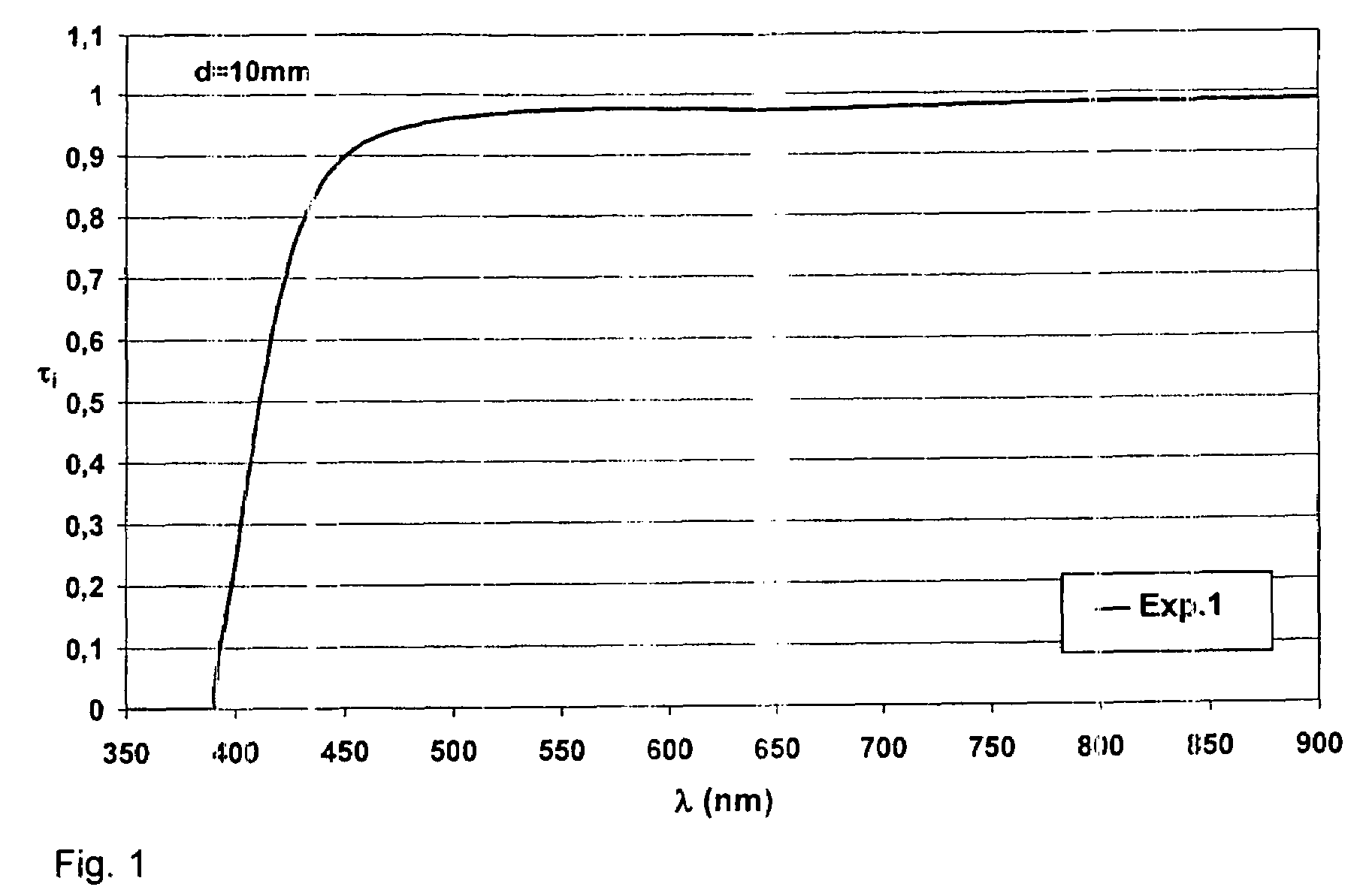
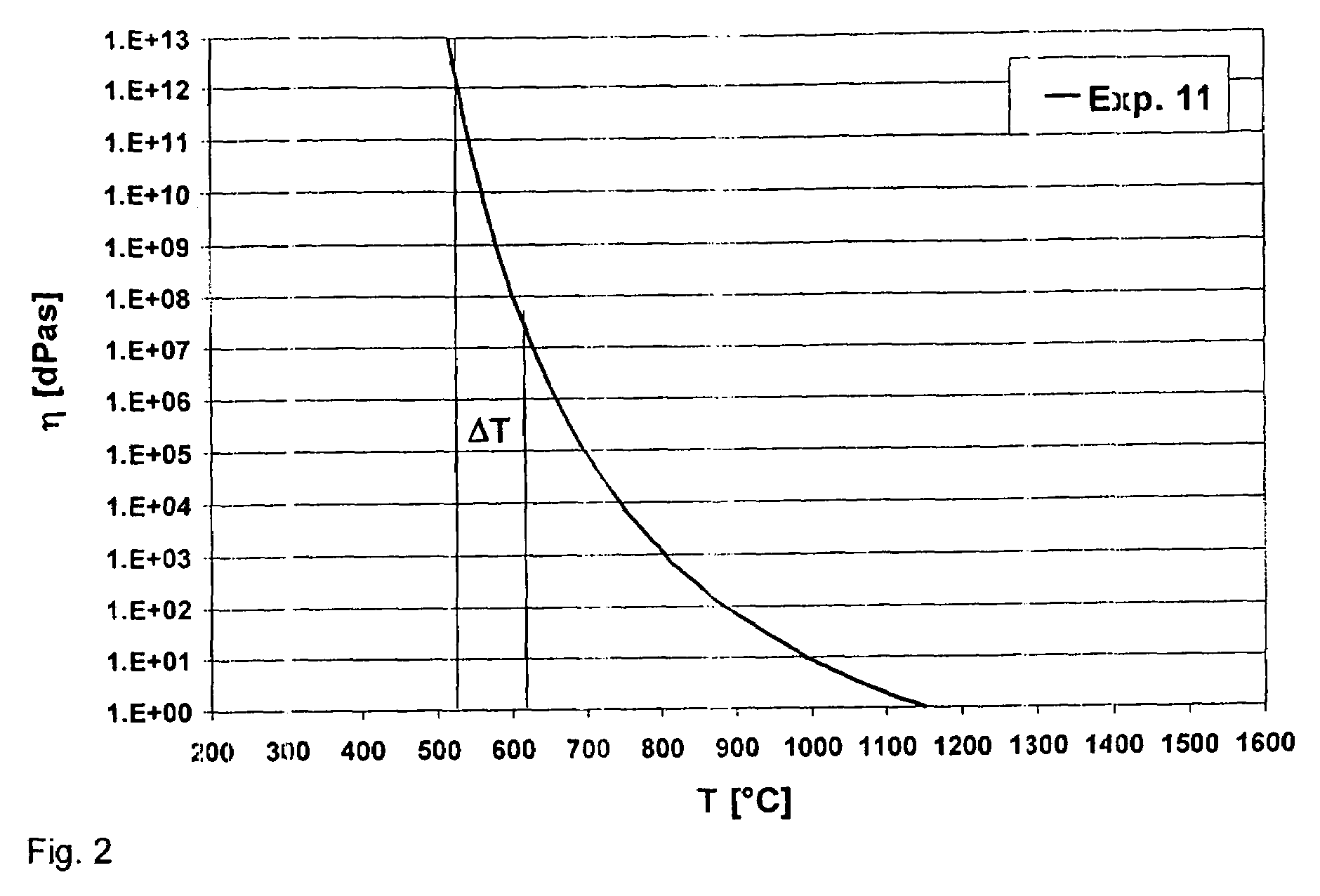
Lead-free and arsenic-free niobium phosphate optical glass
a technology of niobium phosphate and optical glass, which is applied in the field of lead-free and arsenic-free niobium phosphate optical glass, can solve the problems of re-processing, requiring a higher operating expense for processing such miniaturized parts than for bigger components, and increasing the price pressure on glass manufacturers from re-processing. , to achieve the effect of low transformation temperatur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0082]The raw materials for the oxides are weighed out, one or more fining agents, such as Sb2O3, are added and subsequently these ingredients are mixed well. The glass mixture is melted into a continuous melting aggregate at ca. 1100° C. and oxygen is bubbled into the aggregate. Then it is fined (1100° C.) and homogenized. At a casting temperature of approximately 1160° C., the glass can be cast and processed to the desired dimensions. Experience has shown that in a continuous aggregate of high volume, the temperatures can be reduced at least ca. 100 K and the material can be processed by the pressing method close to the final geometry.
[0083]
