTAATTATGG 9pro5-DF2CGTTGAAATCTTCTCCATGCTGTGTGATTGATC10pro5-DR2CTGATTGGGTAGGATCCGCGATATTTATCGACGAACTCAGAT11pro5-IFGAGTCAATTCCGCTGTCGATCAATCACAATGGAGGAC12pro5-IRTACGTAAGTATCAGCACAGG13pro5-checkFCTGCAAACCCATACCTTGCAC14pro5-checkRCATCACTAAATCTCTTAAACGTC15
[0128] First, mutant strains, Bacillus subtilis 168 (aprE::spec, lacI, Pspac-chpA) and Bacil...
example 2
[0141] In the present Example, the flgB-fliH region (4,708 bp) corresponding to 1,690,526 bp to 1,695,233 bp in the genome of Bacillus subtilis 168 was used as the desired DNA sequence, and the DNA sequence was inserted into the target regio for replacement in the host DNA. The sequences of the primers used in the present Example are shown in Table 2. The flow diagram of the present Example is shown in FIG. 7.
TABLE 2Primer sequencesSEQ IDPrimerNucleotide sequenceNO:chpA-RCGCGGATCCTACCCAATCAGTACGTTAATTTTG 6APNC-FCGACAGCGGAATTGACTCAAGC 7flgB-FGCGTTCAGCAACATGTCTGTTTCTCGACAAGGATATTGAGG16fliH-RGCAGCTGCTTGTACGTTGATCCGTACCGTTTATACGAGTC17aprEclone-fFTCTGATGTCTTTGCTTGGCG18aprEclone-fRACAGACATGTTGCTGAACGC19aprEclone-bFATCAACGTACAAGCAGCTGC20aprEclone-bRCTGATTGGGTAGGATCCGCGCCATTATGTCATGAAGCACG21aprEclone-mFGAGTCAATTCCGCTGTCGTTCTCACGGTACGCATGTAG22aprEclone-mRAGAATTAACGCTGCTGCTCC23aprEclone-checkFTTGCAAATCGGATGCCTGTC24aprEclone-checkRTATTGTGGGATACGACGCTG25
[0142] By using the chromosomal DNA of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| drug-resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Drug-resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| drug resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com