Periodic contrast injections and analysis of harmonics for interventional X-ray perfusion imaging
a perfusion imaging and contrast injection technology, applied in the field of perfusion imaging apparatuses, can solve the problems of inability to meet the needs of c-arm type interventional imaging systems, tomographic dynamic perfusion imaging methods for slow rotating interventional imaging systems, where spatial resolution is substantially preserved, and achieve the effects of avoiding or eliminating signal aliasing, reducing temporal signal aliasing, and reducing signal aliasing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
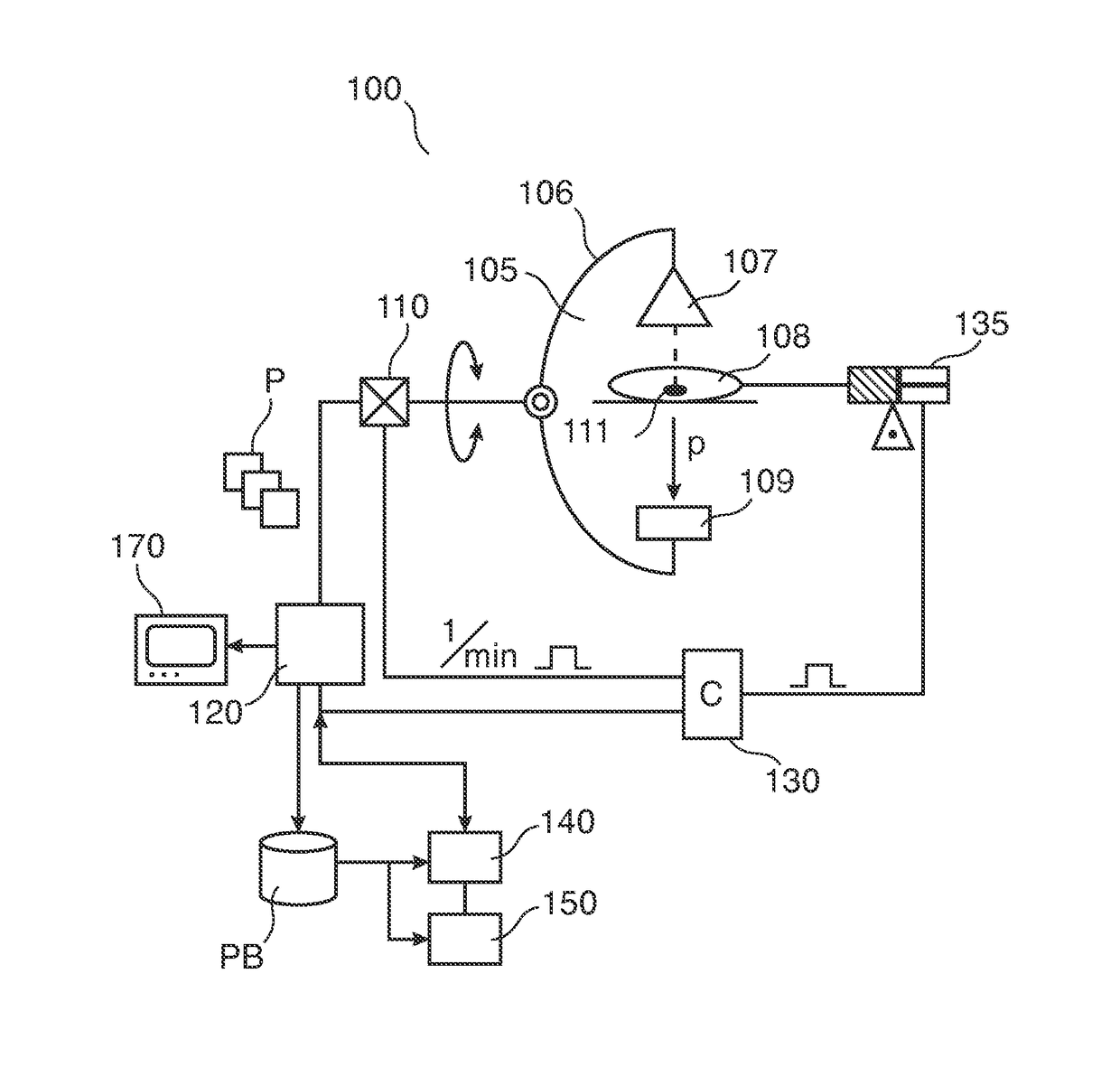
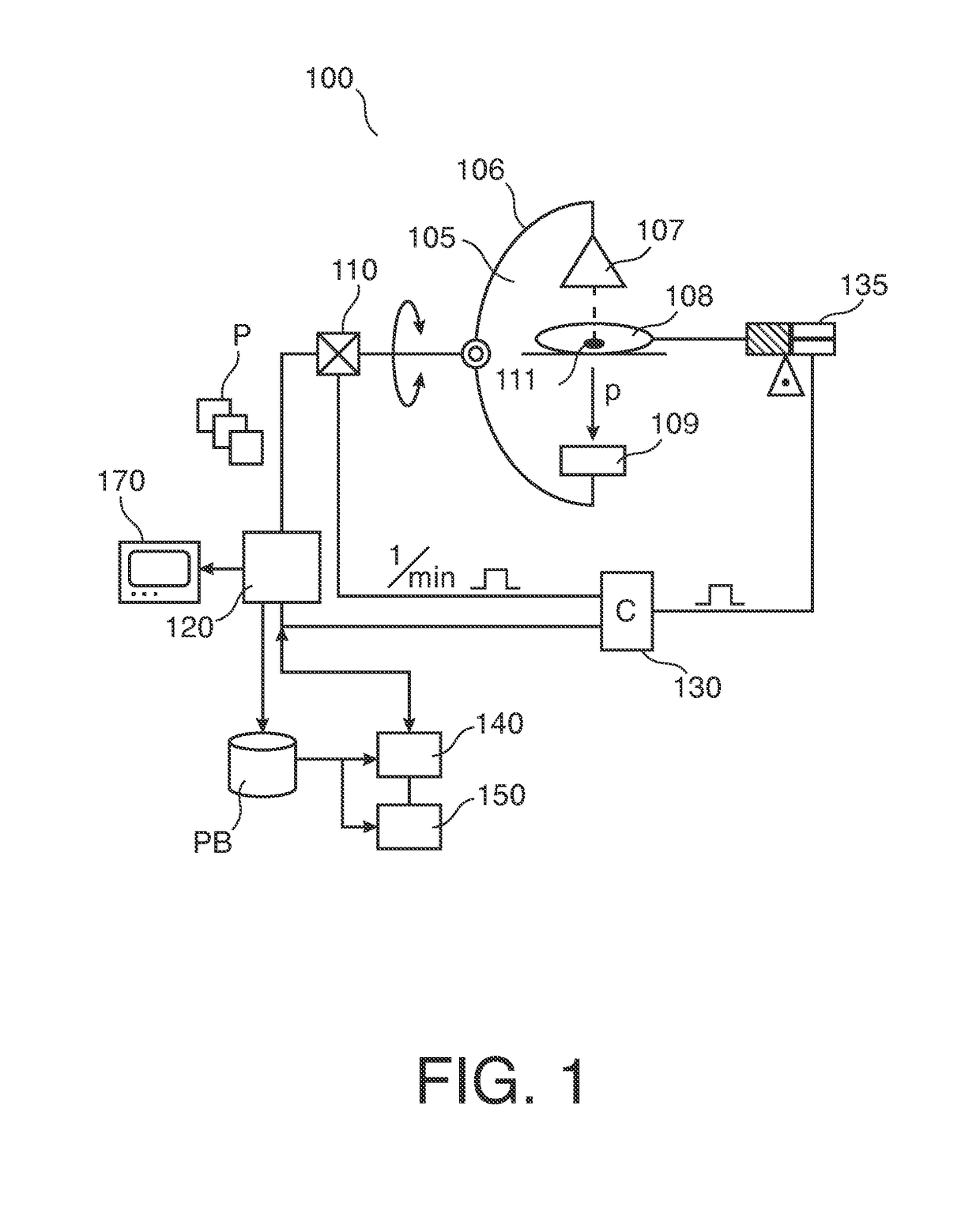
[0036]With reference to FIG. 1, there is shown a perfusion imaging arrangement 100.
[0037]It includes an x-ray imager 105 of the C-arm type. X-ray imager 105 is used to acquire a sequence of x-ray projection images P of an organ of interest 111 to support an intervention.
[0038]In one embodiment, the organ of interest is a patient 108's heart or brain.
