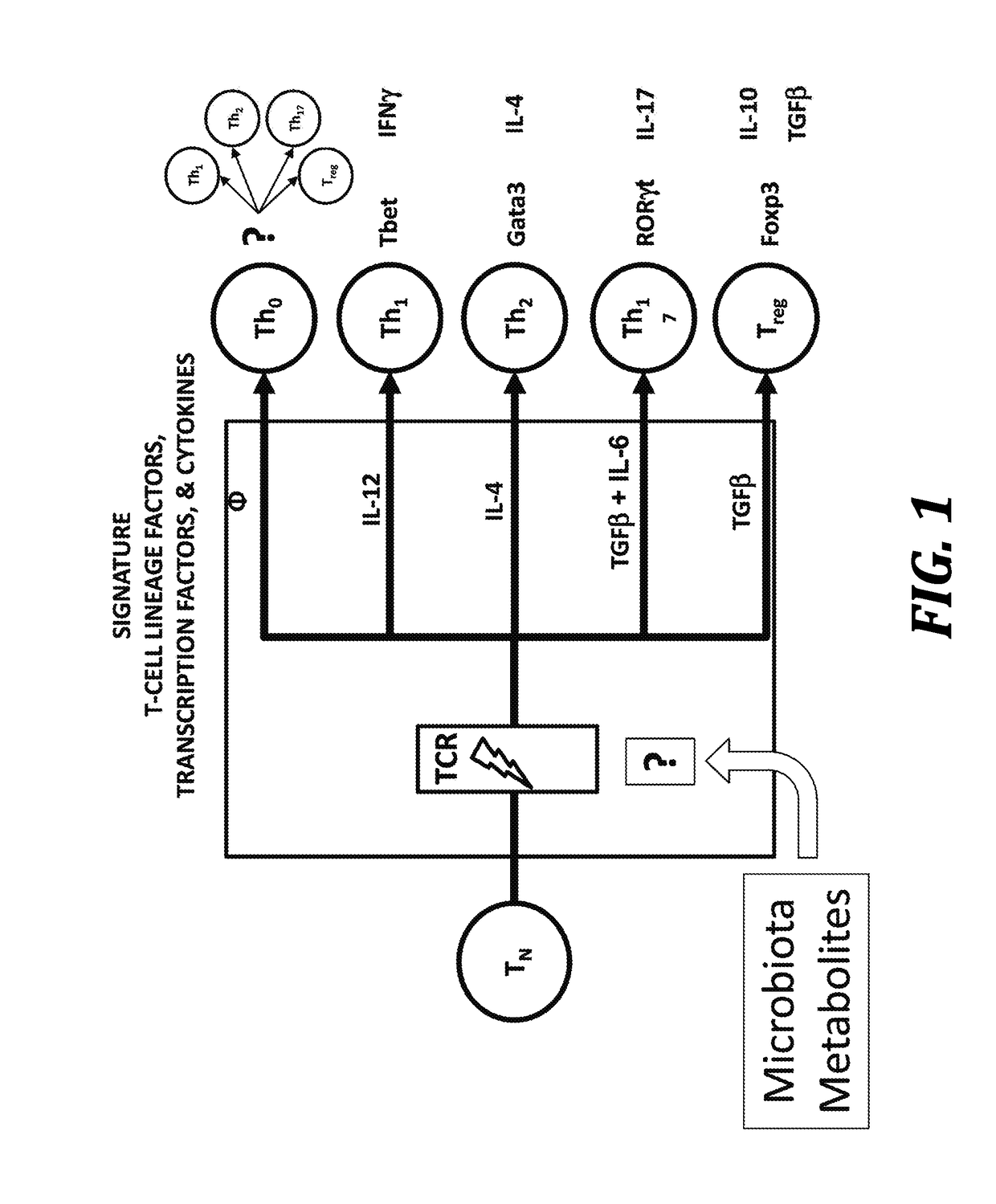
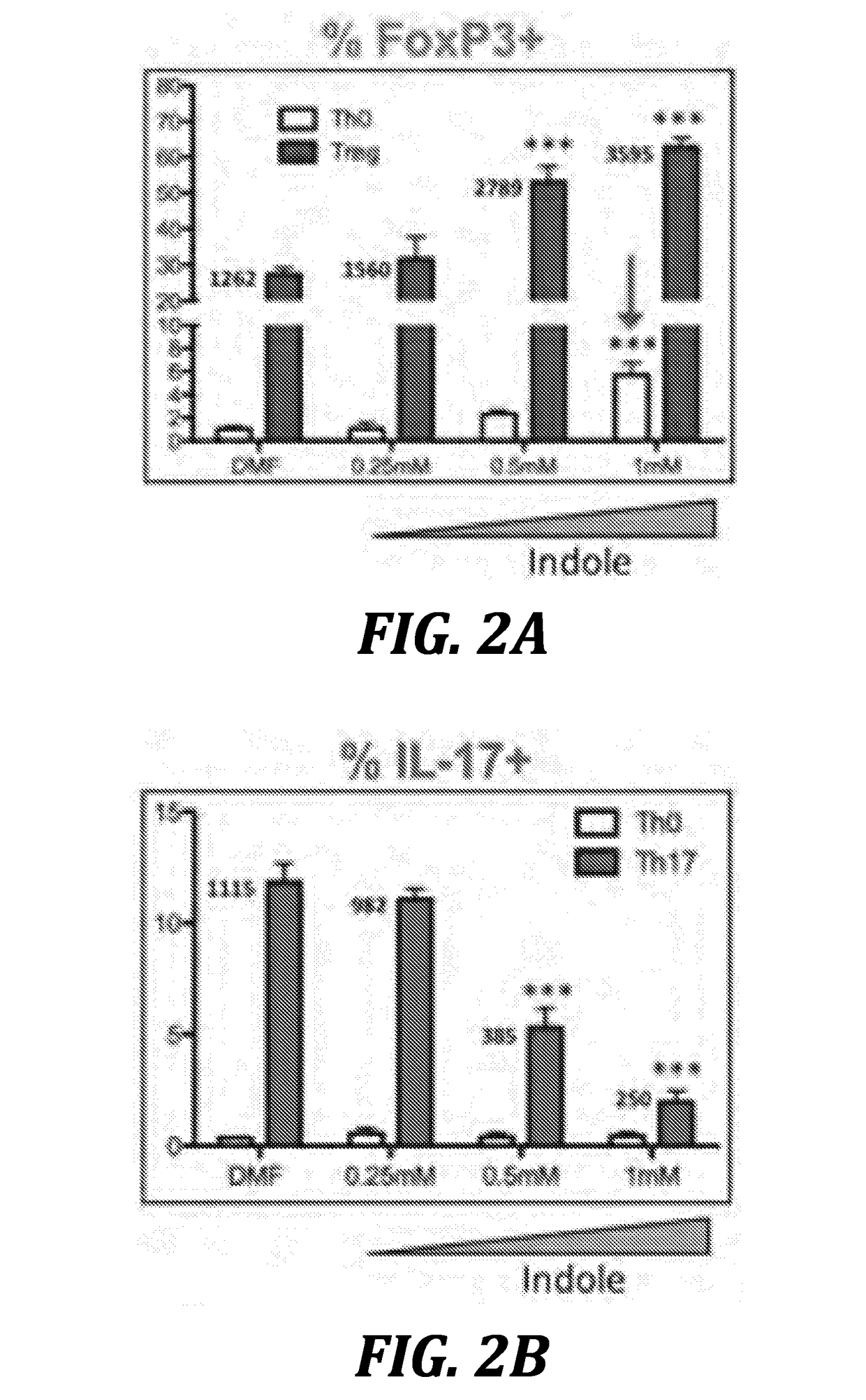
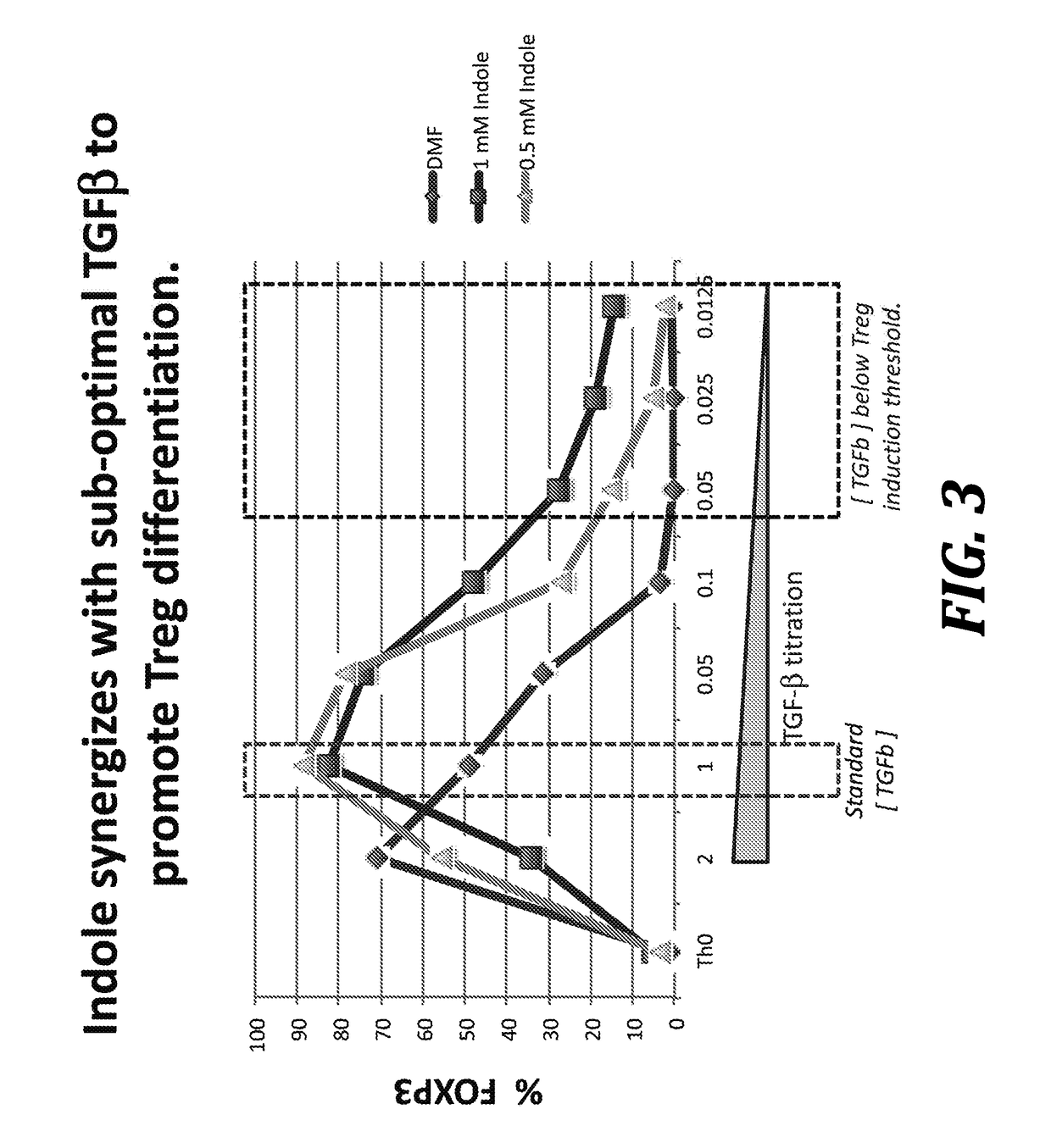
Using microbiota metabolites to differentiate naïve t-cells and related methods to induce or prevent inflammatory conditions
a technology of nave t cells and microbiota metabolites, which is applied in the field of using microbiota metabolites to differentiate nave t cells and related methods to induce or prevent inflammatory conditions, can solve the problems of major hurdles still existing in the translation of this therapeutic strategy, and achieve the effect of increasing the stability of a treg cell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0150]The following is a description of methodology to isolate naïve T cells and assay the effect of any TDMM on the potential differentiation into Treg (or other) cell type.
