Zinc production method using electric furnace dust as raw material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045]Embodiments of a zinc production method according to the present invention will be explained below in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
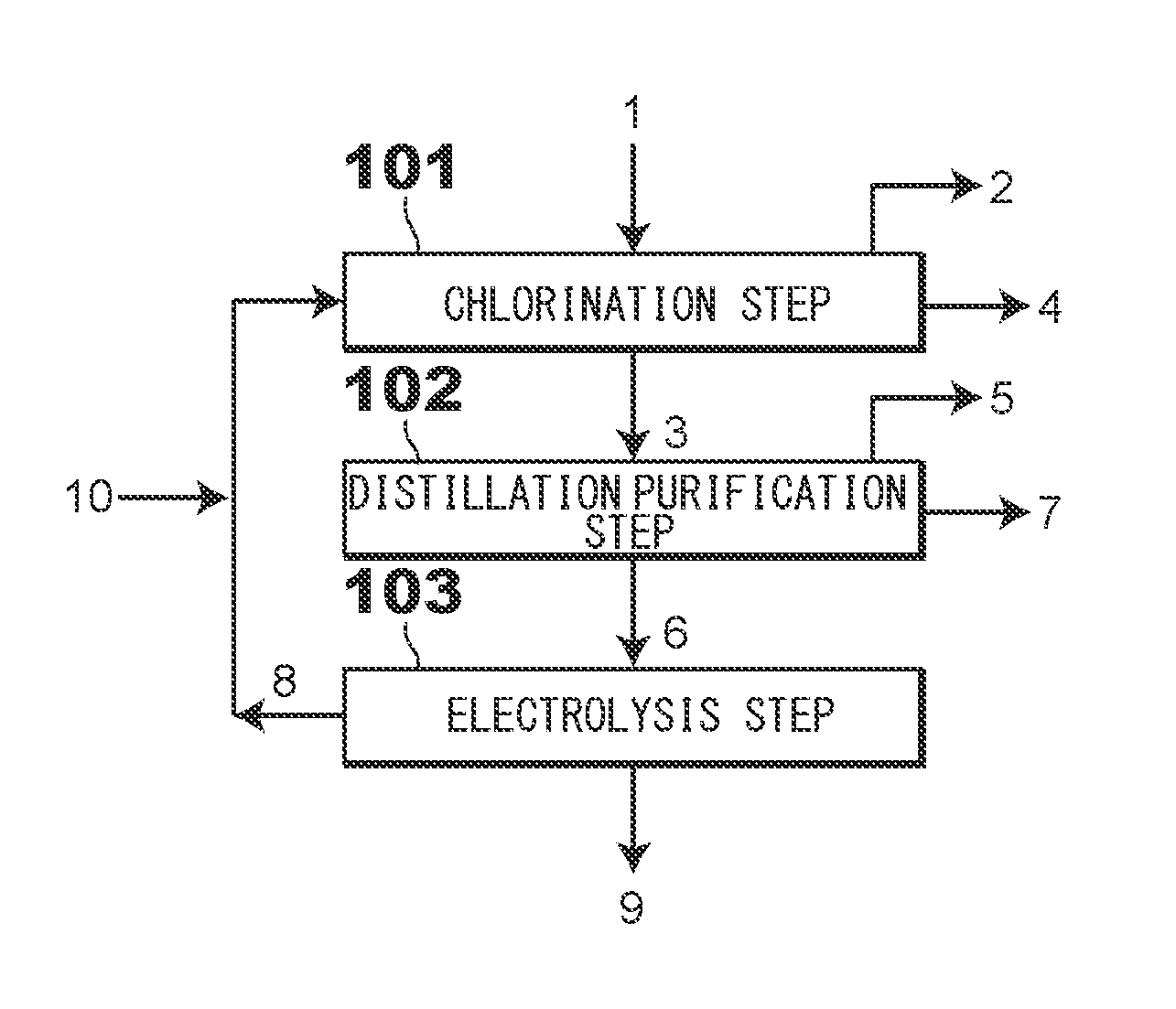
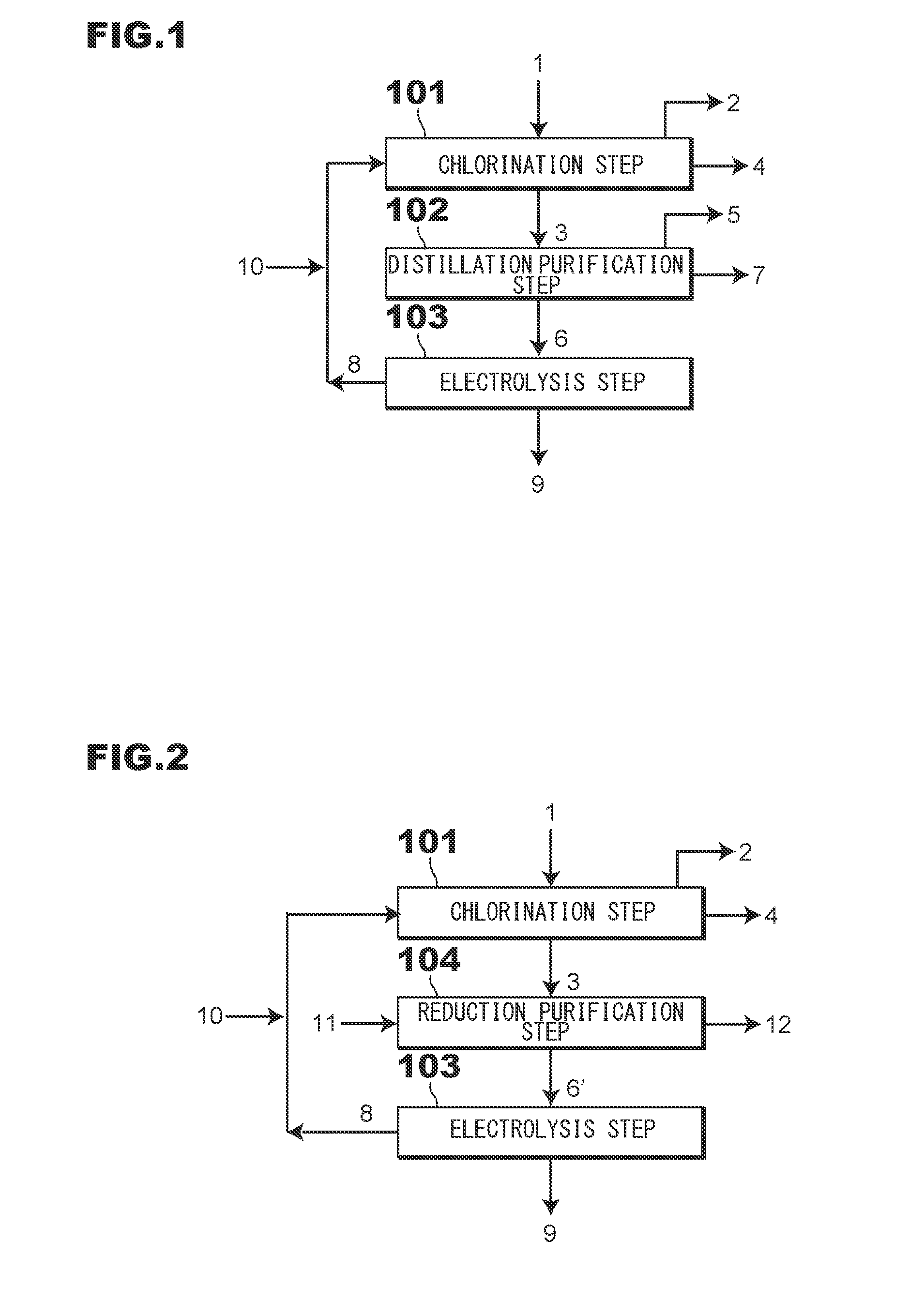
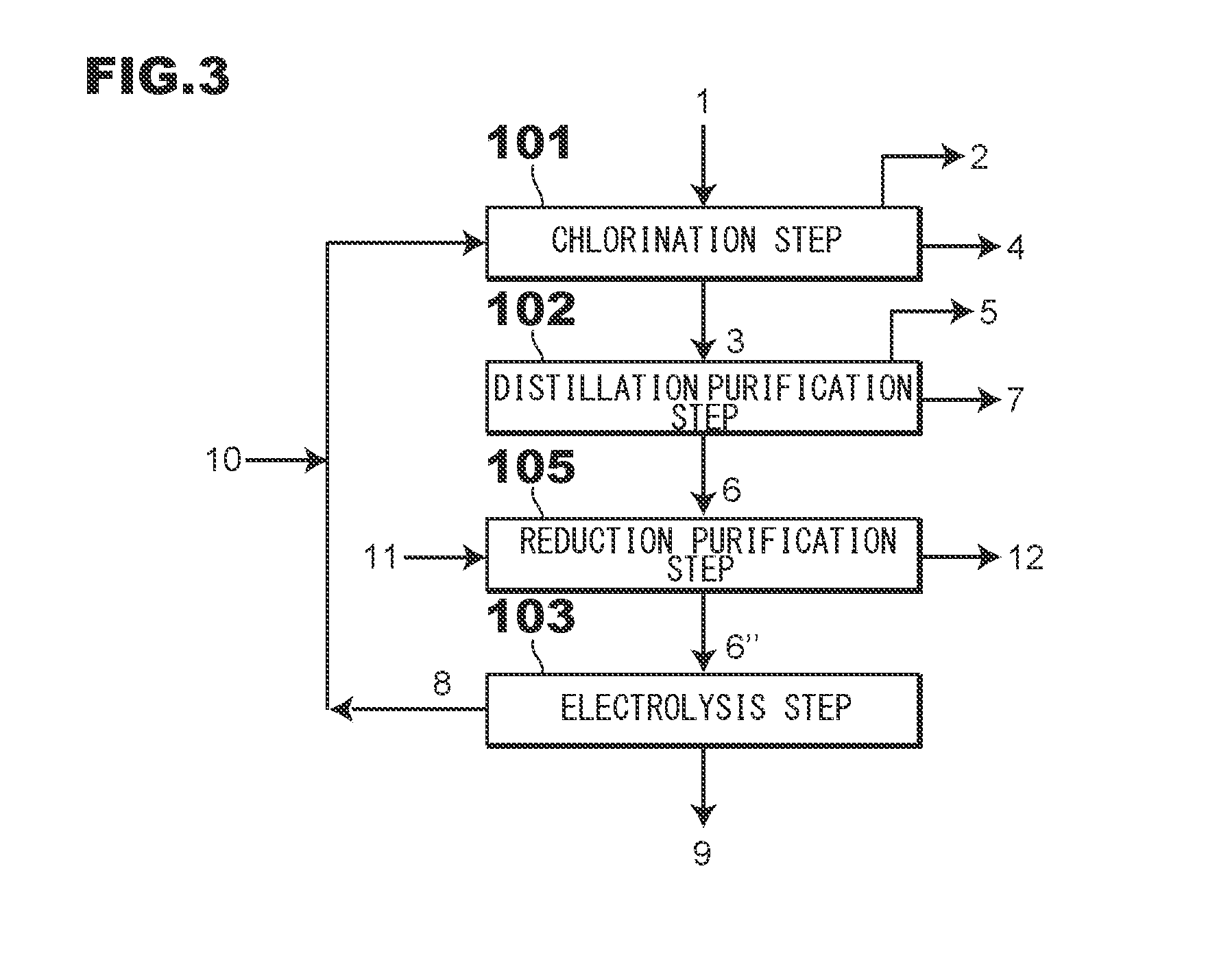
[0046]First, a zinc production method according to an embodiment of the present invention is described in detail with reference to FIG. 1.
[0047]FIG. 1 is a chart showing a process of the zinc production method according to the embodiment of the present invention.
[0048]As shown in FIG. 1, first, at a chlorination step 101, a mixed gas containing a chlorine gas 8 and an oxygen-containing gas 10 is brought into contact with electric furnace dust 1 or secondary dust 1 in a chlorination furnace (not shown), thereby obtaining a zinc oxide component in the electric furnace dust 1 or the secondary dust 1 as crude zinc chloride vapor 3. On the other hand, an iron component in the electric furnace dust 1 or in the secondary dust 1 is not chlorinated and remains as a solid. The chlorination step 101 is a reaction step to obtain the crude...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com