Ceiling support construction and methods
a support construction and ceiling technology, applied in the direction of walls, floors, building components, etc., can solve the problems of low building cost, scarce natural resources and raw materials, and inability to readily obtain conventional building materials such as cement, bricks, wood or steel, if available, and achieves less weight, less handling and transportation of composite sandwich panels, and a greater strength-to-weight ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
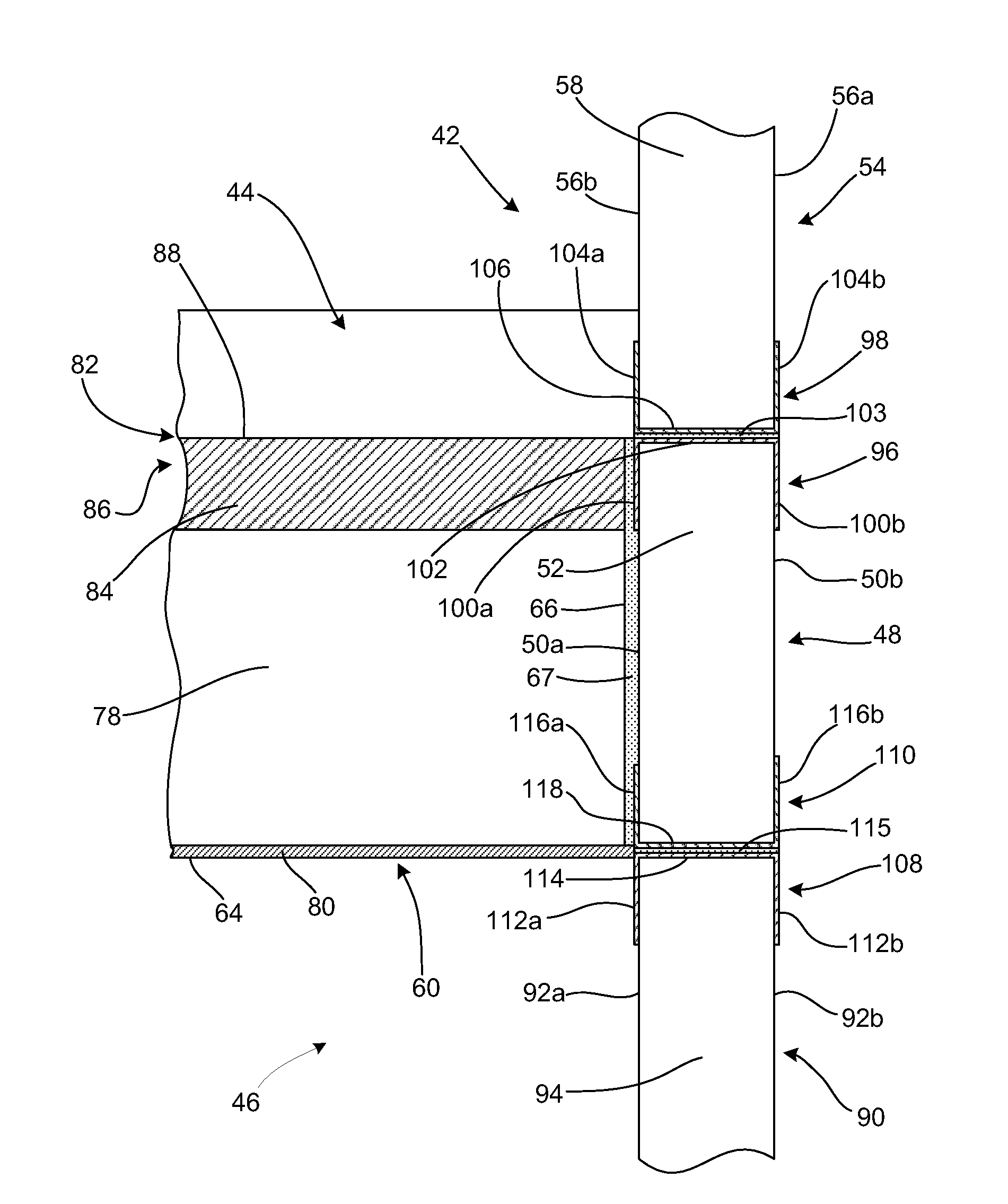
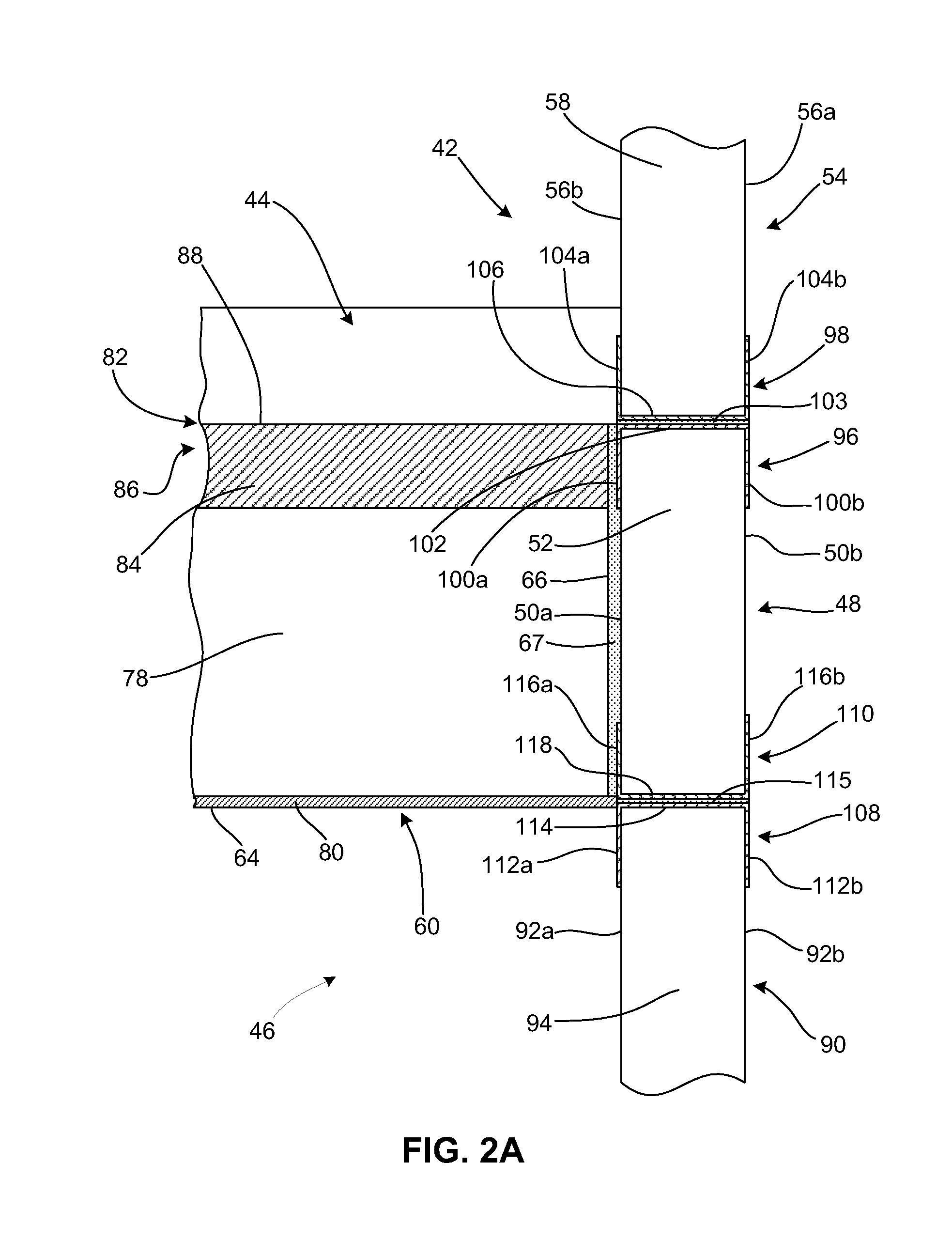
[0034]The present invention is directed to a novel ceiling construction and a novel method for forming a ceiling construction. The ceiling construction makes use of the advantages of sandwich panels with insulative cores to provide support for a ceiling or level of a structure. More specifically, the present invention involves using one or more sandwich panels as walls on a lower level of a structure and adhering a beam to the lower level sandwich panel(s). The beam may also be sandwich panel having a structure similar to the sandwich panel walls. Once adhered, the beam is capable of providing support for a ceiling or additional level of a structure above the lower level.
