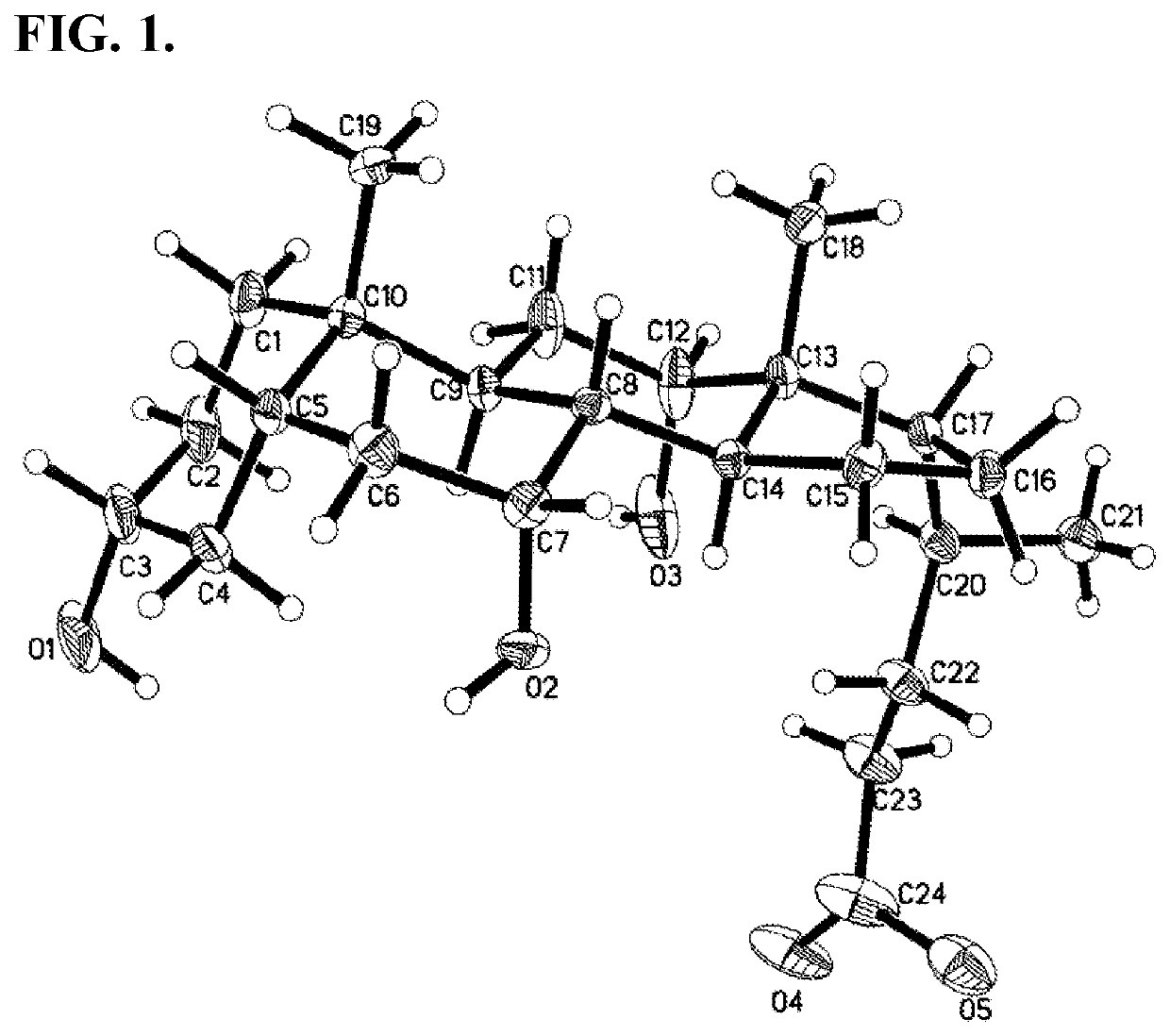
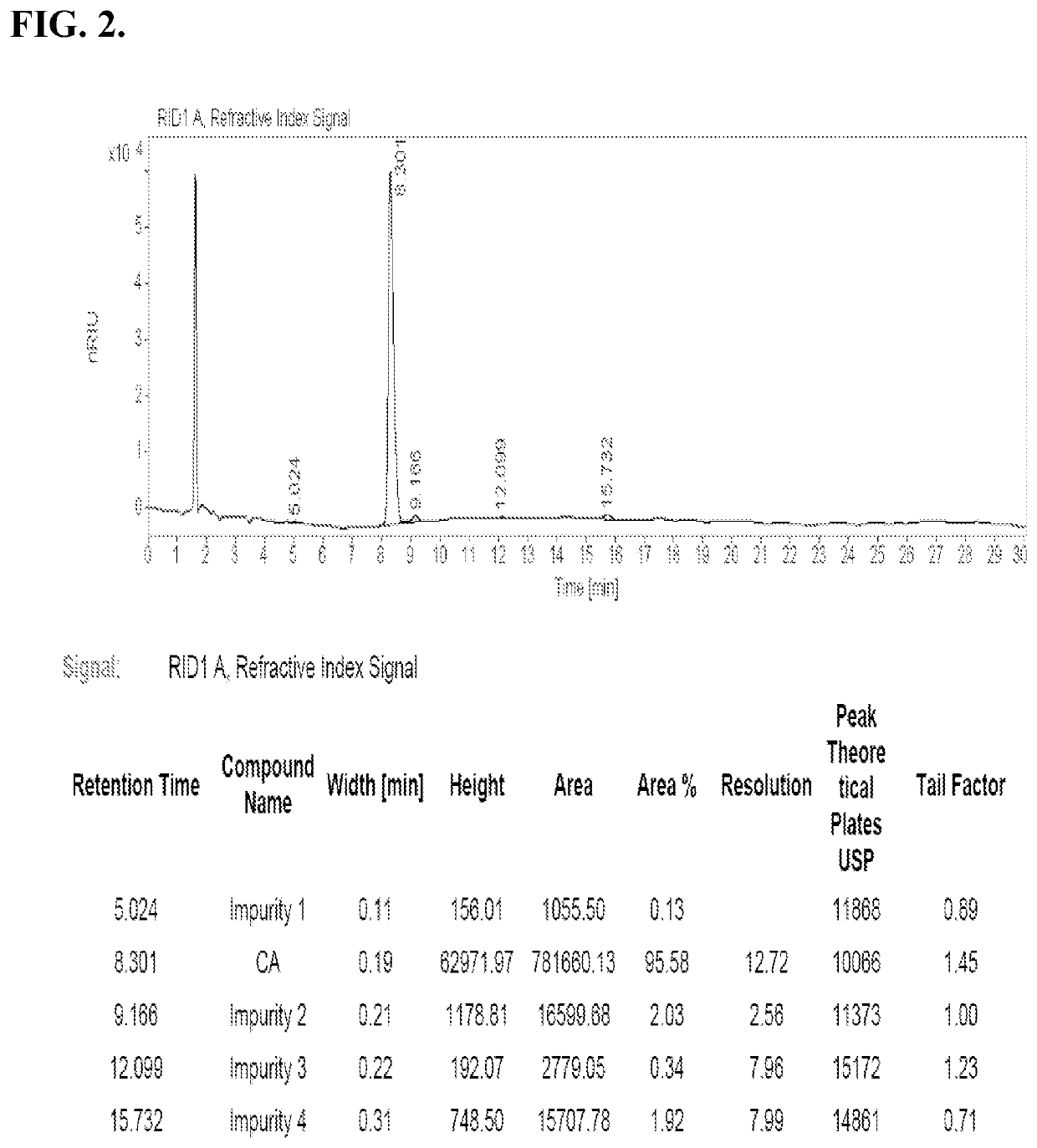
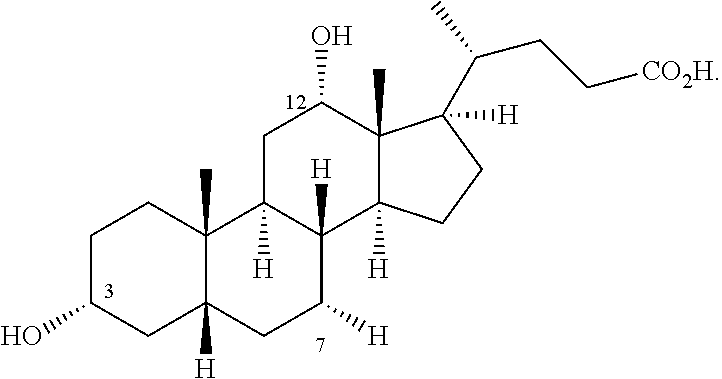
Methods for Preparing Bile Acids
a bile acid and bile acid technology, applied in the field of steroid synthesis, can solve the problems of prion contamination of such sources, and achieve the effect of high purity in the composition of cholic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Cholic Acid from DHEA: Route 1
[0189]
[0190]Step 1
[0191]To a flask was added DHEA (50.00 g, 173.36 mmol, 1.00 eq) and DCM (1.00 L) at 15° C. Then, it was cooled to 0° C., TEMPO (2.73 g, 17.34 mmol, 0.10 eq) was added, and DDQ (86.58 g, 381.39 mmol, and 2.20 eq) was added in portions at 0° C. The reaction mixture was warmed to 25° C. and stirred at 25° C. for 48 hrs, TLC showed one new main spot was formed. The reaction was filtered, and the filtrate was washed with saturated Na2SO3 (100 mL*2) and brine (200 mL*2). The combined organic phase was dried with anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated in vacuum. The residue was purified by column chromatography (PE / EA=50 / 1 to 10 / 1) to afford Compound 1 (39.0 g, 135.35 mmol, 78.08% yield) as white solid. 