Closed loop well twinning methods
a closed loop, wellbore technology, applied in the direction of borehole/well accessories, survey, construction, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming drilling process, achieve the effect of improving the efficiency of drilling operation, reducing the total time required, and improving the placement accuracy of twin wells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 150
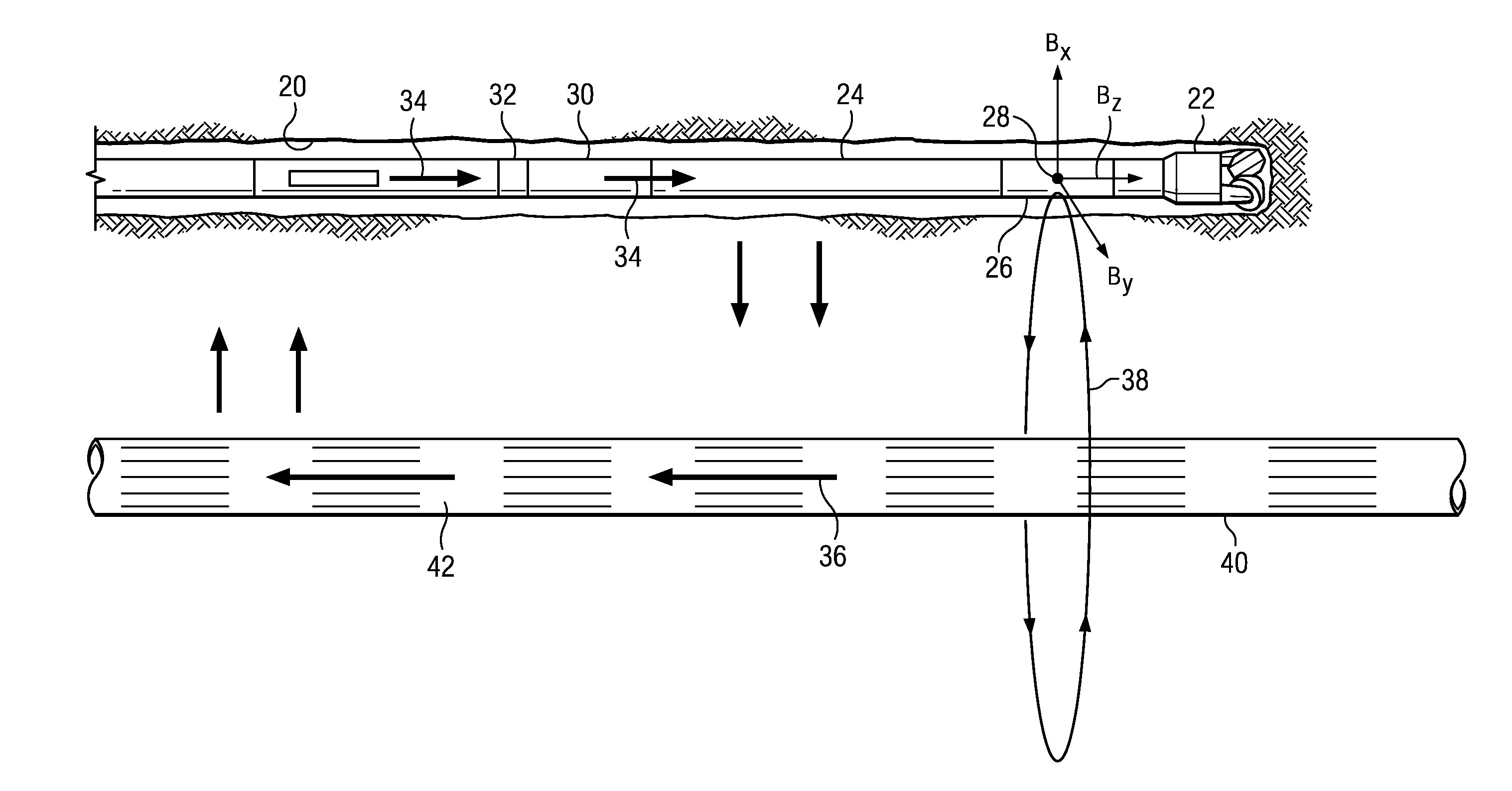
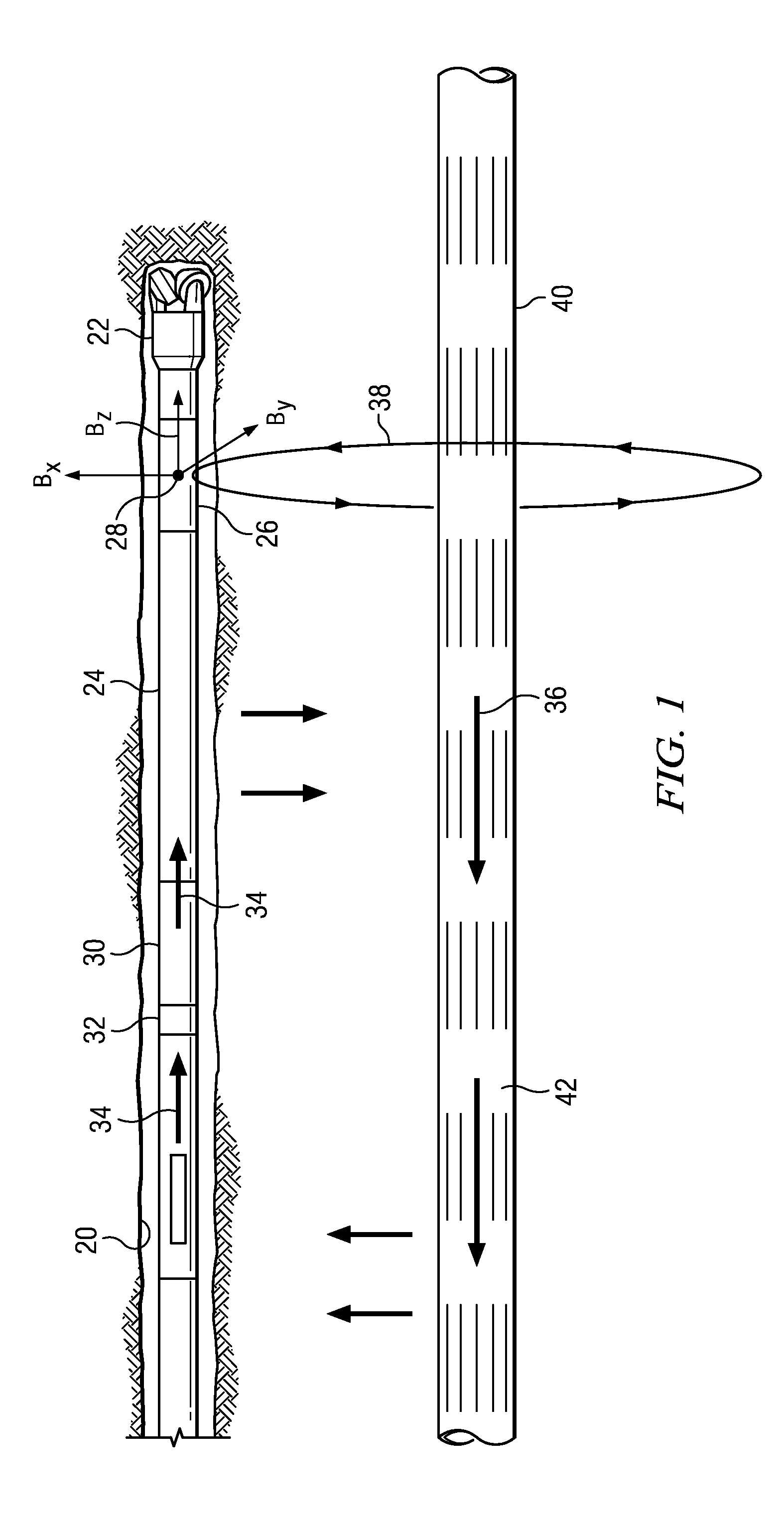
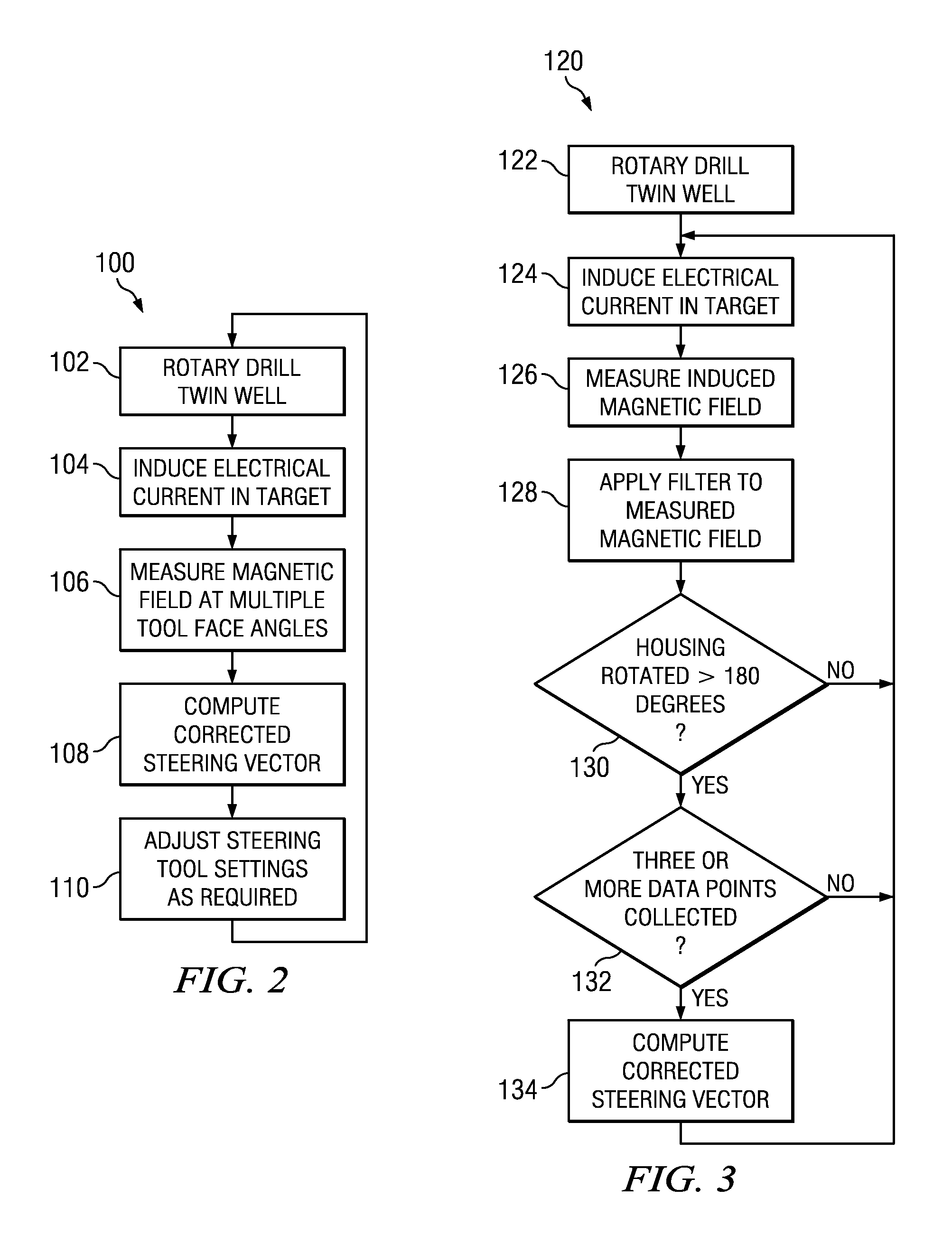
[0038]FIG. 5A depicts a flowchart of yet another disclosed method embodiment 150. Method 150 is intended for use with a rotary steerable tool that rotates with the drill string. Method 150 may be used with a rotary steerable tool in which the magnetic field sensors are deployed in a housing that is rotationally coupled