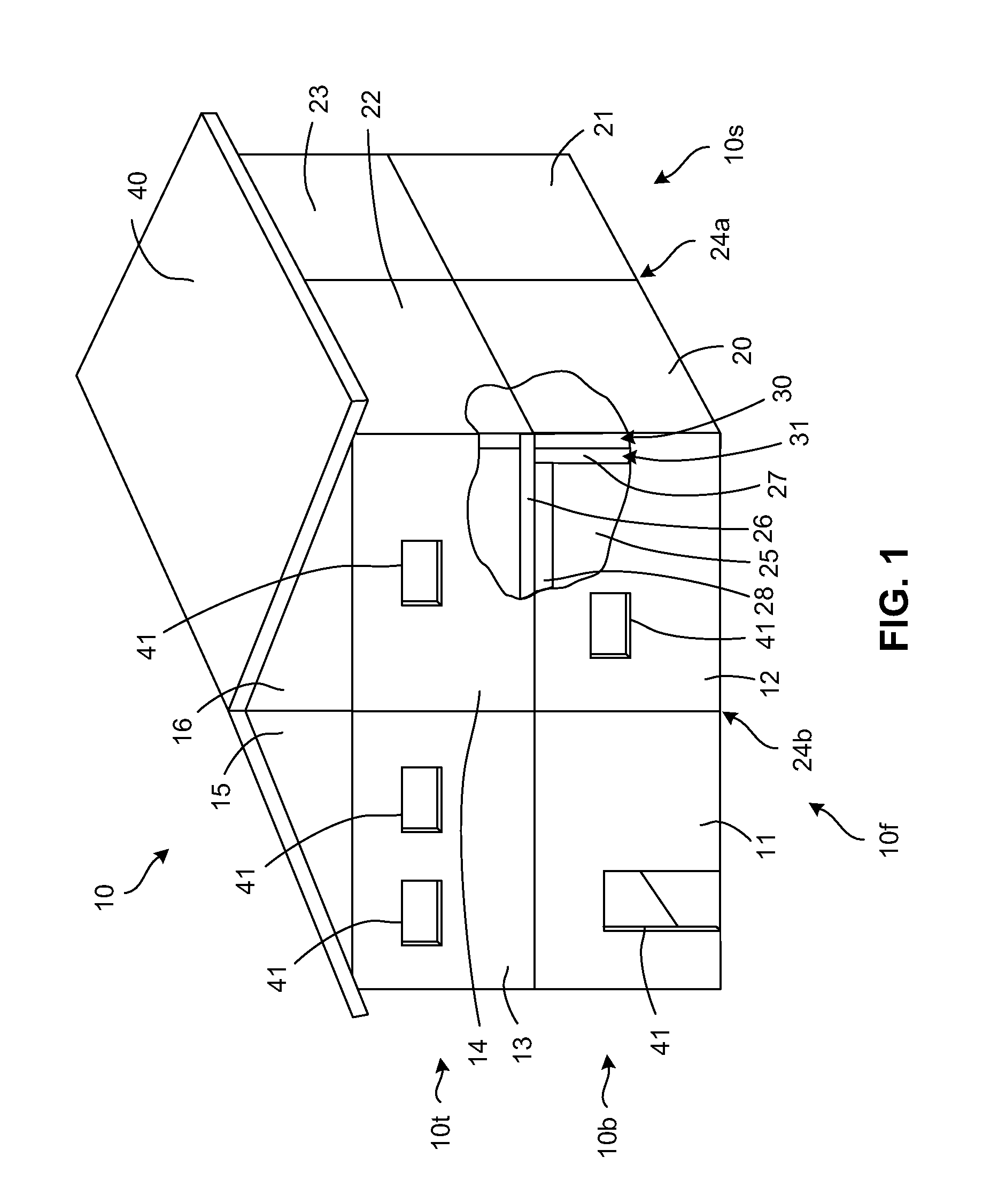
[0035]Referring to FIG. 1, an exemplary monolithic structure 10, for example, a house, is built from a number of sandwich panels that are connected together with bonding material. A front wall 10f of the house 10 is formed from sandwich panels 11-16. A side wall 10s of the house 10 is formed from sandwich panels 20-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com