Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ophthalmic compositions
a technology of ophthalmic compositions and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, which is applied in the field of ophthalmic formulations, can solve the problems of drawbacks in the prior ophthalmic delivery system of bromfenac, and achieve the effects of reducing the risk of ophthalmic complications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
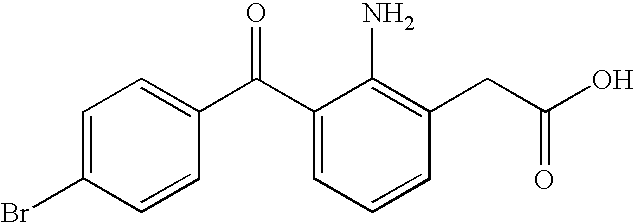
[0069]Polycarbophil (Noveon® AA-1) was slowly dispersed into a citrate buffer solution containing dissolved EDTA and sodium chloride at approximately 50% of the final batch size. The resulting dispersion, which had a pH of a bout 3.0 to 3.5, was stirred with an overhead stirrer until visibly well hydrated. The mixture was sterilized by autoclaving at 121° C. for 20 minutes. The pH was then brought up to approximately 4.0 to 4.4 with 2N sodium hydroxide. Bromfenac sodium was dissolved in a mannitol solution containing dissolved benzalkonium chloride and Poloxamer 407 at approximately 20% of the final batch size. The resulting solution was then sterile filtered (0.22 μm filter) in to the polymer dispersion and stirred for 10 minutes. The pH of the bromfenac-polymer dispersion was brought to 8.3 with 2N sodium hydroxide. Sterile make up water was added to the formulation to final weight and mixed for at least 5 minutes. The formulation was aseptically filled into 5 ml bottles. See Tabl...
example 2
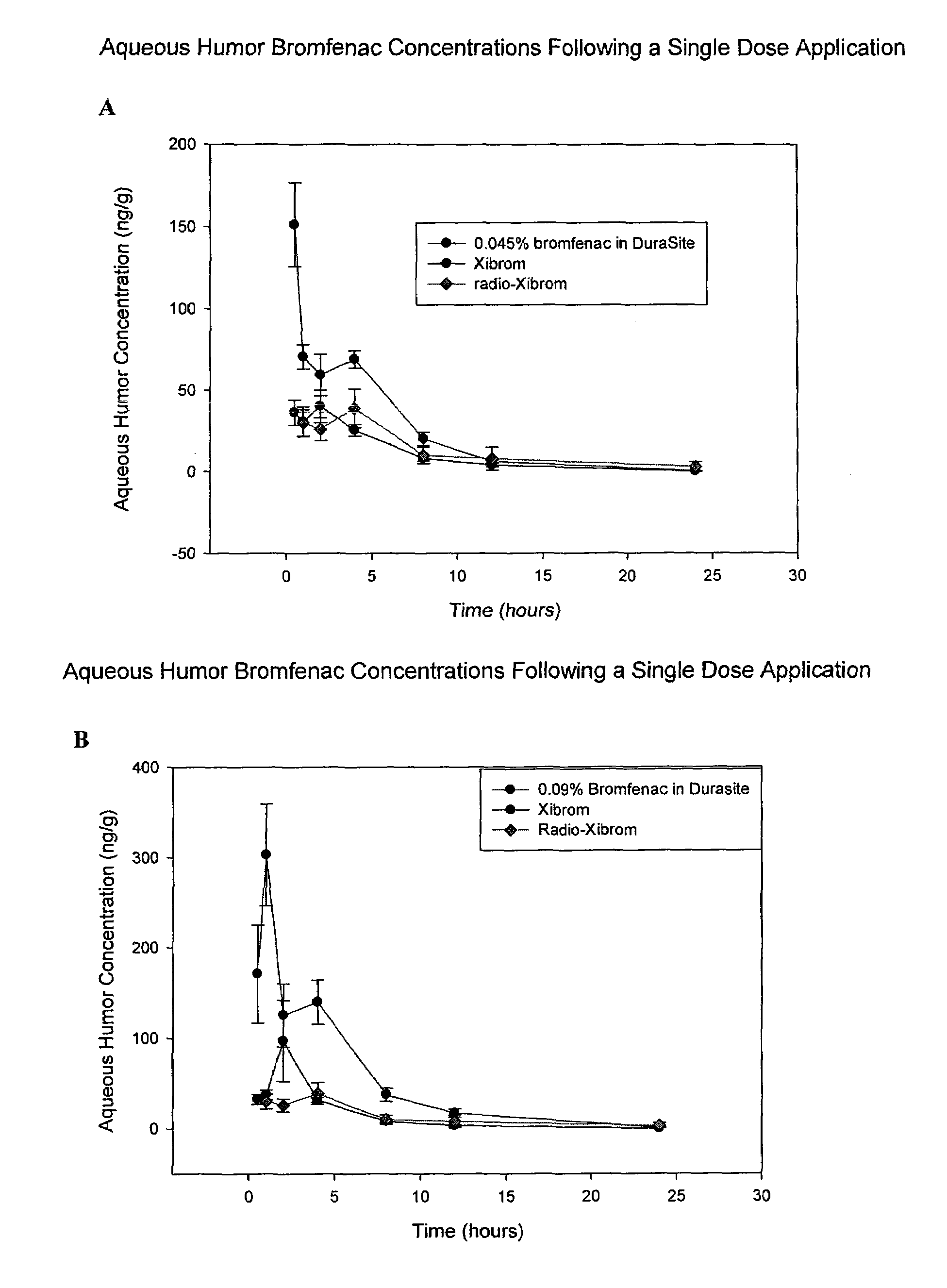
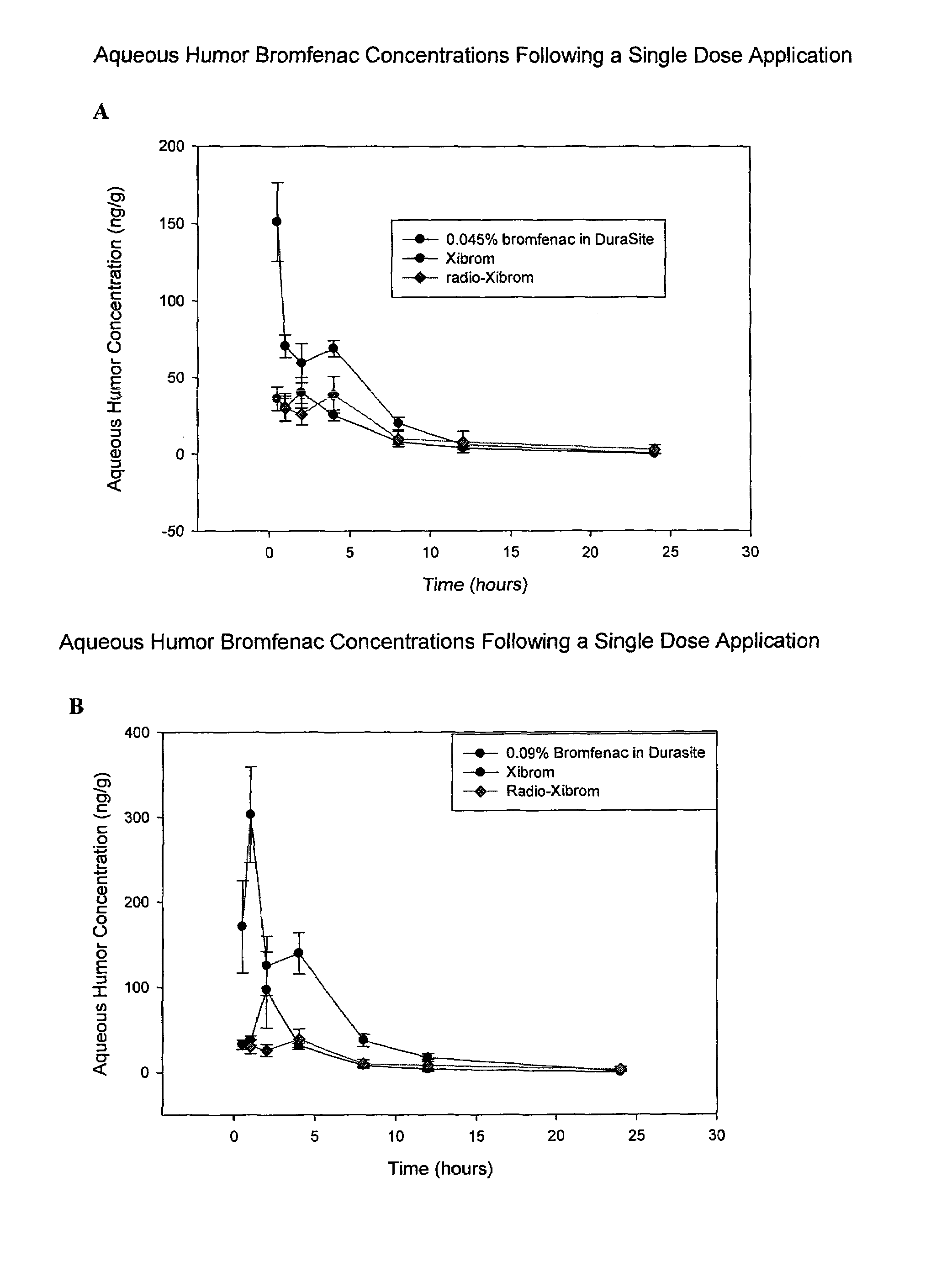
