Method, Digital Electronic Circuit and System for Unsupervised Detection of Repeating Patterns in a Series of Events
a repeating pattern and digital electronic circuit technology, applied in the field of digital electronics and machine learning, can solve the problems of low neural network robustness, high computational intensity of operating such an artificial neural network, and general lack of robustness of artificial neural networks according to the prior art, and achieve the effect of increasing the potential value of neurons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
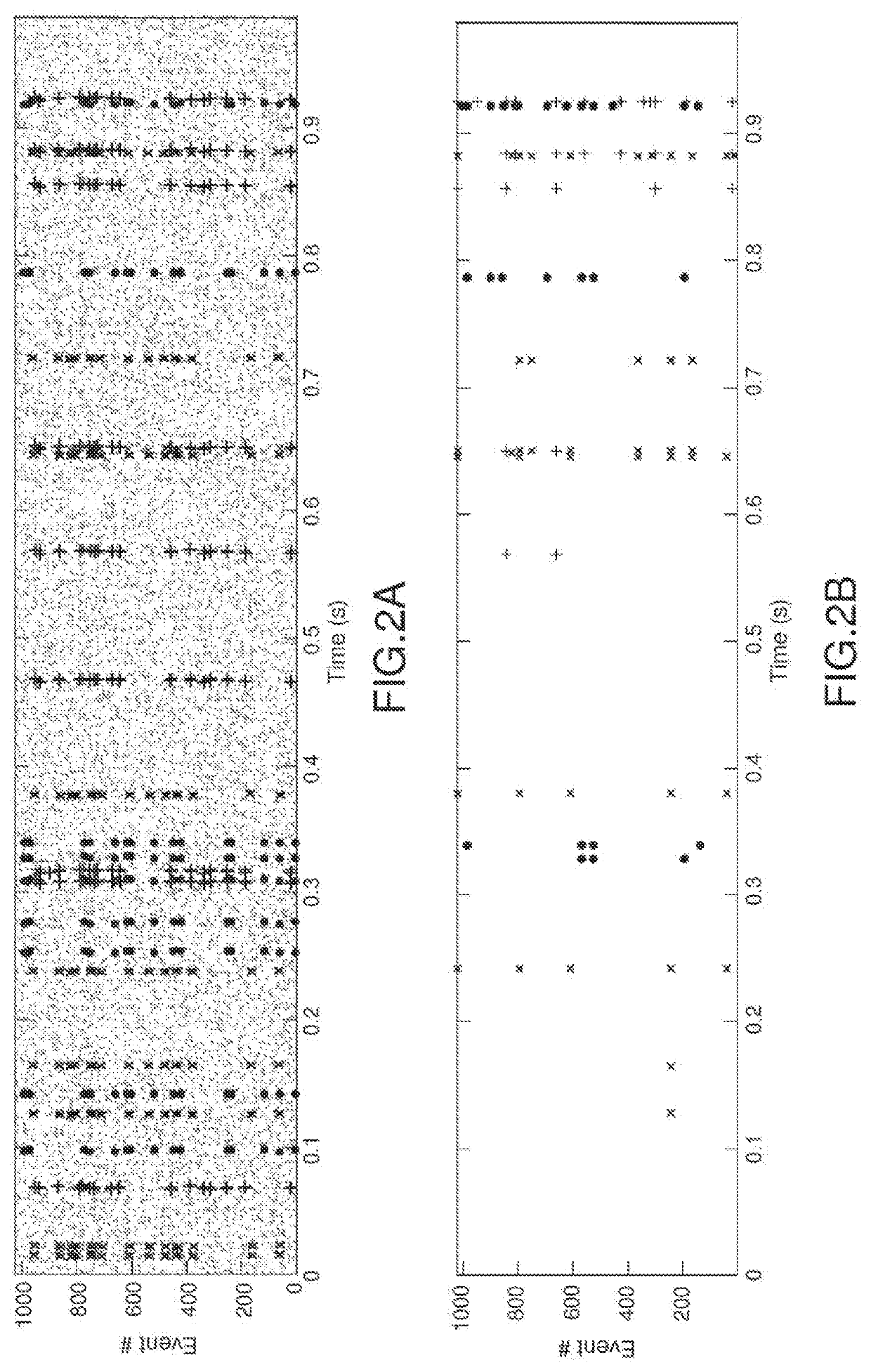
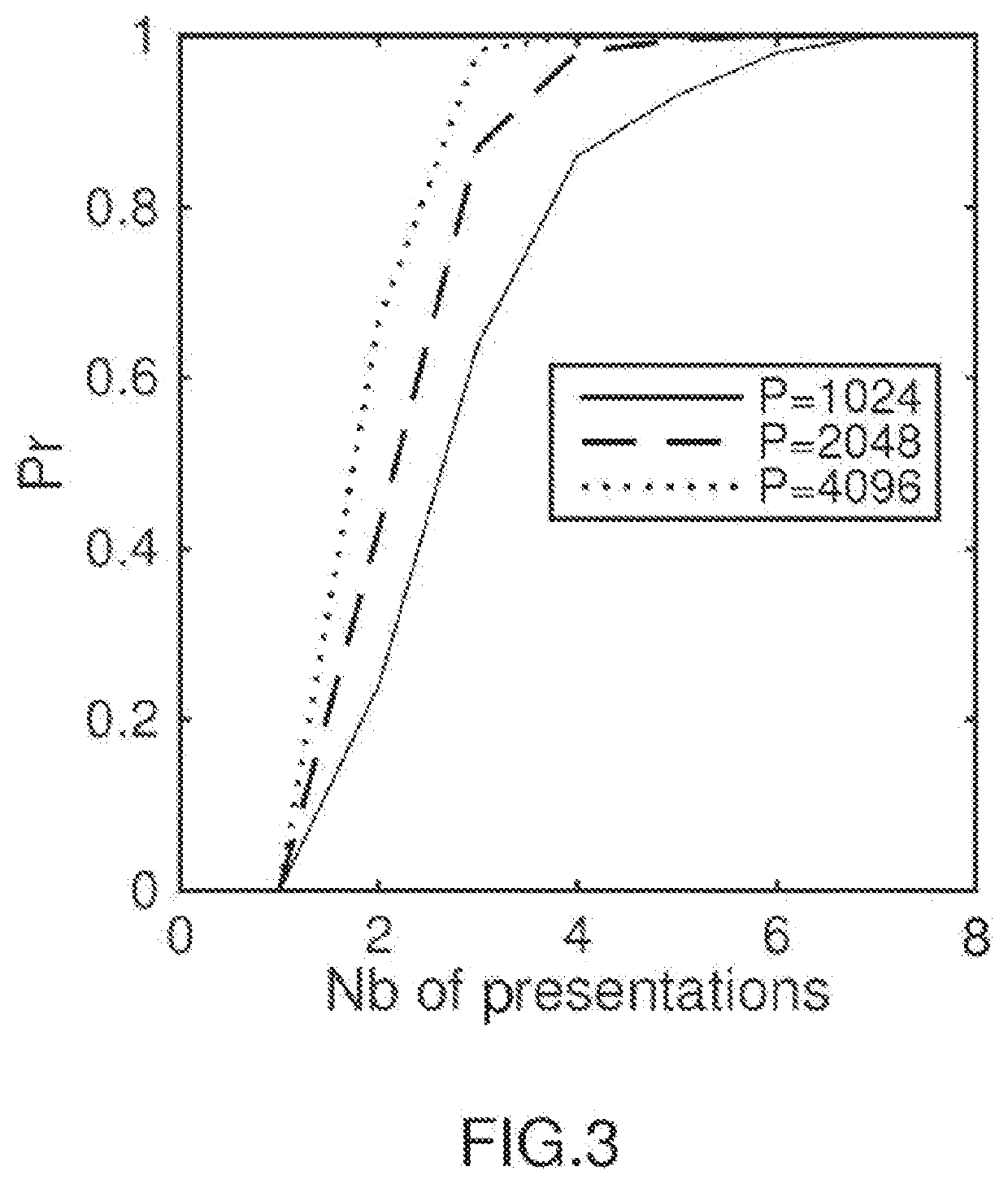
Examples
Embodiment Construction
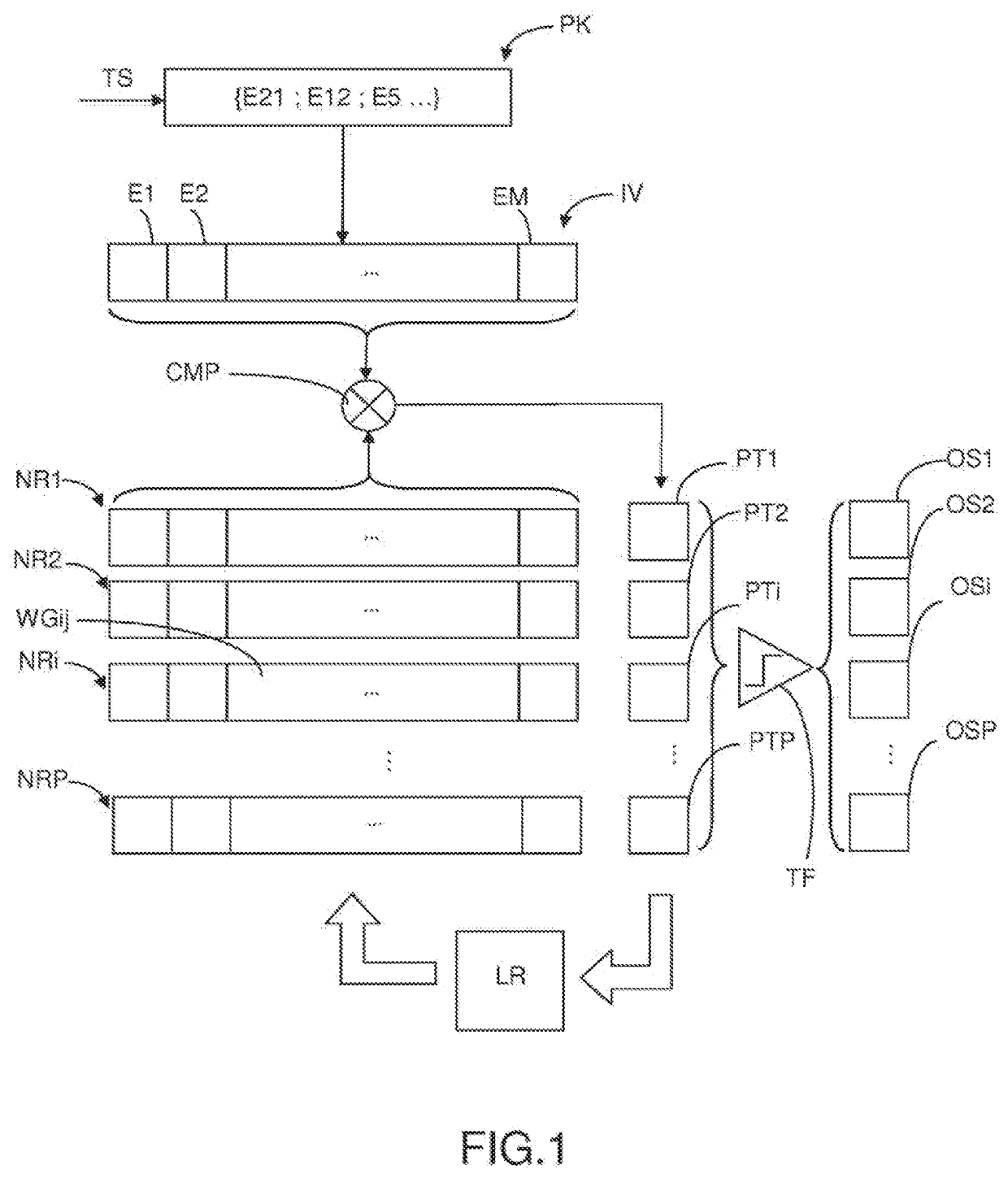
[0020]An object of the present invention is a method of performing unsupervised detection of repeating patterns in a series of events, each event of the series belonging to an event type of an M-element set of event types, the method comprising the steps of:
[0021]a) Providing a plurality of neurons, each neuron being representative of a W-element subset of the set of event types, with 1≤W≤M;
[0022]b) Acquiring an input packet comprising N successive events of the series, with 1≤N
[0023]c) Attributing to at least some neurons a potential value, representative of the number of events of the input packet whose types belong to the W-element subset of the neuron;
[0024]d) for neurons having a potential value exceeding a first threshold TL, replacing nswap≥1 event types of the corresponding W-element subset, which are not common to the input packet, with event types comprised in the input packet and not currently belonging to said W-element subset; and
[0025]e) generat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com