Therapeutic and Diagnostic Method for Ataxia-Telangiectasia
a diagnostic method and ataxia technology, applied in the field of ataxia-telangiectasia therapy and diagnostic method, can solve the problems of severe consequences of atm damage in dna damaged cells, and achieve the effects of reducing neurodegeneration in a-t, and regulating proteasome-mediated protein turnover
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0073]Human tissues and Animal Studies.
[0074]Frozen human mid-brain tissues containing specifically substantia nigra were obtained postmortem from patients with confirmed A-T disease and control individuals (without any known disease). Slides with paraffin-embedded sections of the midbrain tissues were used in immunoflorescence study. Human brain tissues and tissue sections were obtained from the NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders at the University of Maryland under protocols approved by the University of Maryland Institutional Review Board.
[0075]Animal study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. The protocol was approved by the Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center—NO Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee under its assurance with the Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare of the National Institutes of Health.
[...
example 2
Protein Polyubiquitylation and Degradation is Reduced in Cells Deficient in ATM
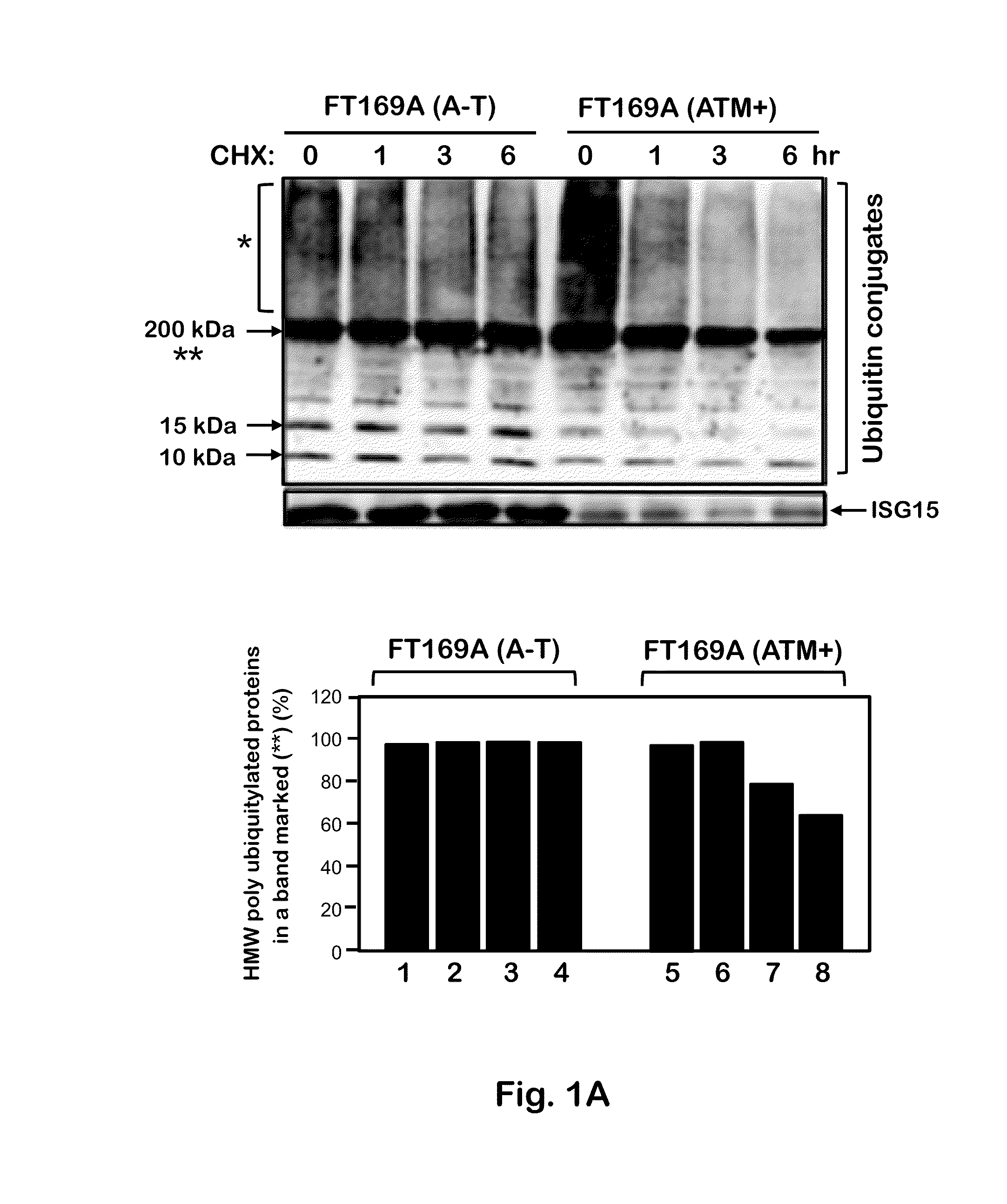
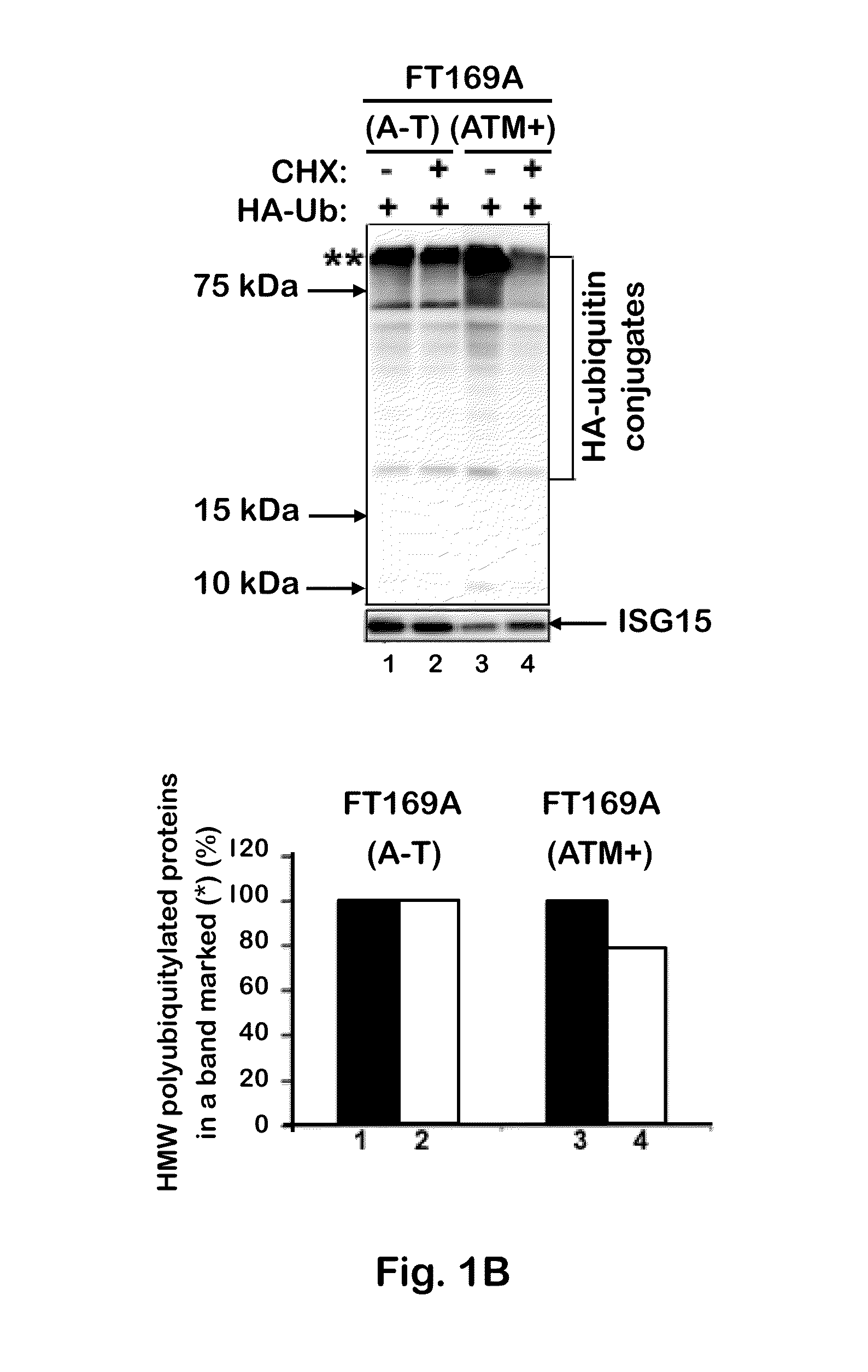
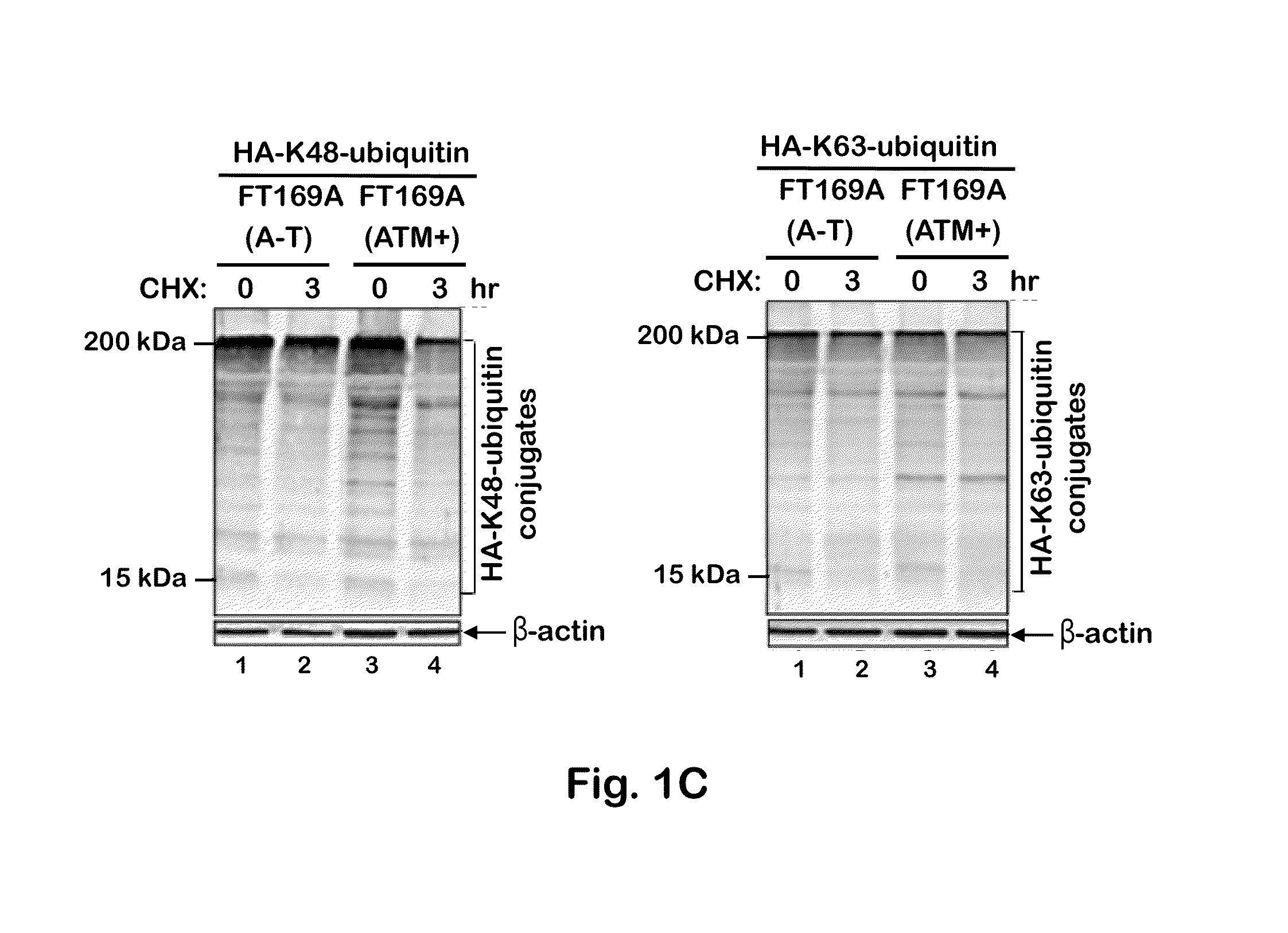
[0092]To test whether the defective ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cellular proteins contributes to neurodegeneration in A-T, the rate of degradation of overall cellular polyubiquitylated proteins was monitored in FT169A (A-T) (ATM null) and FT169A (ATM+) (ATM reconstituted FT169A) isogenic cells as described (71) using the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) (Sigma-Aldrich). In FIG. 1A, FT169A (A-T) (lanes 1-4) and FT169A (ATM+) (lanes 5-8) cells were treated with the protein synthesis inhibitor CHX (10 μg / ml) for 0, 1, 3, and 6 hours. Cell lysates were analyzed using discontinuous (15%) SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin antibody. The symbols * and ** mark the position of high-molecular-weight (HMW) polyubiquitylated proteins. Quantitation of the high-molecular-weight (HMW) polyubiquitylated proteins (shown as **) is shown in the bar graph.
[0093]As shown in FIG. 1A, t...
example 3
ATM Negatively Regulates the ISG15 Pathway
[0106]Previous studies have shown that ISG15 is increased in A-T lymphoblasts (70). Overexpression of ISG15 in tumor cells has been linked to reduced protein polyubiquitylation and turnover (24). To determine whether overexpression of the ISG15 pathway is responsible for reduced protein polyubiquitylation in FT169A (A-T) cells as shown above, the levels of ISG15 and its conjugates were measured in ATM null FT169A (A-T) and ATM-reconstituted FT169A (ATM+) cells using anti-ISG15 antibodies by Western analysis. In FIGS. 3A-3C, extracts of FT169A (A-T) and FT169A (ATM+) cells were analyzed by 5% (FIG. 3A) or 15% (FIG. 3B) SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using either anti-ATM (FIG. 3A) or anti-ISG15 antibody (FIG. 3B). The same membrane shown in FIG. 3B was stripped and re-probed with anti-tubulin antibody to assure equal protein loading. The average band intensity of the free ISG15 protein (error bar represents SEM) from three independent e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com