with the drill string or alternatively in a roll-stabilized housing. The magnetic field sensors may also be deployed in a separate MWD tool deployed above or below the rotary steerable tool in the BHA. When deployed in a roll-stabilized housing, sensors may be stationary with respect to the borehole or rotate relatively slowly with respect to the borehole (as compared to the rotation rate of the BHA). Method 150 is similar to method 120 in that the twin well is rotary drilled at 152 using a BHA including a rotary steerable tool. The rotary drilling operation may include circulating drilling fluid through the drill string, rotating the drill string at the surface, and ...
embodiment 180
[0041]FIG. 6A depicts a flowchart of still another disclosed method embodiment 180. Method 180 is intended for use with a rotary steerable tool in which the magnetic field sensors are deployed in a roll-stabilized housing. Being deployed in a roll-stabilized housing the magnetic field sensors may be non-rotating with respect to the borehole (e.g., in the bias phase) or may rotate slowly with respect to the borehole (e.g., in the neutral phase). The rotation rate in the neutral phase is much less than that of the BHA and other rotary steerable tool components (e.g., in a range from about 1 to about 5 revolutions per minute). For example, in one embodiment the BHA may rotate at 120 revolutions per minute (2 Hz) while the sensors may rotate at −3 revolutions per minute (i.e., in the opposite direction as the BHA). The disclosed embodiments are of course not limited to any particular rotation rates of the BHA and roll-stabilized housing.
[0042]Method 180 is similar to method 120 in that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com