Device and method for bridging a neck of an aneurysm
a neck and aneurysm technology, applied in the field of devices and methods for bridging the neck of an aneurysms, can solve the problems of tissue ischemia (i.e. lack of oxygen and nutrients), death and health care expenditure, and inability to carry out surgery, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing neurological damage, facilitating removal of material, and reducing pain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
I. Overview
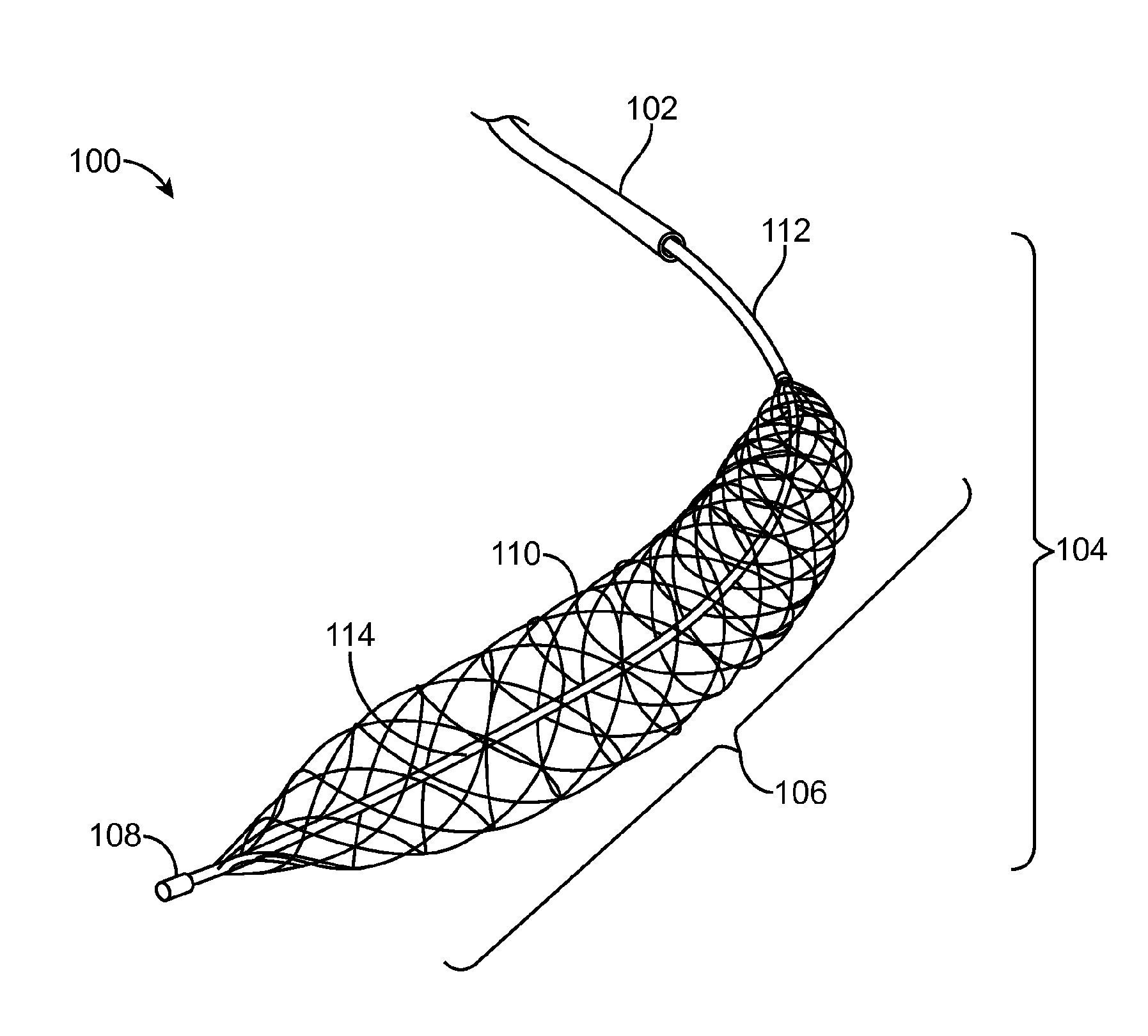
