Transverse flux machine with stator made of e-shaped laminates
a technology of transverse flux and stator, which is applied in the direction of synchronous motors, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/form/construction, etc., can solve the problems of long flux path of machine, high cost and difficulty in manufacture, and achieve the effect of more torqu
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
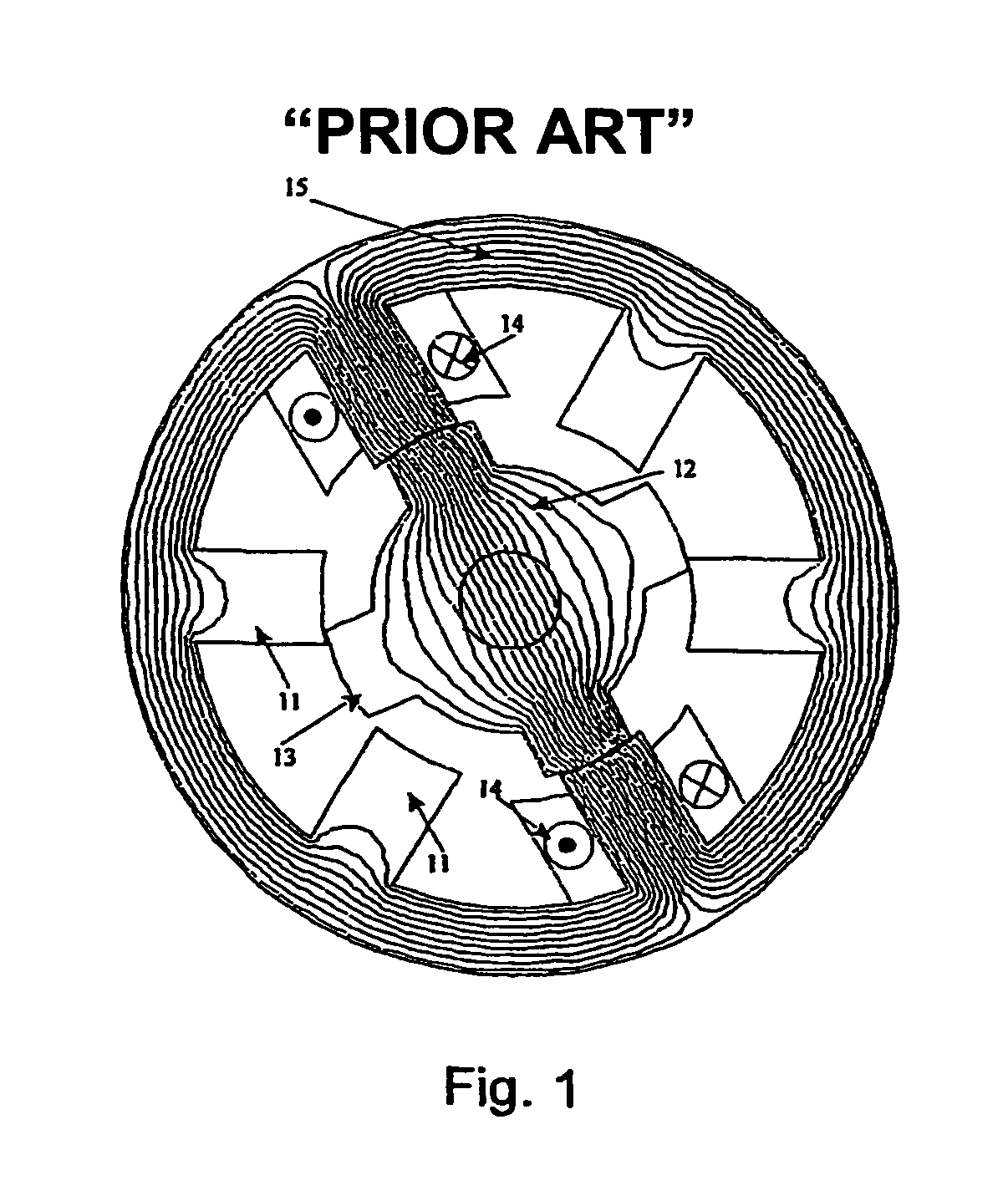
[0025]The electrical machines described in the prior-art have disadvantages that the present invention removes by using standard E-cores. The present invention is described in the following.
