Low-Power Modulation in an Amplifier
a low-power modulation and amplifier technology, applied in low-frequency amplifiers, digital transmission, gain control, etc., can solve the problems of prone to loss of analog to digital conversion, reduce power dissipation, reduce power loss, reduce power loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
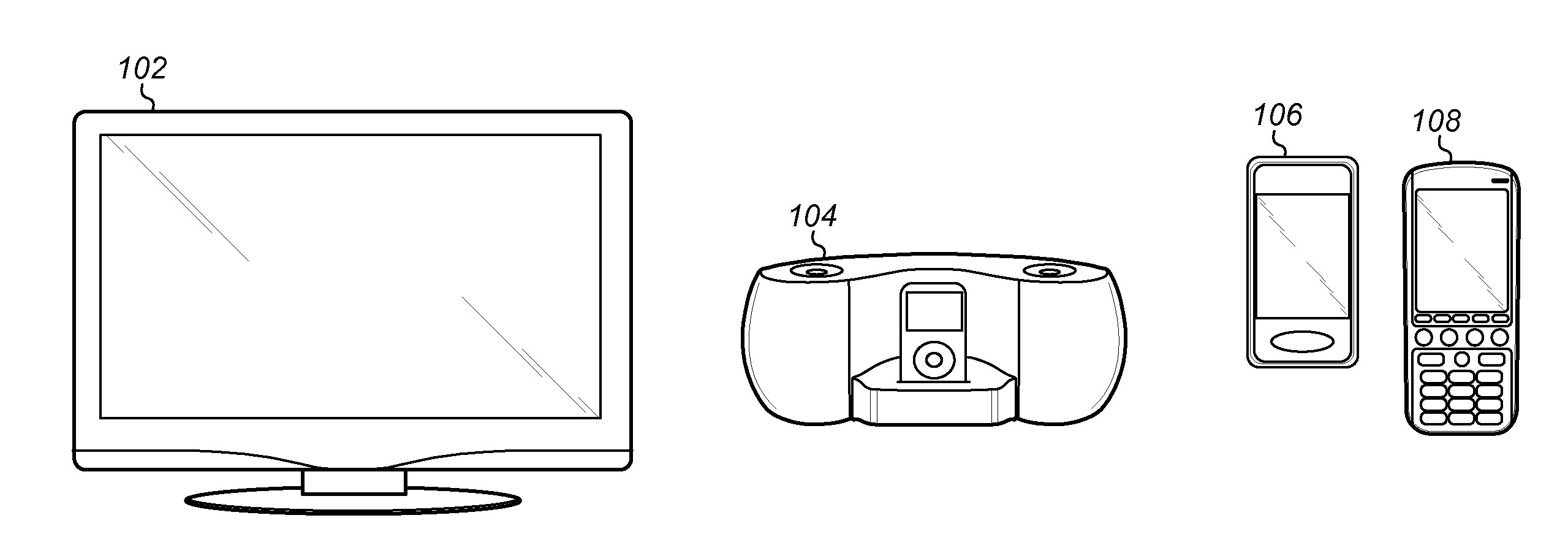
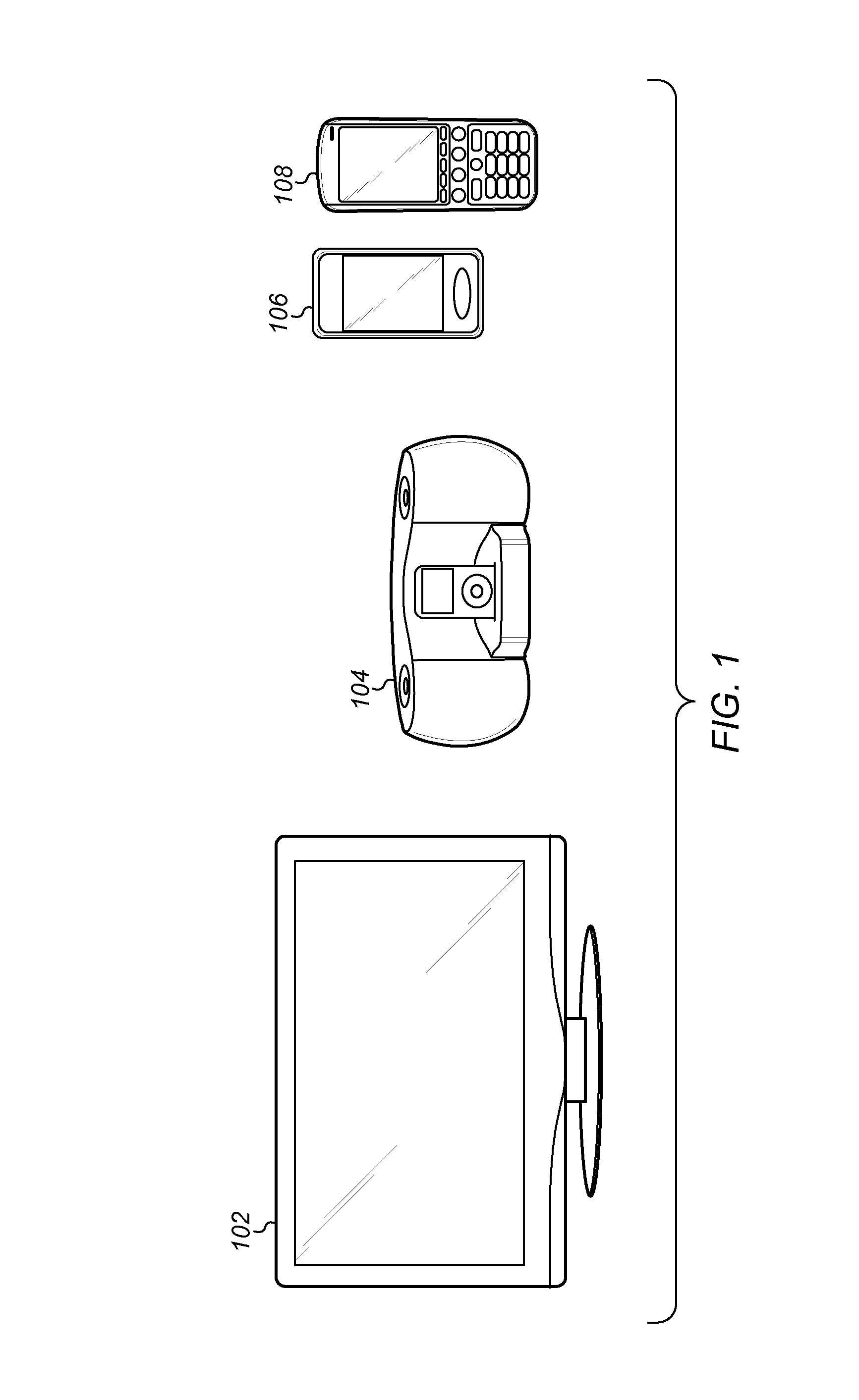
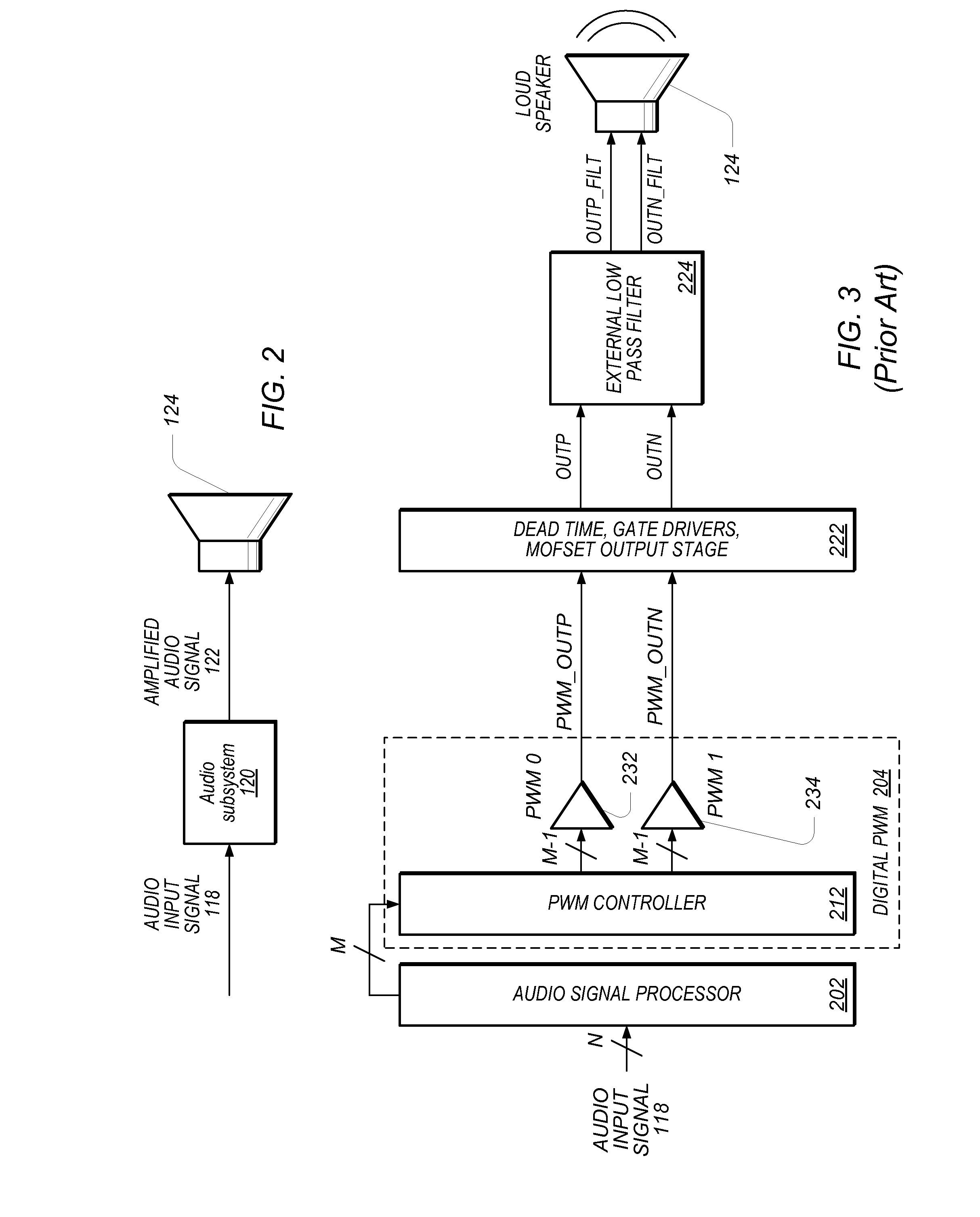
[0027]FIG. 1 illustrates exemplary systems, which may utilize the techniques described above. More specifically, FIG. 1 illustrates exemplary systems, which may utilize an audio subsystem, (which may include an amplifier such as a Class D amplifier), featuring various improvements. As shown, embodiments of the techniques disclosed herein may be used in any one ore more of various systems which involve the amplification of signals. For example, embodiments of the invention may be used in various systems that operate to amplify audio signals for provision to a loudspeaker for audible presentation. It is noted that the various terms or designations for circuits, such as “signal processing”, “auxiliary”, “control”, “indicator”, etc. are merely names or identifiers used to distinguish among these circuits, and these terms are not intended to connote any specific meaning
[0028]As shown, the exemplary systems may include a display device 102; an audio system 104, such as a stereo amplified ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com