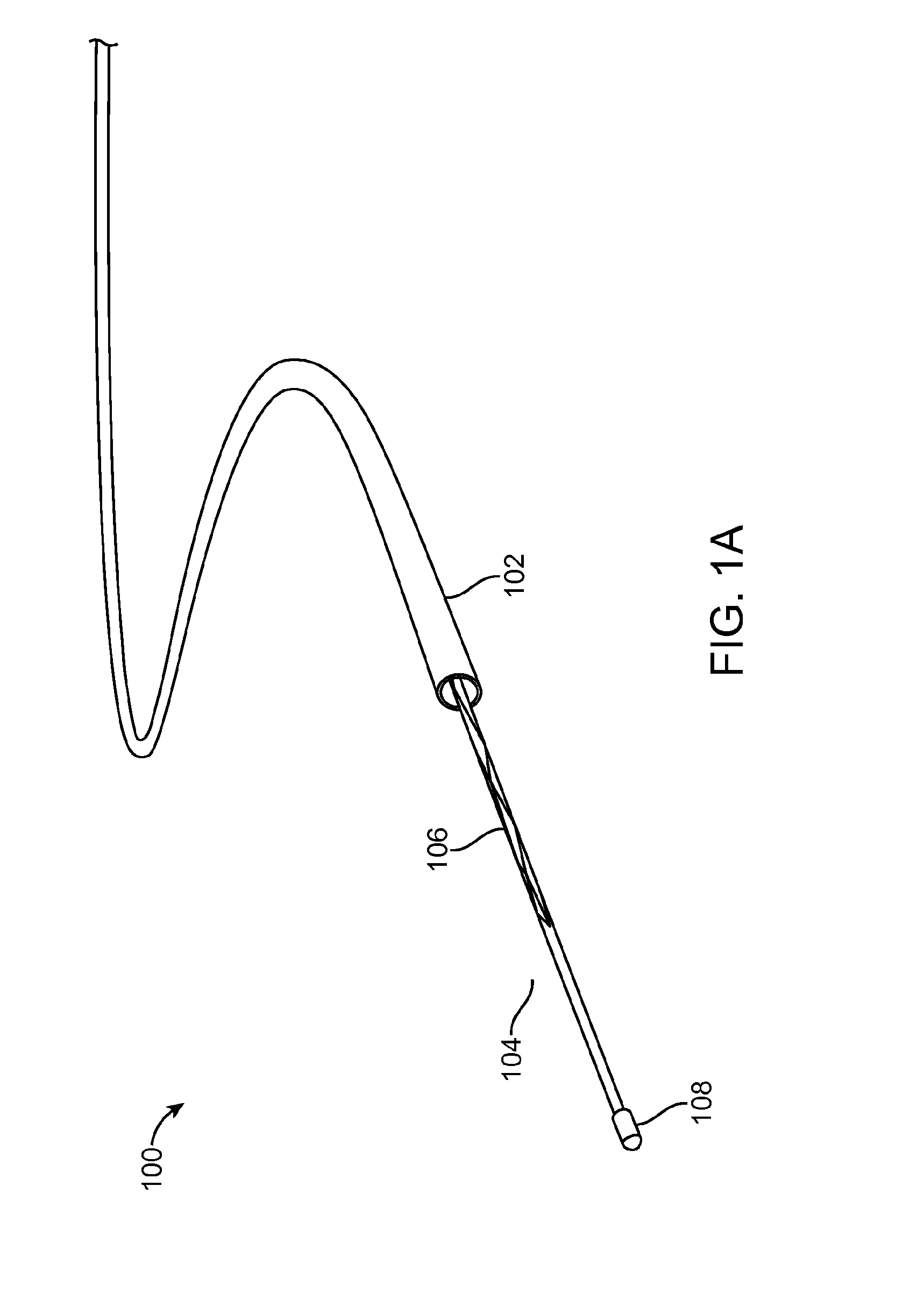
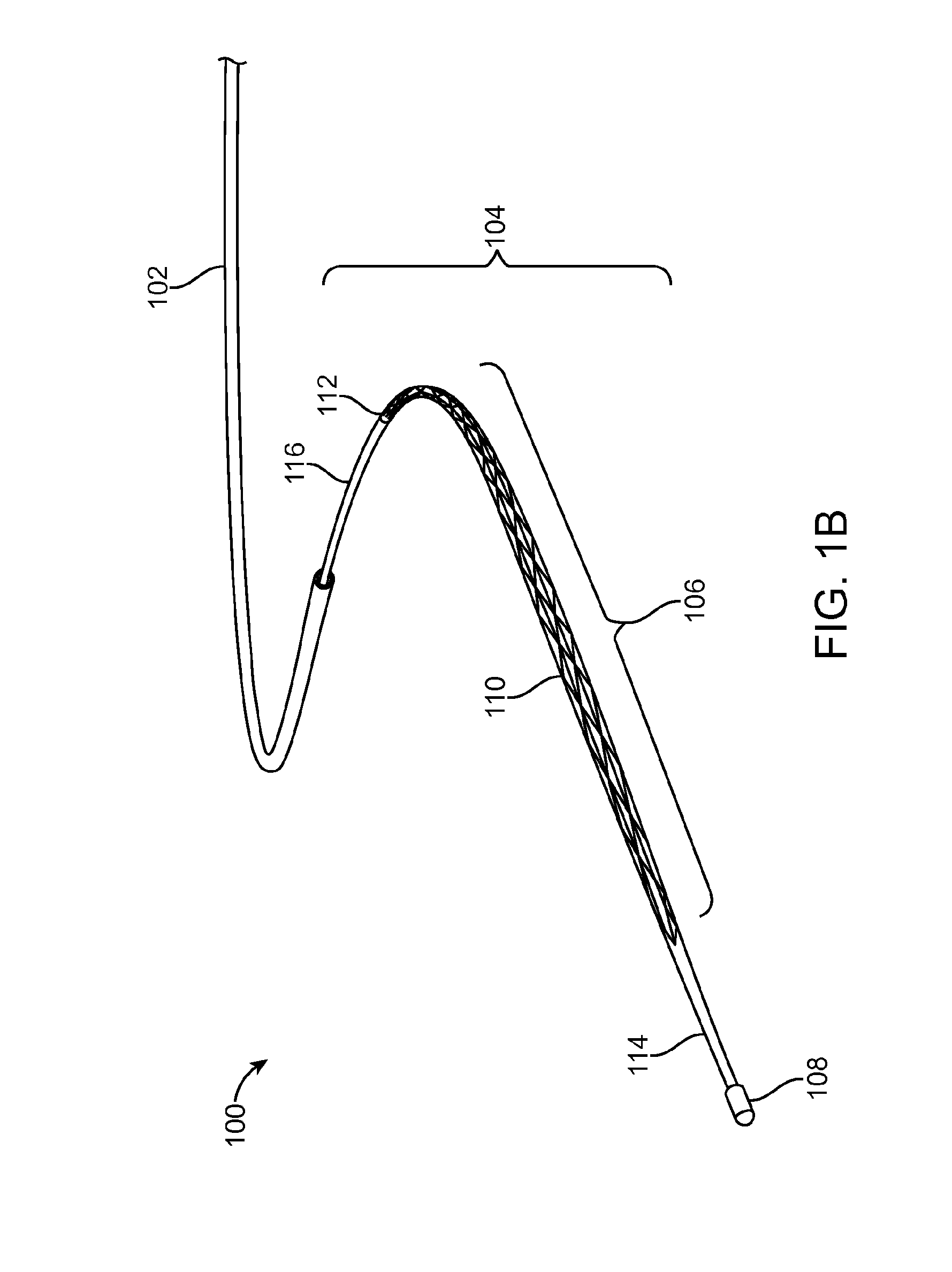
[0077]Embodiments of the invention related to a micro-catheter device having an expandable member. In one embodiment, the expandable member has spirally wrapped (e.g., multiple crossing helixes) and woven filaments in a basket-like configuration. The filaments can be constructed from super-elastic Ni—Ti, with the exception of two filaments constructed from Pt—Ir for radiopacity. In one embodiment sixteen filaments are used, while in another, eight filaments are used.
[0078]The proximal ends of the filaments may be connected to a tubular shaft having a small lumen, while the distal ends of the filaments are interconnected to a common joint. A central pull-wire can be connected to the common joint. The pull-wire can be slideable within the small lumen and may be moved relative to the rest of the microcatheter to cause expansion and contraction of the expandable member.
[0079]The expandable member can have a relaxed configuration with a diameter in a range from about 1 mm to a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com