[0071]In this example, the formulations of 0.09% and 0.045% bromfenac in DuraSite®, prepared according to Example 1, were compared with Xibrom® and Radio-Xibrom® in providing bromfenac to the aqueous humor of the eye in pigmented rabbits (n=6). In a first experiment, separately, the formulation of 0.09% bromfenac in DuraSite®, Xibrom® and Radio-Xibrom® (C carbon 14 labeled bromfenac in Xibrom from literature reference JOURNAL OF OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS, 24(2), 2008, 392-398) were topically administered to pigmented rabbits in the amount of 1 drop per eye (approximately equal to about 25 microliters per eye). Xibrom was administered to one eye and the bromfenac DuraSite solution to the other. The concentrations of bromfenac in the aqueous humor of the eye were determined by removing the aqueous humor and measuring concentrations by LCMS (see FIG. 1A). In a second experiment, the bromfenac concentrations provided by 1 drop per eye of the formulation of 0.045% bromfenac in...
example 3
[0072]The formulation of 0.09% bromfenac in DuraSite®, prepared according to Example 1, was ophthalmically administered to pigmented rabbits in the same manner as Example 2, TID for a period of 14 days. At the end of the 14-day period, rabbits were sacrificed in accordance with the related regulatory and NIH guidelines for animal studies, and the concentration of bromfenac was measured using LCMS. In this experiment, the retina was separated from the choroid and tissue concentrations of bromfenac were measured. The concentration of bromfenac in the retina tissue from this 0.09% bromfenrac formulation on average, was found to be 34±10.4 ng per gram of tissue.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| w/w | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com