Polymerase-template complexes
a polymerase and template complex technology, applied in the direction of enzymology, enzyme stabilisation, transferases, etc., can solve the problems of unable to optimize specific variables (conditions) that optimize certain sequencing reactions, such as nanopore based sequencing, and achieve the effect of increasing the processivity of the template-polymerase complex and the processivity of the polymerase template complex formed in high-temperature solution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example embodiments
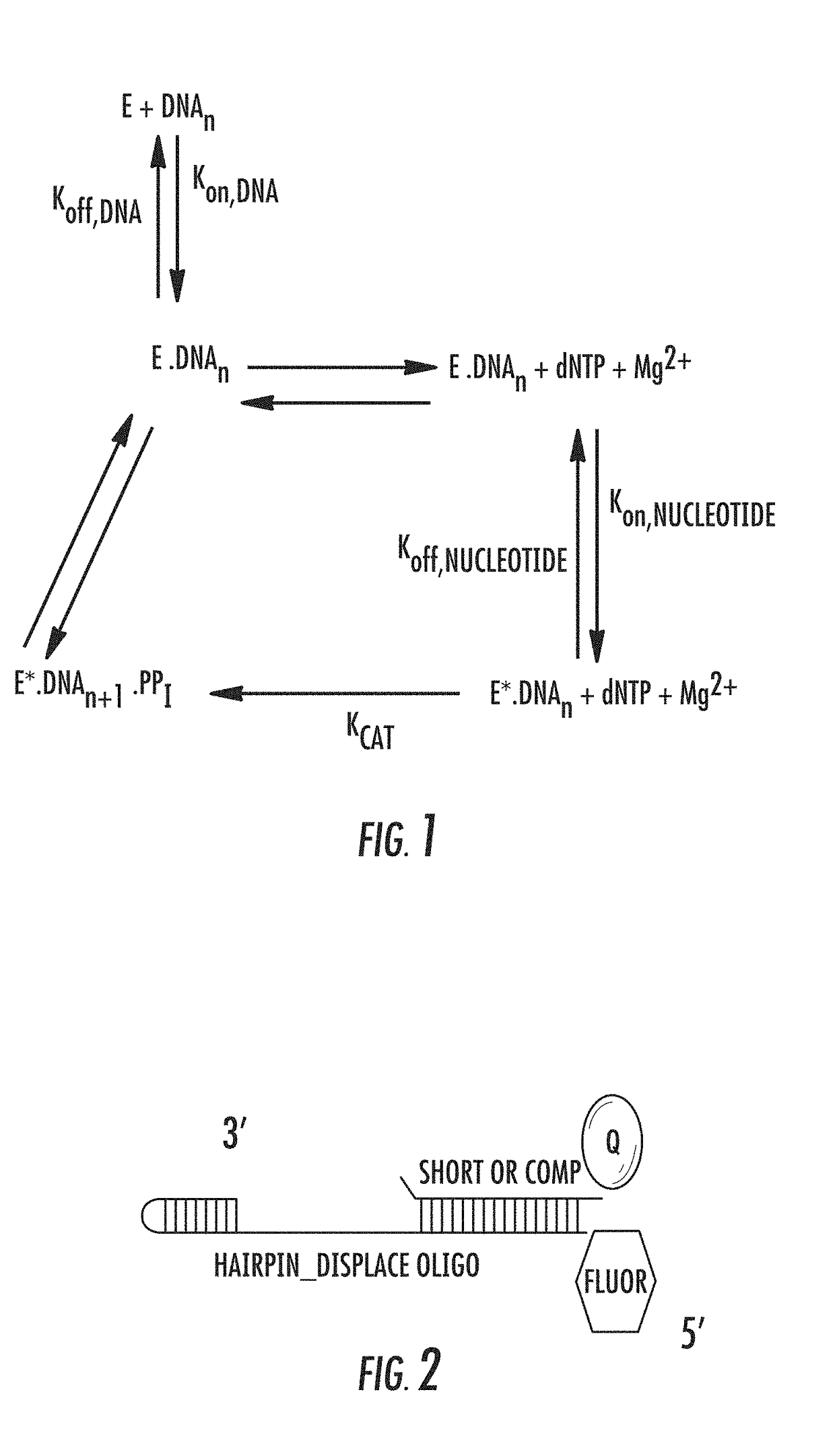
[0080]In certain example embodiments, the present disclosure provides methods and compositions for enhancing the processivity of the polymerase during template-dependent polynucleotide synthesis in the presence of a high concentration of salt. In other example embodiments, the present disclosure provides methods and compositions for enhancing the processivity of the polymerase during template-dependent polynucleotide synthesis in the presence of low nucleotide concentrations and high temperatures. The methods and compositions provided are applicable to methods of template-dependent DNA synthesis, including DNA amplification and sequencing. Sequencing methods include sequencing-by-synthesis of single polynucleotide molecules, such as nanopore sequencing of single DNA molecules.