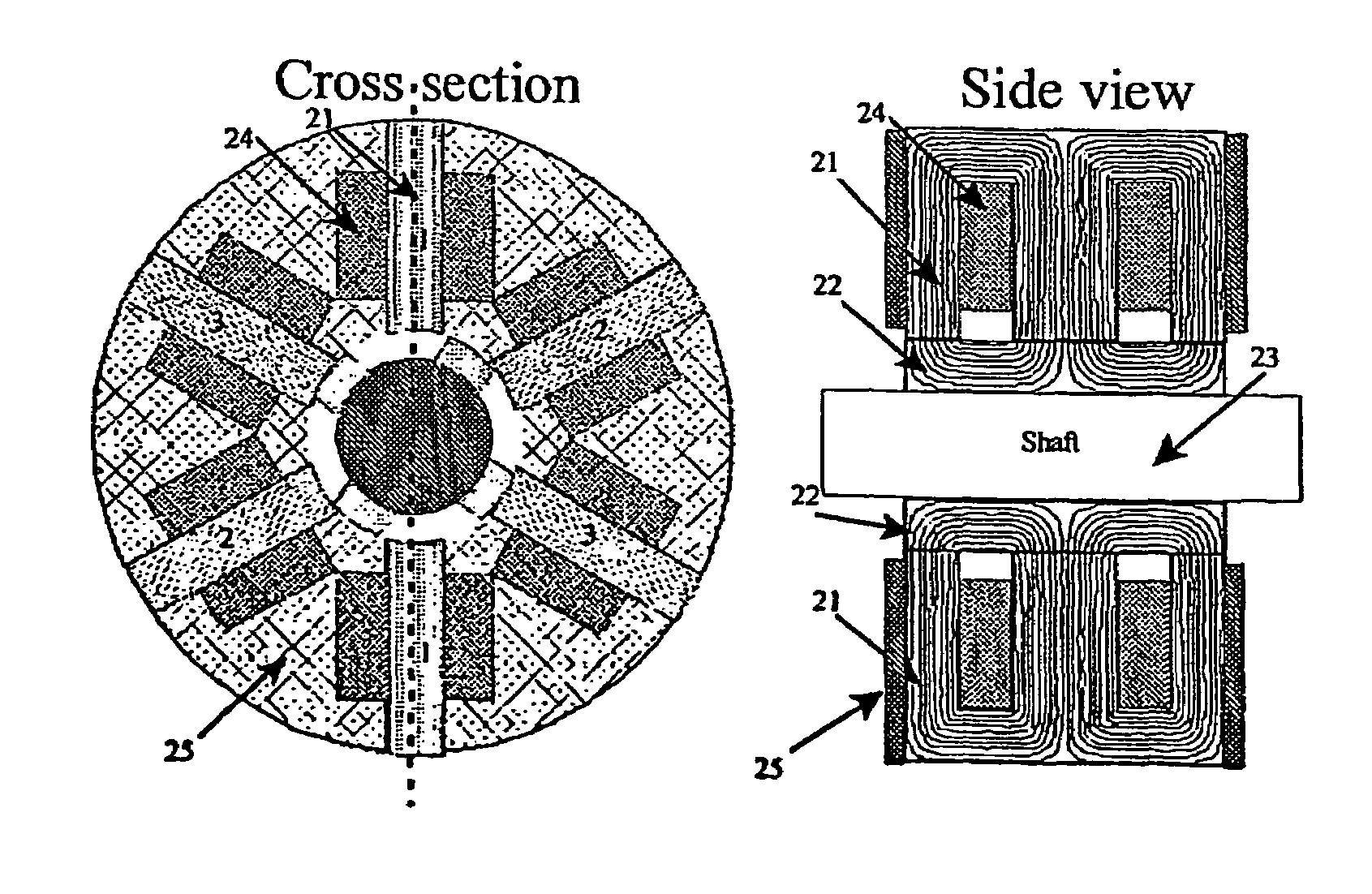
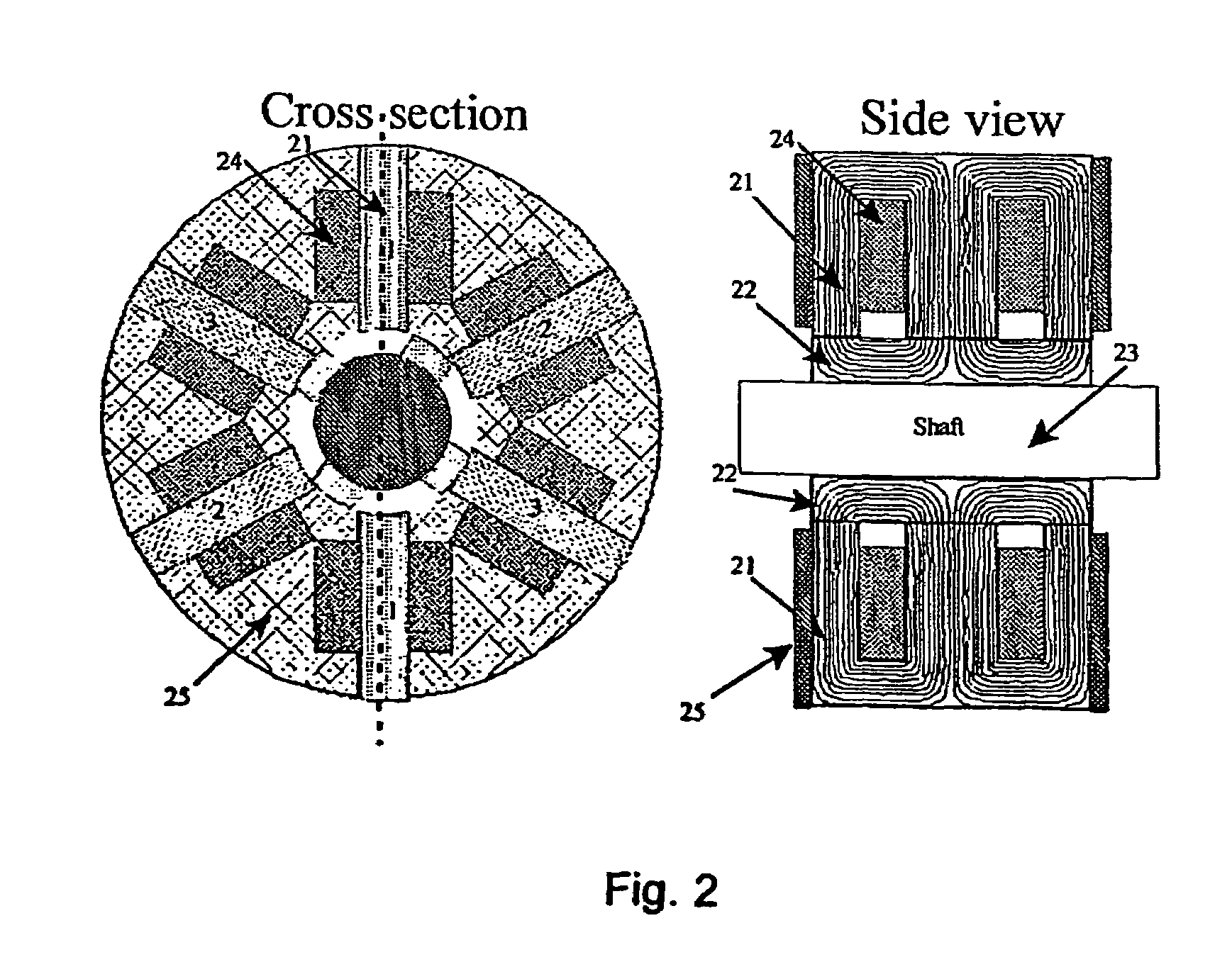
[0026]FIG. 2 illustrates an embodiment of an E-core transverse flux machine where the principle of using E-cores is adapted on the classical SRM. E-cores are traditionally used for single-phase transformers or as rectifier inductors and are characterised by having the shape of the letter ‘E’ and being constructed from oriented sheet steel which results in a higher flux densities and lower losses. E-cores are also made and sold in standard geometric forms, which can be a large advantage when producing small quantities of the E-core transverse flux machine.
[0027]By using E-cores 21 and its yoke / rotor section 22 the flux-path is short when compared to the classical SRM as the steel in the stator-yoke and rotor-yoke is non-existent. The yoke / rotor section is mounted on the shaft 23. The coils 24 will...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com