Limiting strain relaxation in iii-nitride hetero-structures by substrate and epitaxial layer patterning
a technology of iiiinitride and hetero-structure, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, lasers, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the design space of devices, affecting the performance of lds, and unable to fully realize the expected inherent advantages of device manufacturers, etc., and achieves the effect of higher alloy composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030]In the following description of the preferred embodiment, reference is made to the accompanying drawings which form a part hereof, and in which is shown by way of illustration a specific embodiment in which the invention may be practiced. It is to be understood that other embodiments may be utilized and structural changes may be made without departing from the scope of the present invention.
[0031]Overview
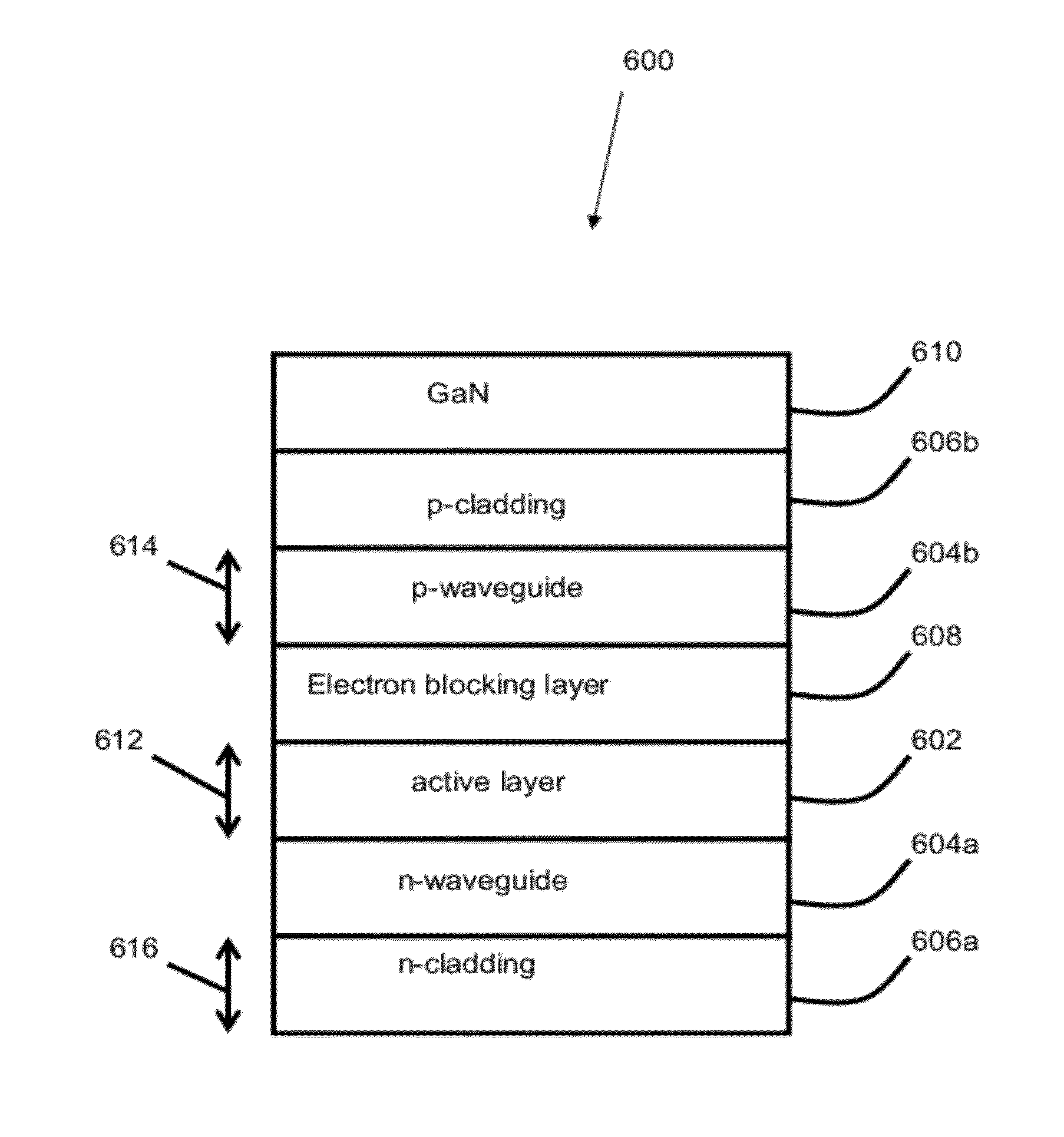
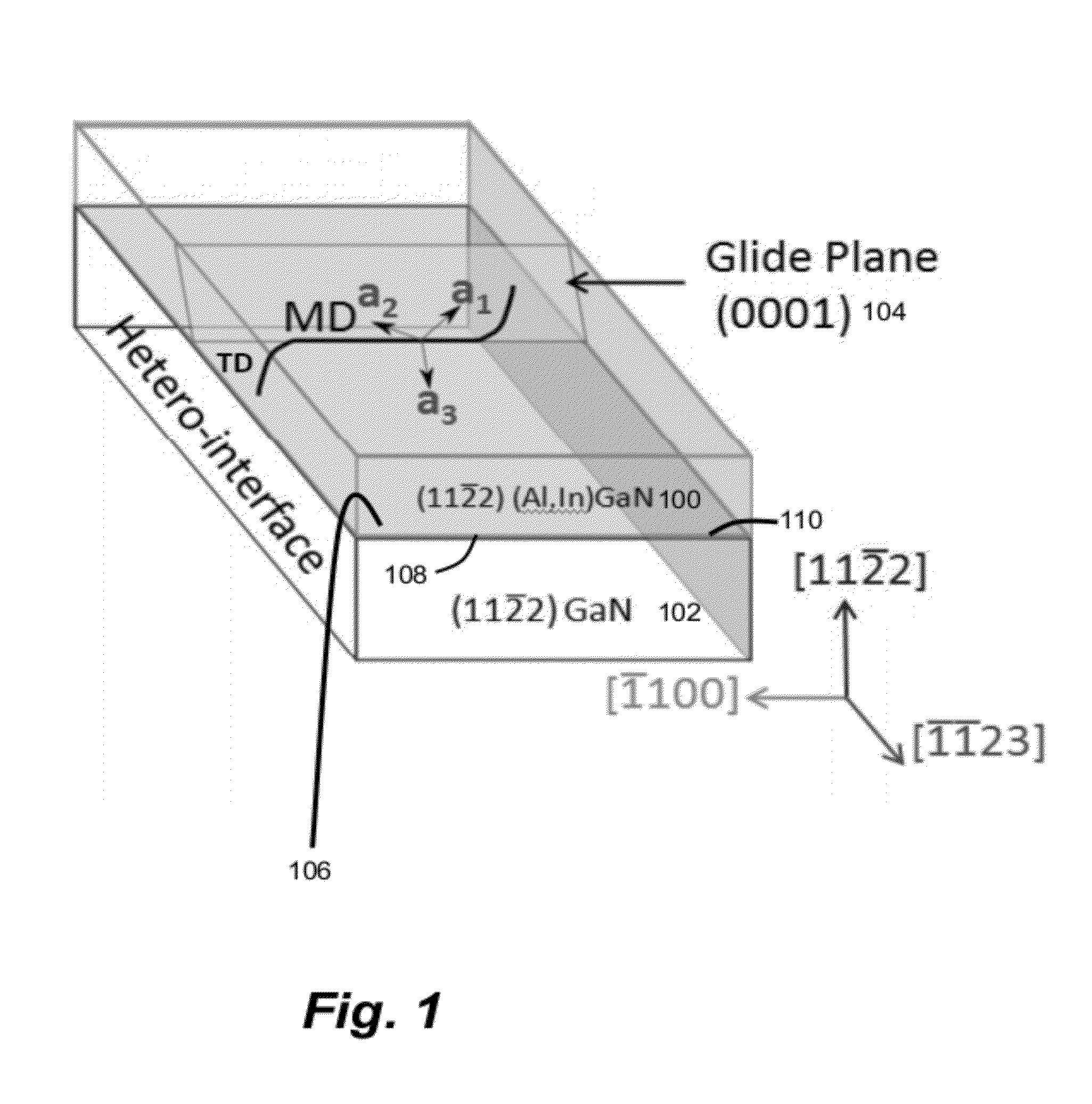
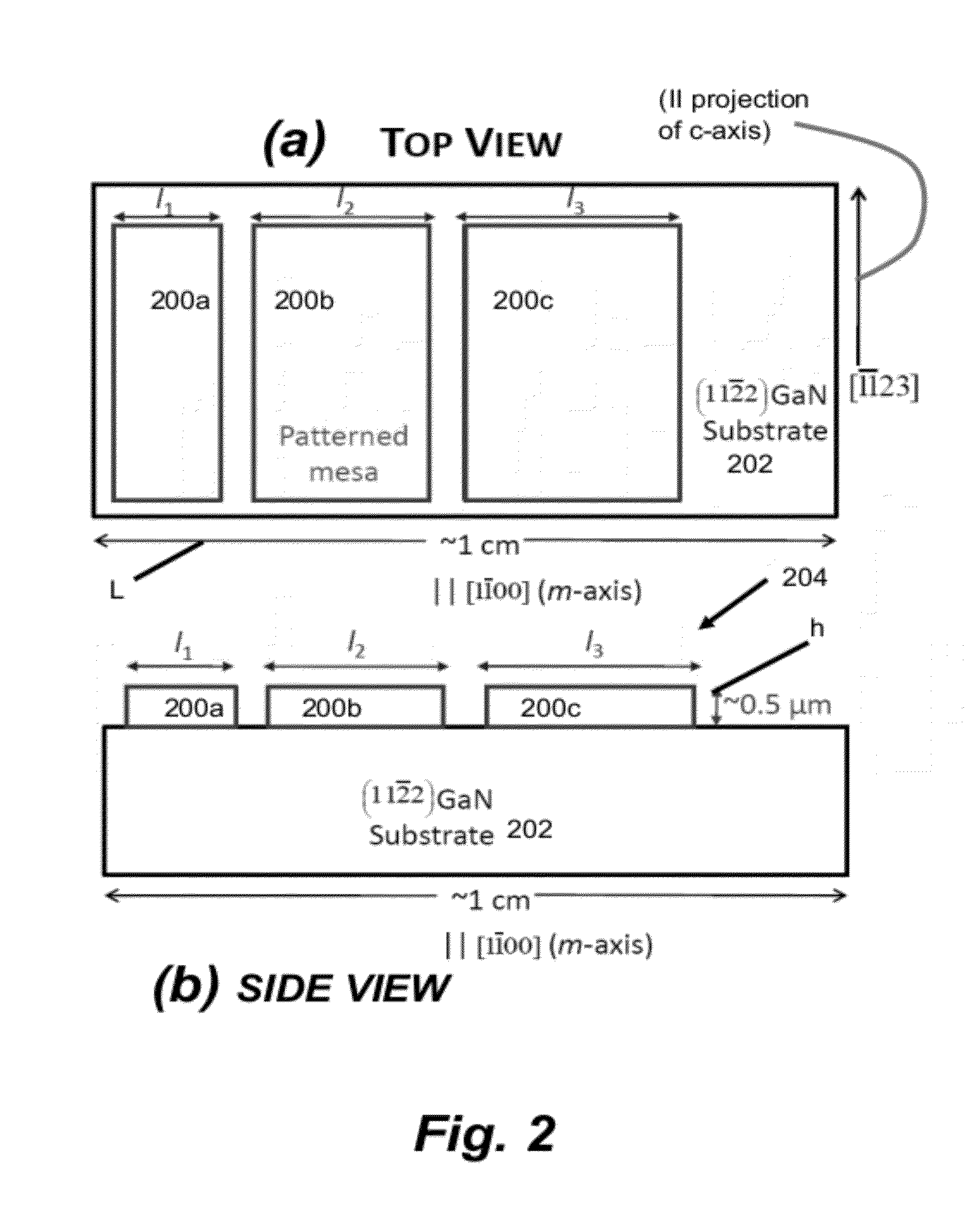
[0032]State of the art commercial III-nitride devices are based on coherent growth of hetero-epitaxial films on a III-nitride substrate. As mentioned above, this limits the thickness / composition of strained III-nitride films and limits the device design space. Using higher composition strained epilayers leads to the formation of MDs at heterointerfaces, which can degrade device performance [1]. The current invention provides a work-around to the MD formation process by limiting the glide length of pre-existing Threading Dislocations (TDs).
[0033]Nomenclature
[0034]GaN and its te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com