Method and Apparatus for Cleaning Delicate Textiles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
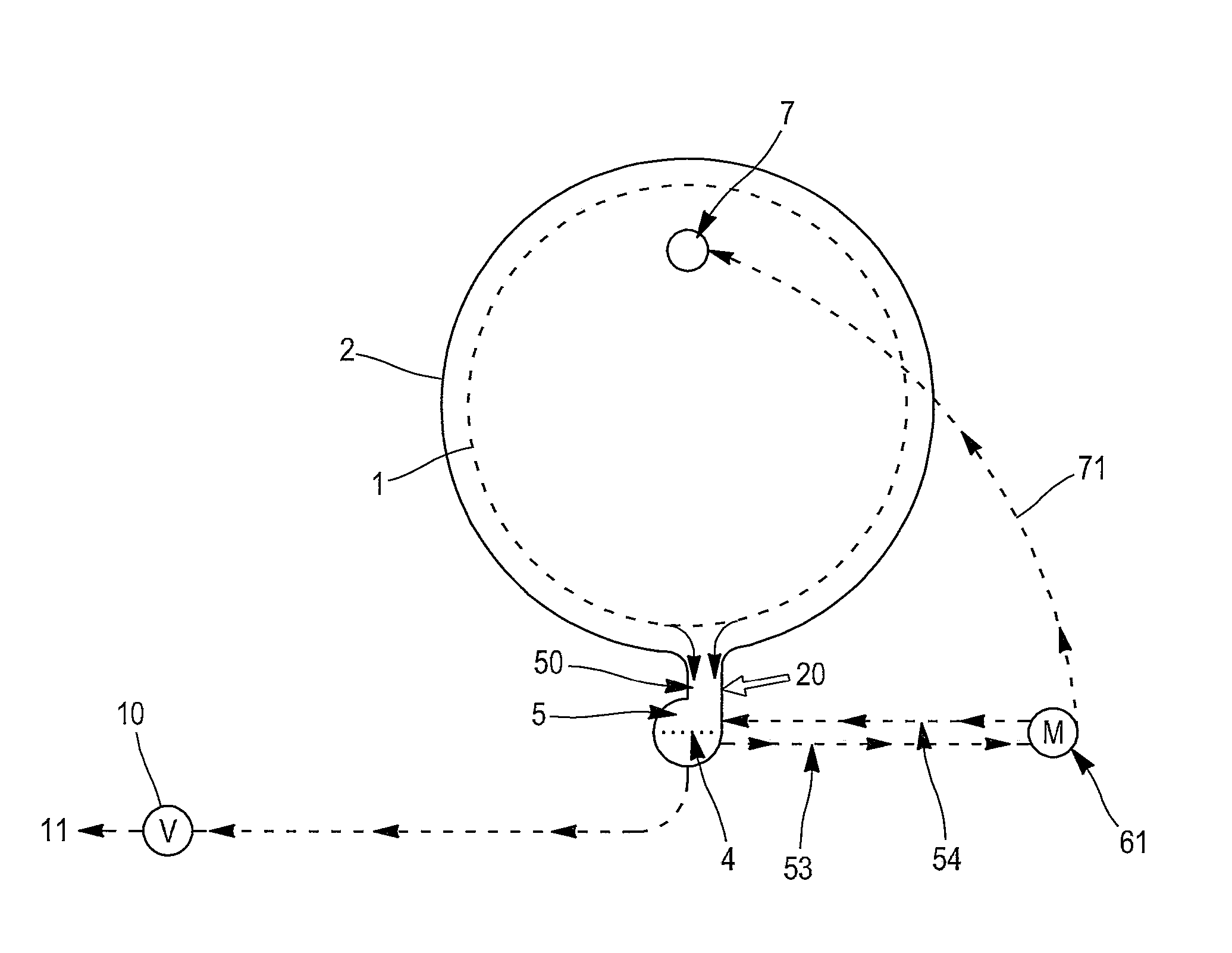
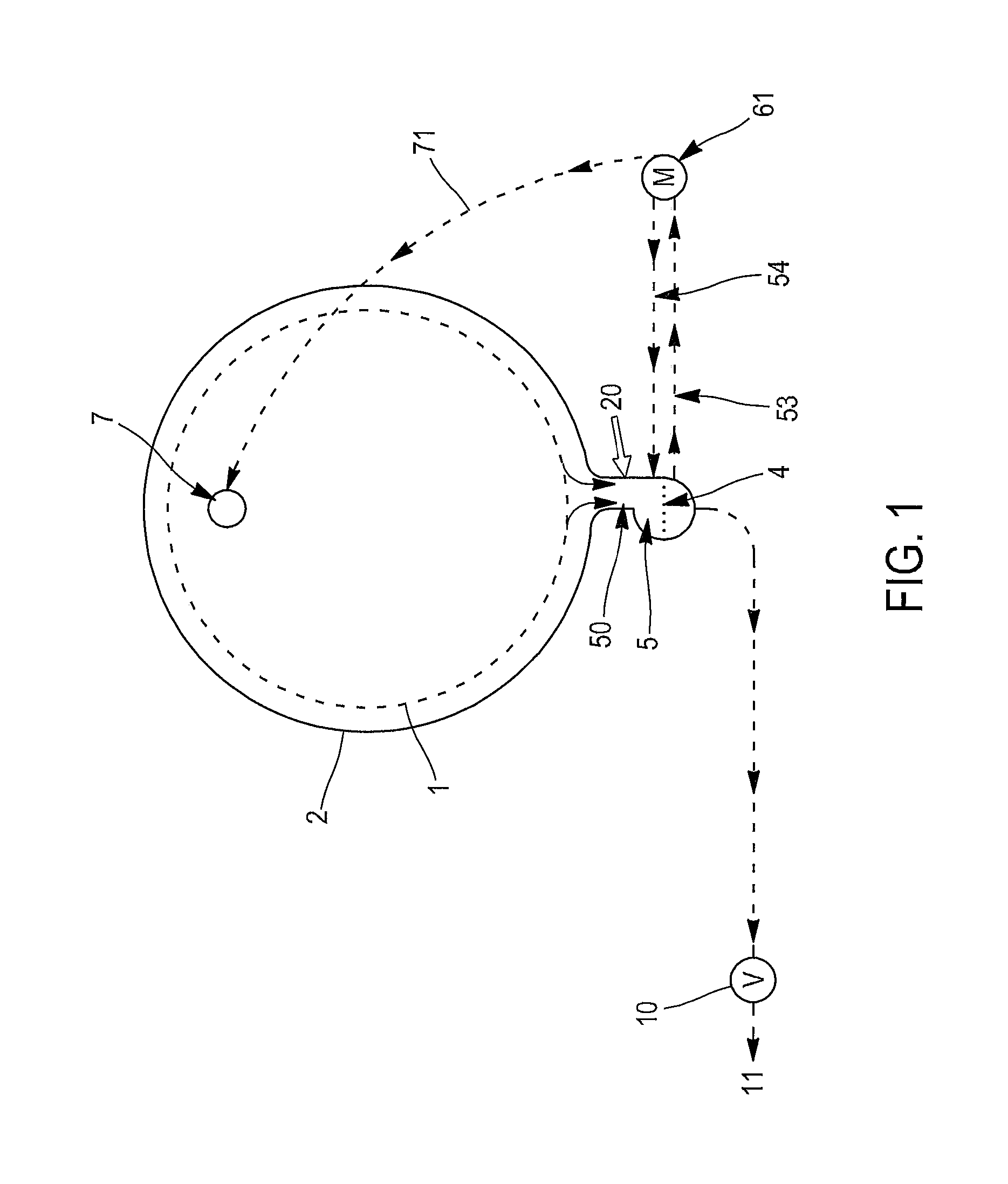
[0053]As explained in relation with the invention, said warm mixture is fully mixed thanks to pump 62 and connections 51, 52 between said pump 62 and the first container 5.
second embodiment
[0054]the invention will preferably be used to introduce the warm mixture into the drum 1 at low pressure. This allows much higher loading ratio in the drum since the mixture enters the drum 1 from its top.