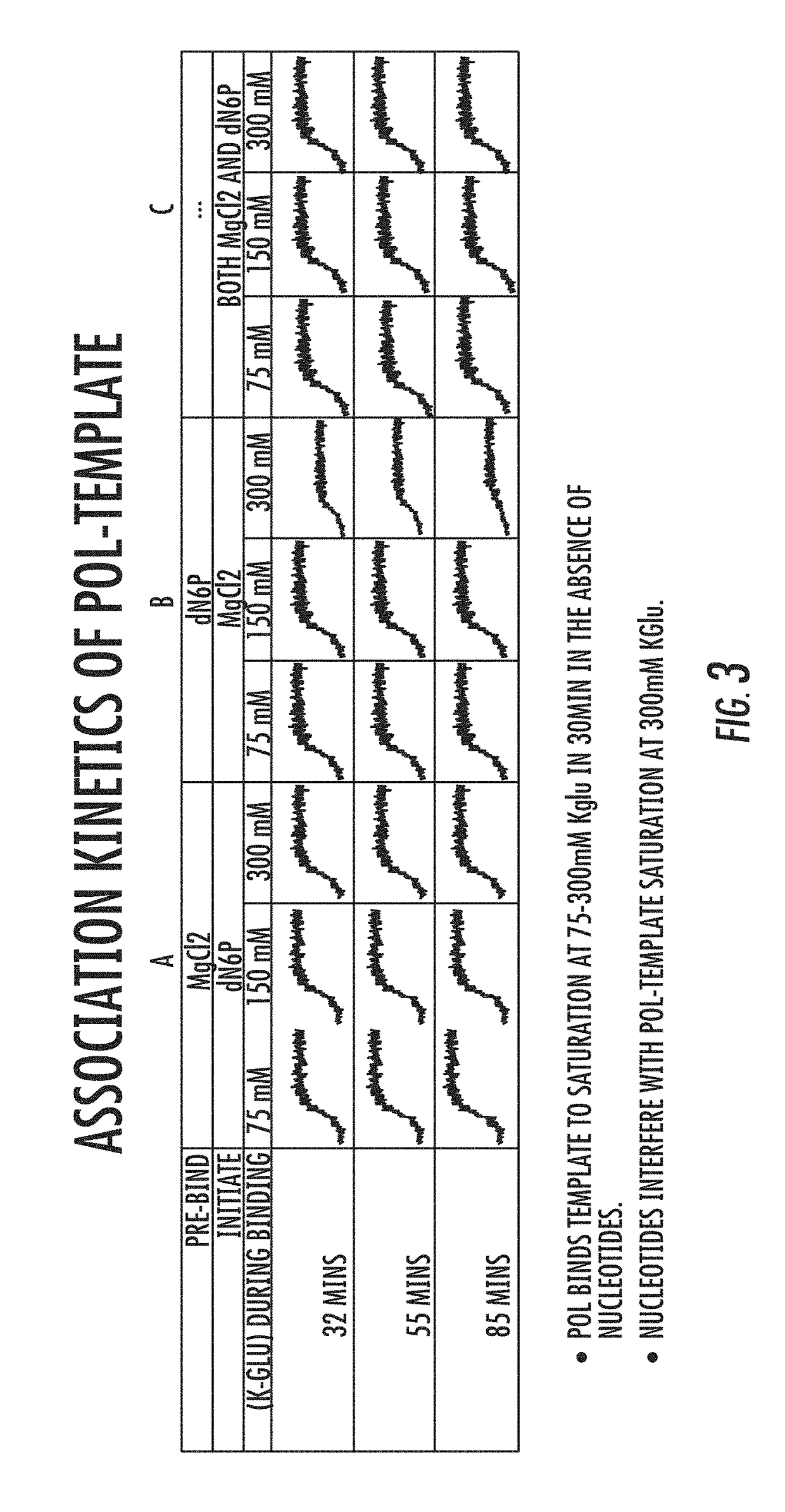
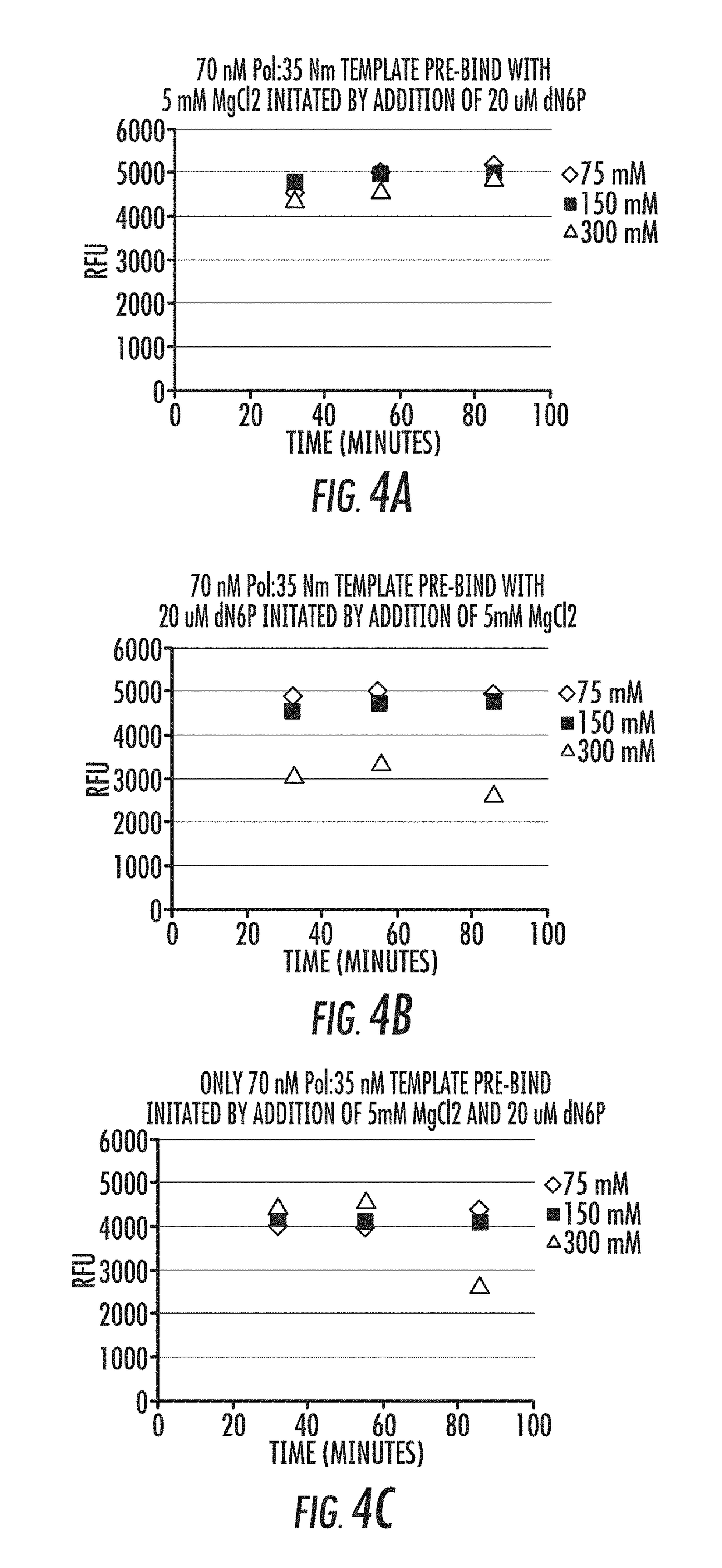
[0081]As illustrated in FIG. 1, the processivity of a polymerase, such as a DNA polymerase, is directly related to the formation of the polymerase-template complex and the incorporation of dNTP by the enzyme. U...
example 1
Pol6 Mutants
[0177]DNA of SEQ ID NO: 3 encoding the WT-Pol6 (SEQ ID NO: 2) was purchased from a commercial source (DNA 2.0, Menlo Park, Calif.). The sequence was verified by sequencing.
[0178]Site directed mutagenesis was performed to mutate one or more amino acids of the putative nucleotide / DNA binding site of parental variant Pol6-44-X1 (SEQ ID NO:4). Pol6-44-X1 was derived from wild-type Pol6 to comprise the following substitutions: S366A T529M A547F D44A (SEQ ID NO:4). Pol6-67-X2 was derived from wild-type Pol6 to comprise the following mutations: S366A T529M A547F N545L Y225L D657R Y242A (see SEQ ID NO: 14).
[0179]The Pol6 variants like 44-X1 were expressed as a fusion protein having an N-terminal His-tag (see underlined sequence in SEQ ID NO:4) and SpyCatcher domain (bolded italic sequence in SEQ ID NO:4).
Mutagenesis Protocol
[0180]The primers for each mutagenesis reaction were designed using the NEB base changer protocol and ordered in 96-well plate format from IDT.
[01...
example 2
n and Purification
[0185]Variants of the parental polymerase Pol6-44-X1 (SEQ ID NO:4), and the Pol6-67-X2 (SEQ ID NO: 14) were expressed and purified using a high throughput method as follows.
[0186]DNA encoding variants in expression plasmid pD441 vector were transformed into competent E. coli, and glycerol stocks of the transformed cells were made. Starting from a tiny pick of the glycerol stock, grow 1 ml starter culture in LB with 0.2% Glucose and 100 μg / ml Kanamycin for approximately 8 hrs. Transfer 25 μl of log phase starter culture into 1 ml of expression media (Terrific Broth (TB) autoinduction media supplemented with 0.2% glucose, 50 mM Potassium Phosphate, 5 mM MgCl2 and 100 μg / ml Kanamycin) in 96-deep well plates. The plates were incubated with shaking at 250-300 rpm for 36-40 hrs at 28° C.
[0187]Cells were then harvested via centrifugation at 3200×g for 30 minutes at 4° C. The media was decanted off and the cell pellet resuspended in 200 μl pre-chilled lysis buffer (20 mM P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com