1H NMR, (400 MHz, CDCl3); δ=6.21 (s, 2H), 5.78-5.71 (m, 1H), 2.66-2.55 (m, 1H), 2.53-2.46 (m, 1H), 2.46-2.35 (m, 2H), 2.22-2.13 (m, 2H), 2.08-2.01 (m, 1H), 1.92 (td, J=3.1, 13.0 Hz, 1H), 1.80-1.69 (m, 3H), 1.56-1.50 (m, 1H), 1.48-1.42 ...
example 2
Synthesis of Cholic Acid from DHEA: Route 2
[0218]
[0219]Step 1
[0220]To a mixture of DHEA (20.00 g, 69.34 mmol, 1.00 eq) and 2-pyridylmethanamine (37.49 g, 346.70 mmol, 35.37 mL, 5.00 eq) in toluene(250.00 mL) was added PTSA (358.23 mg, 2.08 mmol, 0.03 eq) at 25° C., the mixture was stirred at 120° C. for 2 hrs with Dean-Stark apparatus. Then the reaction mixture was diluted with EA (400 ml), washed with saturated NaHCO3 (100 ml*2) and water (100 ml*2). The organic layer was concentrated. The residue was triturated by EA (30 ml) at 25° C. to afford Compound 13 (23.40 g, 57.80 mmol, 83.36% yield, 93.5% purity) as white solid. 1H NMR, (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ=8.54 (d, J=4.1 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (dt, J=1.7, 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.19-7.11 (m, 1H), 5.40 (br d, J=4.9 Hz, 1H), 4.70-4.53 (m, 2H), 3.63-3.48 (m, 1H), 2.54-2.43 (m, 1H), 2.38-2.25 (m, 3H), 2.15-2.03 (m, 2H), 1.96-1.85 (m, 3H), 1.75-1.70 (m, 1H), 1.64-1.36 (m, 6H), 1.26-1.10 (m, 2H), 1.07 (s, 3H), 1.03 (br d, J=4.5 Hz, 1H), 0....