[0151]Mesenteric lymph node (MLN) and spleen are harvested from WT or FOXP3EGFP C57Bl / 6 mice and homogenized. Spleen tissue is subjected to red blood cell lysis and pooled into a single cell suspension for counting. Counted cells are resuspended in sterile FACS buffer (PBS++ with 05% bovine serum albumin) at a concentration of ˜5×107 cells / mL and stained for 45 minutes at 4° C. with anti-CD4 and anti-CD25 fluorophore-conjugated monoclonal antibodies (mAb). After two washes, the stained cells are resuspended at ˜6×106 cells / mL in FACS buffer and immediately sorted. High purity (>95%) CD4+ CD25− naïve T cells (1×106 cells / mL) are cultured in anti-CD3 mAb (5 μg / mL) and anti-CD28 mAb (2 μg / mL) coated plates in the presence of TGF-β (5 ng / mL), IL-2 (100 U / mL), and desired TDMMs or a solvent control for at least 72 ho...
example 2
[0153]The following is an additional description of an exemplary procedure that was used to isolate naïve T cells and induce differentiation in vitro.
[0154]Cell Isolation
[0155]CD4+ CD25− T cells were isolated to high purity (>98%) from the pooled spleen and mesenteric lymph nodes of C57BL / 6 mice (Jackson Labs) with a BD FACS Aria II flow cytometer. Fc Block (BD), αCD4-efluor450 (eBioscience clone GK1.5) and αCD25-PECy7 (eBioscience clone PC61.5) antibodies were used for staining before sorting.
[0156]In Vitro T Cell Differentiation
[0157]Isolated cells were cultured at an initial concentration of 1×105 cells / well in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 2-mercaptoethanol, gentamicin, penicillin, streptomycin, and 10% FCS (all from Life Technologies) in a 96-well round bottom plate (Falcon) coated with 5 μg / mL αCD3 (BioXcell clone 145-2C11) and 2 μg / mL αCD28 (BioXcell clone 37.51) for 72 hours. For Th1-skew: 5 ng / mL IL-12 (Peprotech cat. #210-12) and 10 g / mL αIL-4 (BioXCell clone 11B11) were add...
example 3
[0158]The following is a description of methodology to characterize the subset of stimulation conditions and resulting differentiated iTreg cells.
[0159]Naïve T cells are cultured for 3 days using concentrations of cytokines and TDMMs that resulting in a significant increase in the levels of iTreg cells. After 72 h, cells are stimulated with PMA / ionomycin (10 ng / mL PMA, 1 mM ionomycin). For flow cytometry, cells are treated with Golgi plug (Brefeldin A) for four hours and then stained with fluorophore-conjugated mAbs against both inflammatory (e.g., IL-6, IL-12, IL-17, TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory (e.g., IL-10, IL-35, TGF-β) cytokines. Samples are stained with the maximum number of antibodies. Furthermore, expression of established Treg markers (FOXP3, CD25hi, CD103, CD62L, GITR, PD-1, CD152, CD127, ICOS, Granzyme-B) [Vignali, D. A., L. W. Collison, and C. J. Workman, Nat Rev Immunol 8(7):523-32. (2008); Chen, J., et al., Int Immunopharmacol 11(5):610-7 (2011)] and markers of an infl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com