Display device and electronic device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
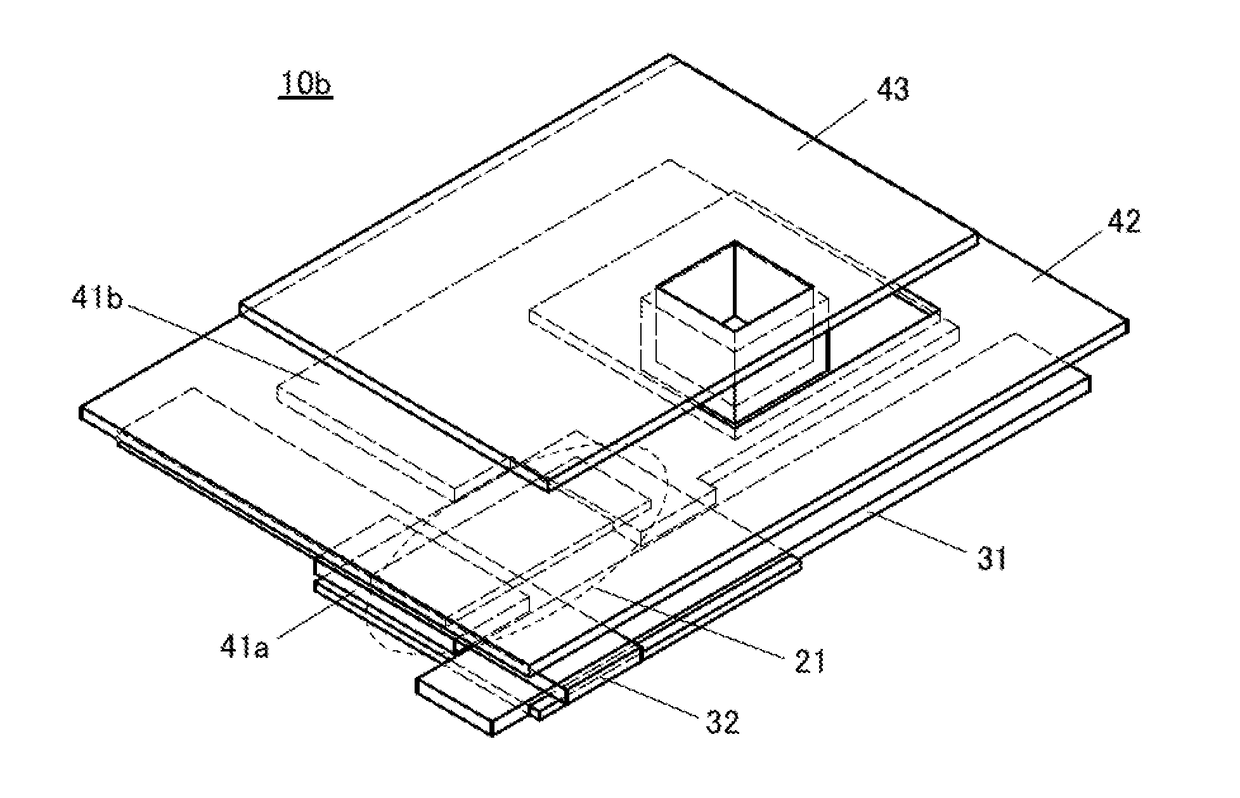
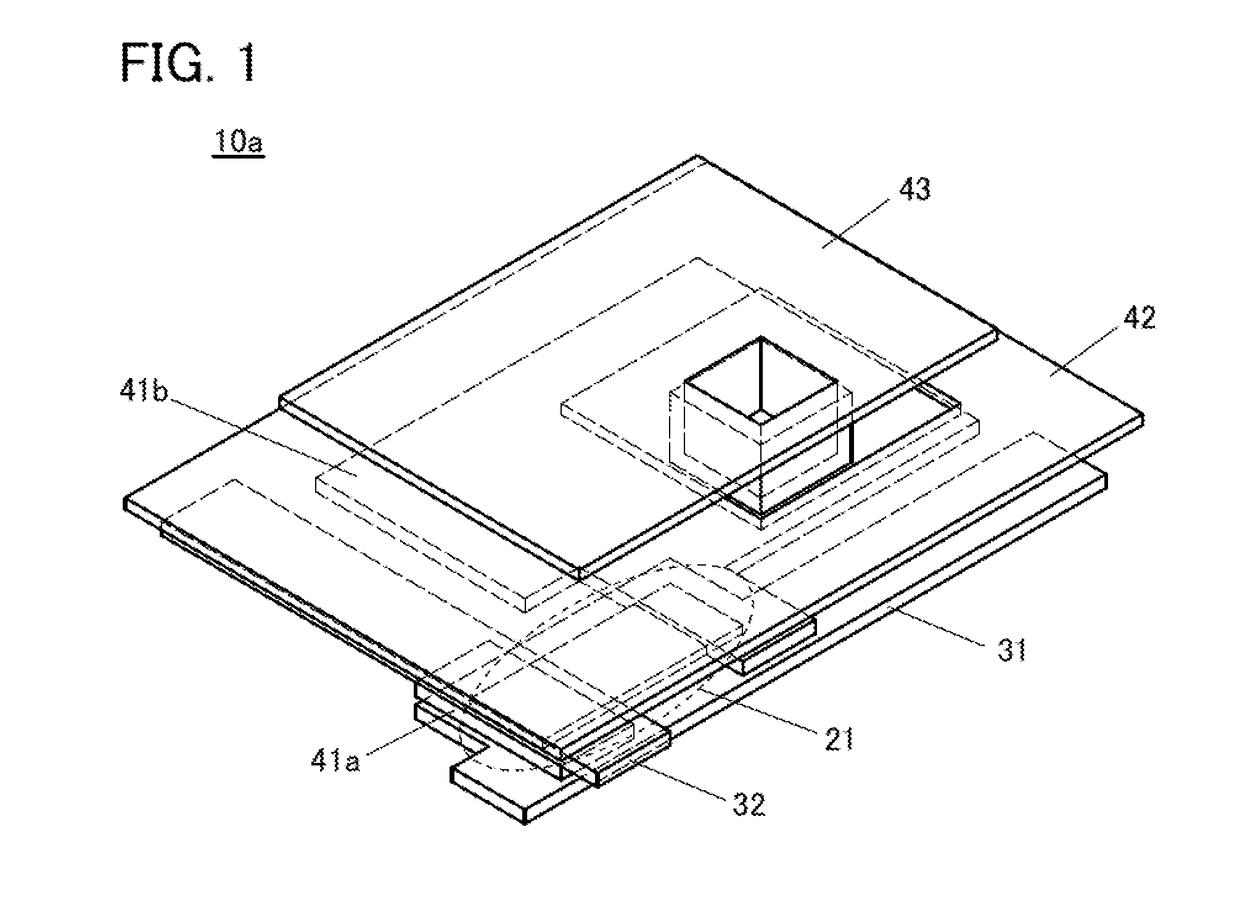
[0049]In this embodiment, a display device in one embodiment of the present invention is described.
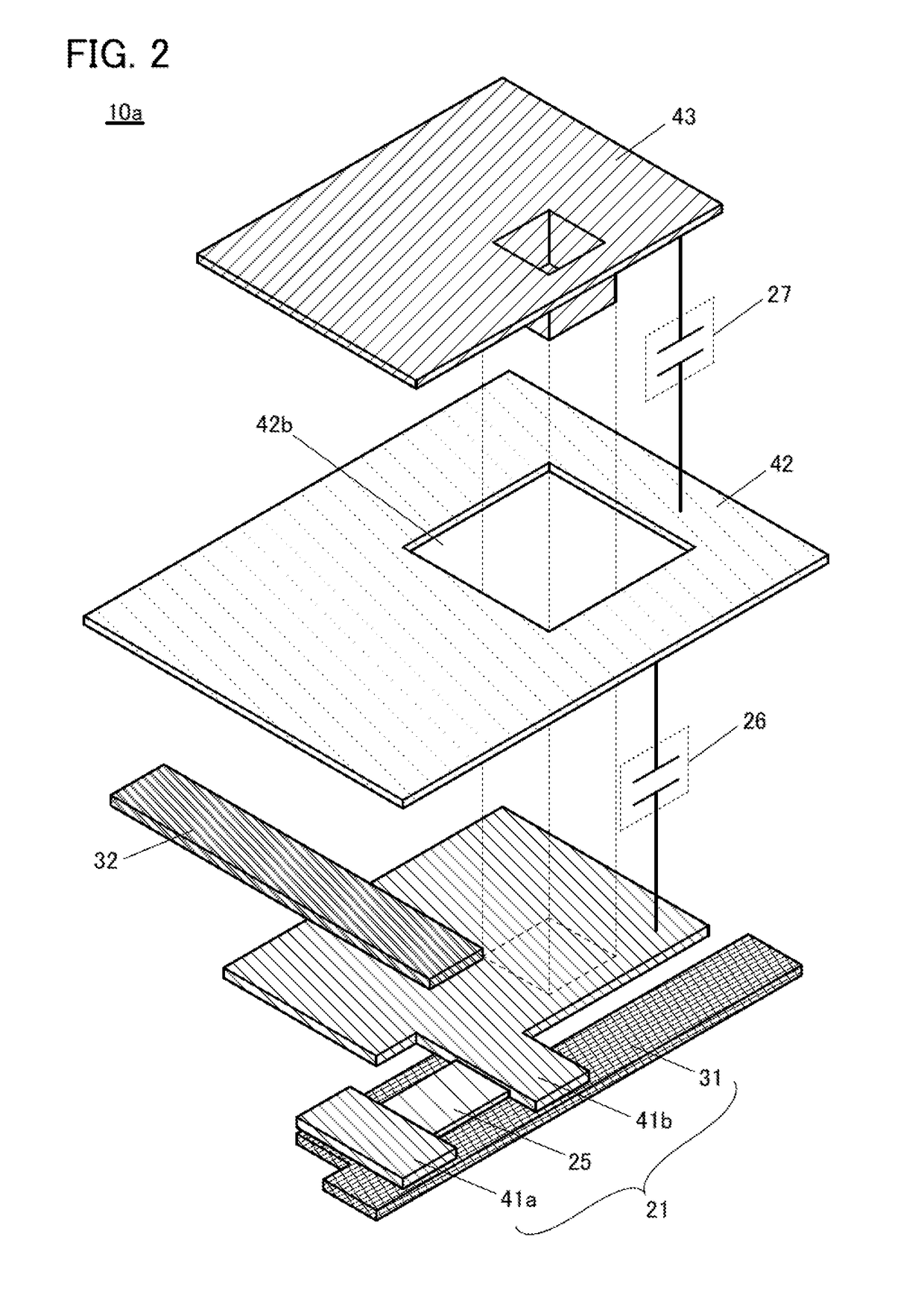
[0050]The display device in one embodiment of the present invention includes a first conductive layer, a second conductive layer, and a liquid crystal element. In the liquid crystal element, a liquid crystal layer is positioned between a third conductive layer and a fourth conductive layer.
[0051]The first to fourth conductive layers transmit visible light and include a region where the first to fourth conductive layers overlap with each other. The second conductive layer is positioned between the first conductive layer and the third conductive layer.
[0052]An insulating layer is positioned between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer. An insulating layer is positioned between the second conductive layer and the third conductive layer. Therefore, two capacitors each including the second conductive layer as an electrode are stacked.