example 3
Synthesis of Cholic Acid from Ac-DHEA
[0250]
[0251]Step 1
[0252]To a flask was added Ac-DHEA (50 g, 151.30 mmol, 1.0 eq) and toluene (1 L), 2-pyridylmethanamine (37.49 g, 346.72 mmol, 35.37 ml, 5.0 eq) was added to the reaction at 15° C., followed by adding PTSA (781.64 mg, 4.54 mmol, 0.03 eq) at 15° C. The reaction was heated to 110° C. with Dean-Stark apparatus for 2 hours. The reaction was cooled to 15° C., EA (1 L) was added to the reaction. The resulting mixture was washed with saturated NaHCO3 (2*100 ml) and water (2*100 ml). The organic layer was concentrated in vacuo. The residue was re-crystallized by EA (65 ml) to give compound 25 (54.0 g, 84.86% yield) as light yellow solid.
[0253]Step 2
[0254]To a 100 ml flask was added compound 25 (10 g, 23.78 mmol, 1.00 eq) sodium ascorbate (9.42 g, 47.55 mmol, 2.00 eq) and Cu(OTf)2 (19.78 g, 54.69 mmol, 2.30 eq) at 25° C. Acetone (90 mL) and MeOH (90 mL) was added to the flask to prepare a solution. After stirred at 25° C. for 5 mins, O2 (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydrogen pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydrogen pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com