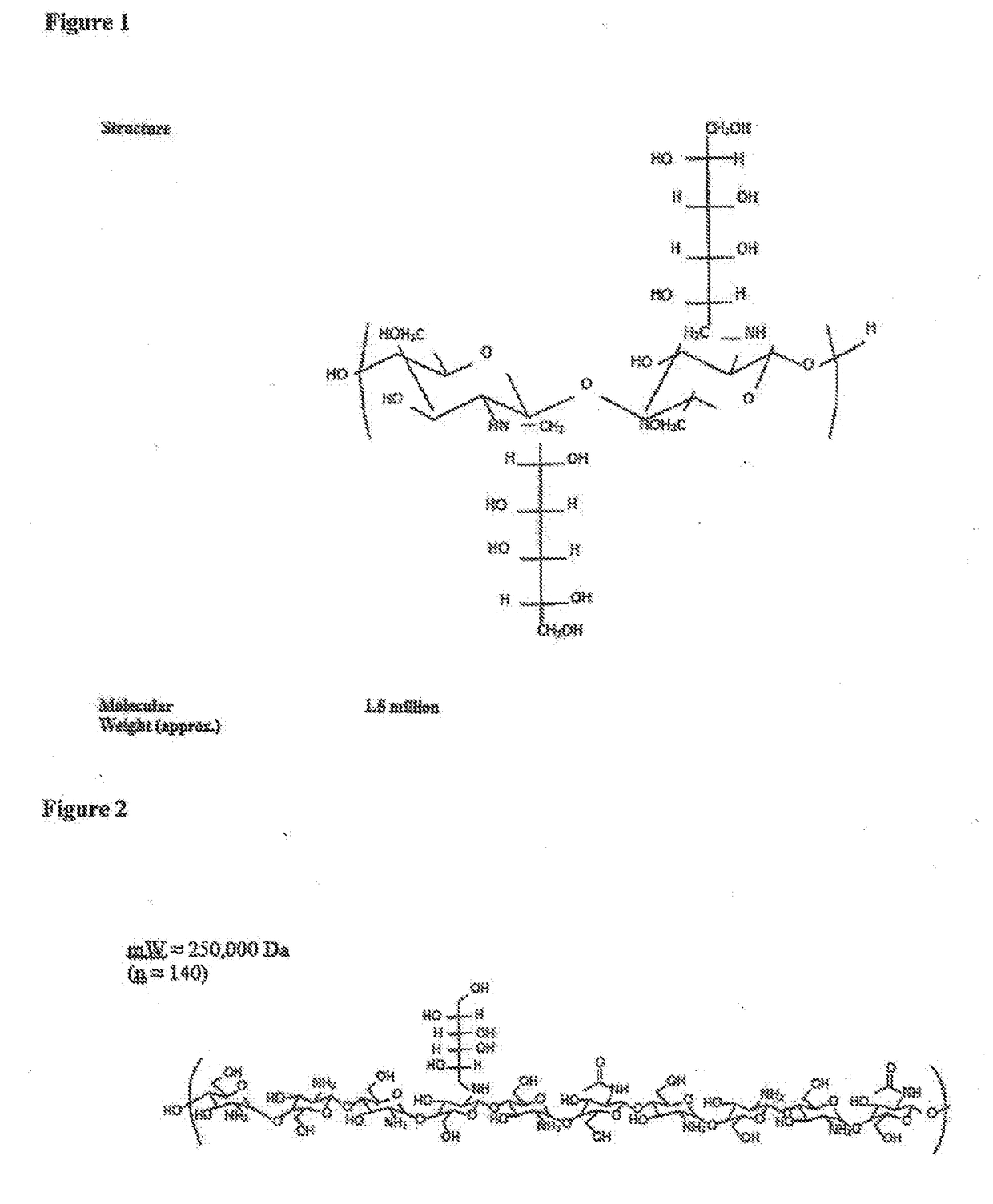
Chitosan-Derived Compositions
a technology of compositions and chitosan, applied in the direction of lung cancer vaccines, anti-cancer medical ingredients, therapy, etc., can solve the problems of difficult injection or dispensing in biomedical applications, ineffective conventional treatments to the degree desired, and dissolved in aqueous solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0191]Exemplary Process for the Preparation of Glycated Chitosan (GC)
[0192]Glycated chitosan is obtained by reacting chitosan with a monosaccharide and / or oligosaccharide, preferably in the presence of an acidifying agent, for a time sufficient to accomplish Schiff base formation between the carbonyl group of the sugar and the primary amino groups of chitosan (also referred to herein as glycation of the amino group) to a predetermined degree whereby a predetermined percent (%) glycation of the chitosan polymer is achieved. This is followed by stabilization by reduction of Schiff bases and of their rearranged derivatives (Amadori products). NMR tracings are used to verify the bonding of the monosaccharides and / or oligosaccharides to the chitosan polymer, whereas chemical measurement of remaining free amino groups, such as via a ninhydrine reaction, is used to assess the degree of glycation.