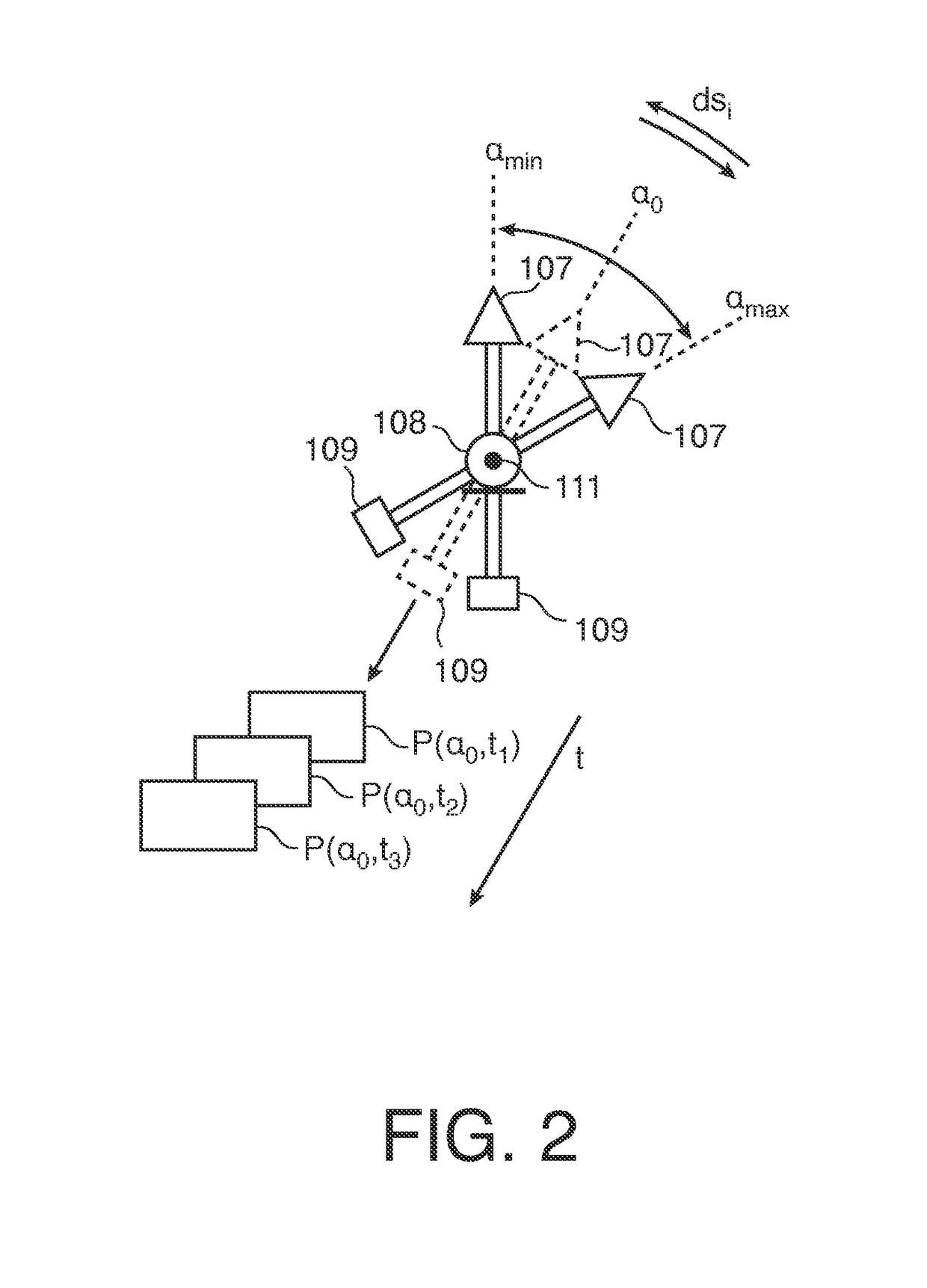
[0039]Patient 108 is placed on an examination table. Imager 105 comprises a rigid C-arm structure 106 journaled on a bearing. Journaling allows rotation of C-arm 140 around a at least one axis passing through journaling. C-arm structure 106 can thus be positioned at various rotation angles α around organ of interest 111.
[0040]C-arm 106 carries at one of its ends an x-ray source 107 and at the other end a detector 109 in opposed spatial relationship to said x-ray source 107. Detector 109 includes an array of detector cells (not shown).
[0041]During an imaging session, x-rays are emitted from x-ray source 107. X-rays pass through organ of i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com