TABLE IMELTING EXAMPLE FOR 100 KG OF CALCULATED GLASS(ACCORDING TO EXEMPLARY GLASS 11)Oxide% by weightRaw materialWeight (g)P2O520.83P2O58,836.2Ba(H2PO4)2see belowCa(H2PO4)2see belowLi3PO4see belowNb2O532.85Nb2O532,925.5Bi2O314.00Bi2O314,033.5WO314.03WO314,042.0GeO25.00GeO25,002.2Li2O3.05Li3PO47,881.1K2O1.02KNO32,184.6Cs2O5.13Cs2CO35,931.4BaO2....
example 2
[0084]Table II comprises examples of glasses according to the present invention, namely exemplary glasses 1 to 14
[0085]
TABLE IIEXEMPLARY GLASS COMPOSITIONS 1 TO 7 (BASED ON OXIDECONTENT IN % BY WEIGHT) AND THEIR PROPERTIESExample No.1234567% by% by% by% by% by% by% byweightweightweightweightweightweightweightP2O520.3320.8322.8320.8321.6220.1820.91GeO26.105.005.005.003.004.266.03Li2O3.051.023.053.052.502.502.82K2O1.023.051.021.021.000.981.04Cs2O5.135.135.135.004.995.29Nb2O538.6238.6232.8532.8533.8536.0237.58Bi2O314.2312.2314.0014.0014.0013.687.76MgOBaO2.0302.004.005.003.834.07CaOSrOTiO2WO314.2314.0314.0314.0314.0313.5914.40MoO30.010.010.010.010.010.01Sb2O30.410.100.100.100.100.100.10Σ100.0100.0100.0100.0100.1100.14100.0Σ R2O4.079.199.199.198.508.479.15Σ RO2.030.002.004.005.003.834.07Σ Nb2O5 + WO3 + Bi2O367.0864.8760.8860.8861.8863.2959.73Propertiesnd (7 K / h)1.936281.913011.873821.886601.885761.912871.88734νd (7 K / h)20.6120.4622.6622.4722.2921.3622.08Pg.F0.63570.63710.62710.62830.6296...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Abbe number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com