example 2
[0193]Sterile Filtration
[0194]While conventional 1500 kDa galactochitosan, described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,747,475, is relatively simple to synthesize, the sterilization with, for example a 0.22 micron filter, is impossible without compromising the integrity of the filter, thus rendering the conventional glycated chitosan unsuitable for GMP production and human use. In contrast, the new viscoelastic glycated chitosan described herein has significant advantages with regard to GMP production and sterile filtration due to unexpected and beneficial physiochemical properties. For example, at a molecular weight (M.W.) of 250,000 Da (250 kDa), sterile filtration with a 0.22 micron filter is highly feasible, with a flow rate of 100 ml / min without loss of material during filtration.
example 3
[0195]Viscosity of Glycated Chitosan (GC)
[0196]GC Preparations of Higher Molecular Weight Display Higher Viscosities (Measured in Cp):
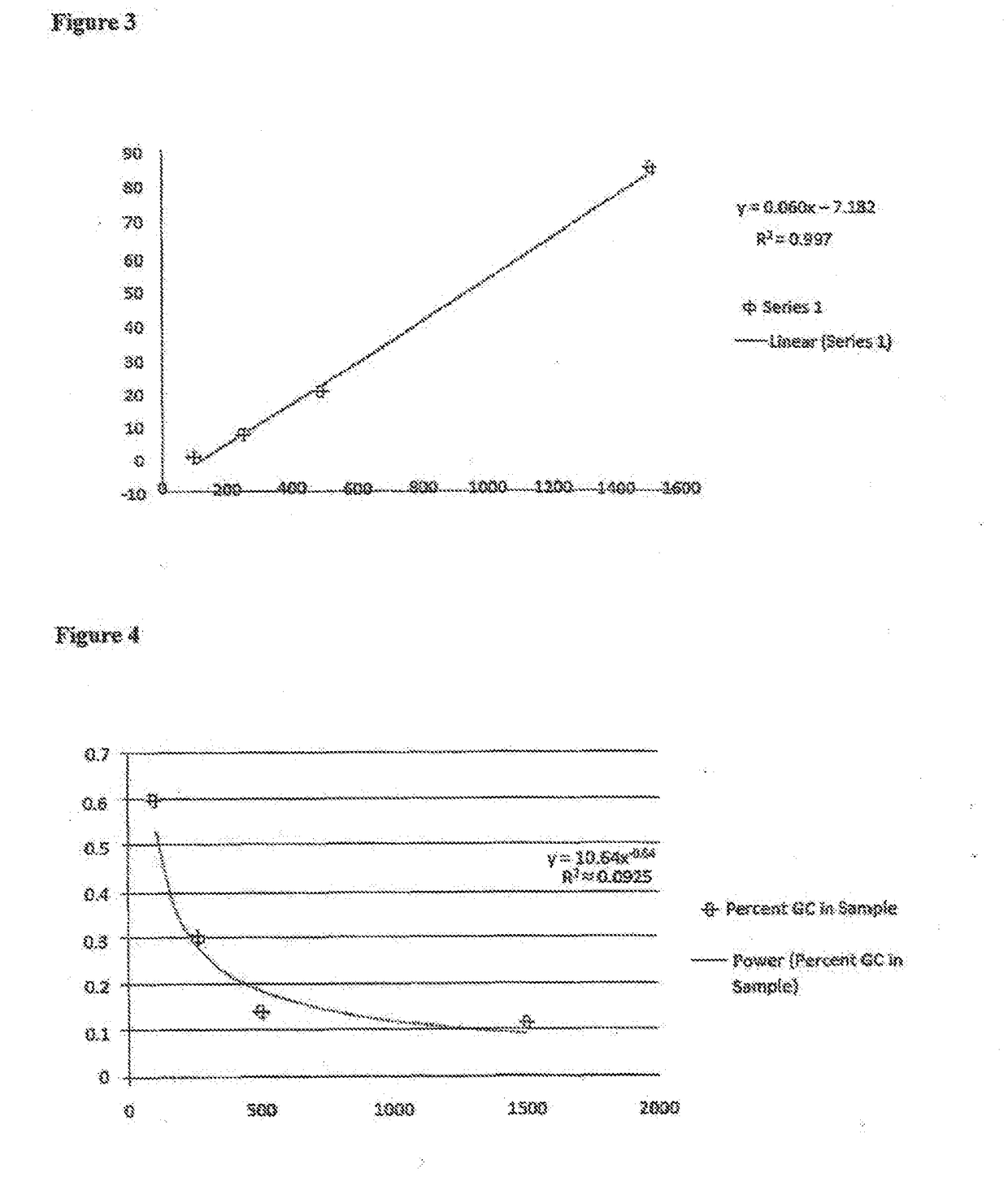
kDa of GCCp1000.9142507.6850020.79150084.7
[0197]FIG. 3 shows viscosity (in Cp; y-axis) vs. molecular weight (in kDa; x-axis) in samples of GC with molecular weights ranging from 100 kDa to 1,500 kDa. The concentration of GC in solution in this experiment decreased with increasing molecular weight, ranging from 0.6% (100 kDa) to 0.11% (1,500 kDa).
[0198]Very surprisingly, it was found viscosity increases linearly with increasing molecular weight only if the concentration of GC in the sample is reduced with increasing molecular weight. The table and FIG. 4 shows the percent of GC in solution of the samples used in the viscosity experiment above.
[0199]The results clearly show that 1) GC preparations of higher molecular weight correlate with higher viscosities (measured in Cp), and 2) the correlation between viscosity and molecular weight is not linear if ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weights | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com