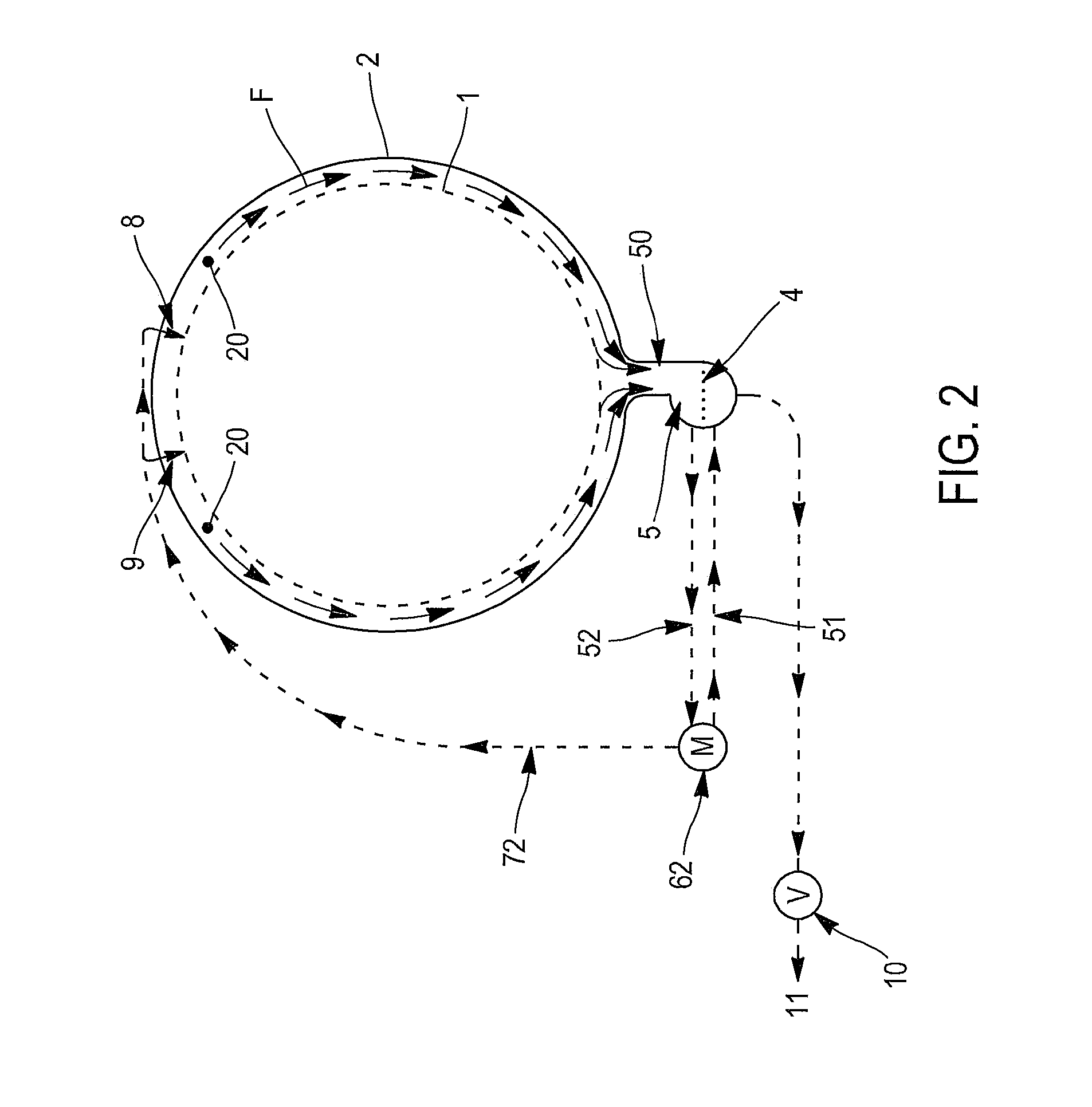
[0055]FIG. 3 illustrates a kind of combination of first and second embodiments. It relates to an apparatus comprising two pumps 61, 62; a first pump 61 is dedicated to the spraying means 7, the second pump 62 is dedicated to the injections means 8, 9. Both pumps 61, 62 are connected to the first container 5, to circulate the warm mixture.
[0056]As shown in FIG. 3 a second container 3 can be provided for another fluid such as a conditioner composition. Water is preferably introduced through the second container 3 which, however, is not compulsory.
[0057]The injections of the different compositions or mixtures are made successively.
[0058]A method for cleaning delicate textiles will now be described, susceptible to be implemented in apparatuses as described above.
[0059]Once textiles ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com