[0053]The two capacitors transmit l...
embodiment 2
[0184]In this embodiment, an operation mode that can be employed in the display device in one embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to FIGS. 19A to 19C.
[0185]A normal driving mode with normal frame frequency (typically, higher than or equal to 60 Hz and lower than or equal to 240 Hz) and an idling stop (IDS) driving mode with low frame frequency are described below.
[0186]Note that the IDS driving mode refers to a method in which after image data is written, rewriting of image data is stopped. This increases the interval between writing of image data and subsequent writing of image data, so that power that would be consumed by writing of image data in that interval can be reduced. The IDS driving mode can be performed at frame frequency that is 1 / 100 to 1 / 10 of the normal driving mode, for example. A still image is displayed by the same video signals in consecutive frames. Thus, the IDS driving mode is particularly effective when displaying a still image. Wh...
embodiment 3
[0195]A metal oxide that can be used for a semiconductor layer of a transistor disclosed in one embodiment of the present invention is described in this embodiment. Note that when a metal oxide is used for a semiconductor layer of a transistor, the metal oxide may be referred to as an oxide semiconductor.
[0196]An oxide semiconductor is classified into a single crystal oxide semiconductor and a non-single-crystal oxide semiconductor. Examples of a non-single-crystal oxide semiconductor include a c-axis aligned crystalline oxide semiconductor (CAAC-OS), a polycrystalline oxide semiconductor, a nanocrystalline oxide semiconductor (nc-OS), an amorphous-like oxide semiconductor (a-like OS), and an amorphous oxide semiconductor.
[0197]A cloud-aligned composite oxide semiconductor (CAC-OS) may be used for the semiconductor layer of the transistor disclosed in one embodiment of the present invention.
[0198]Note that the non-single-crystal oxide semiconductor or the CAC-OS can be suitably used...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com