Motor-assisted variable geometry turbocharging system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
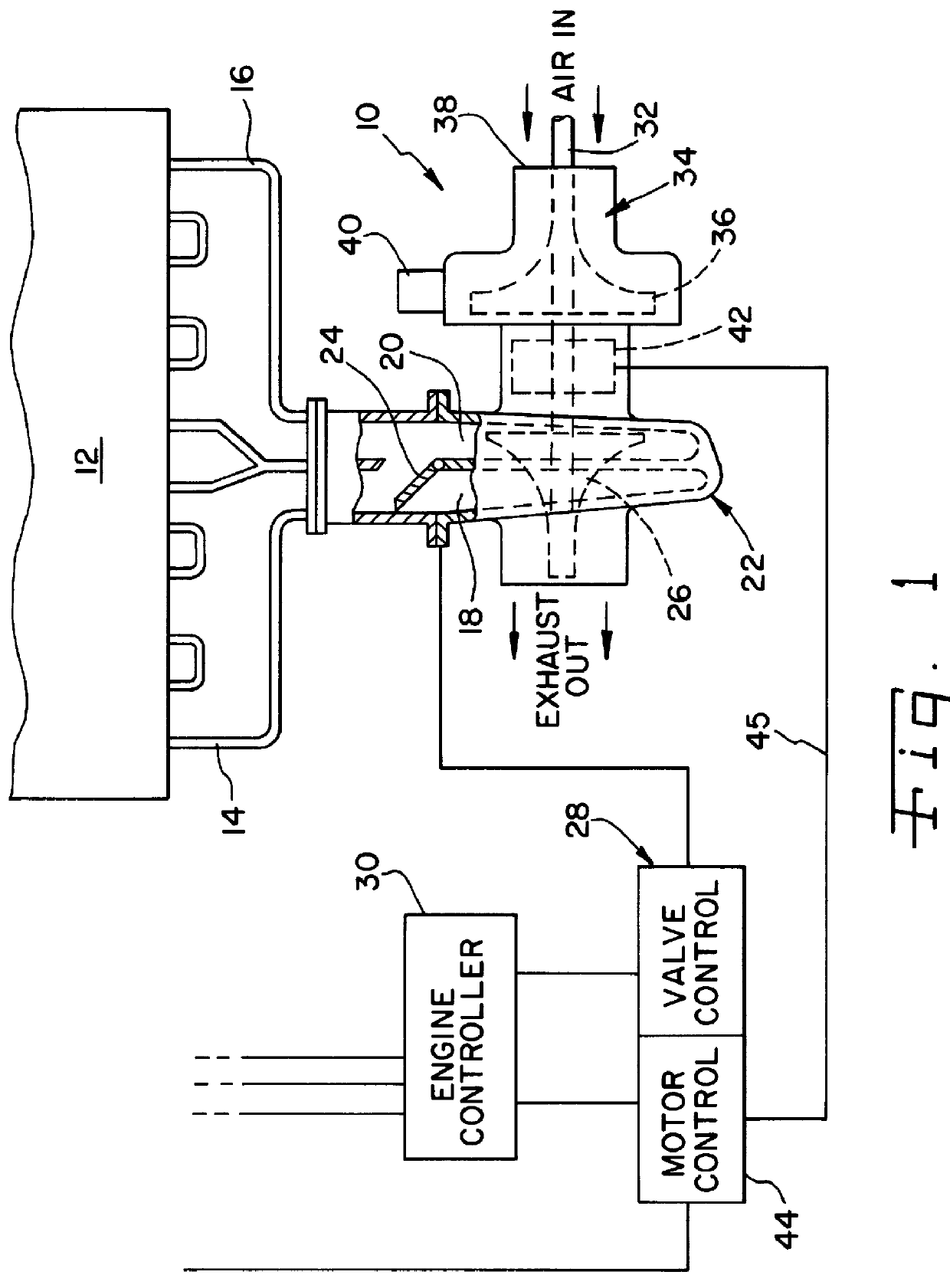
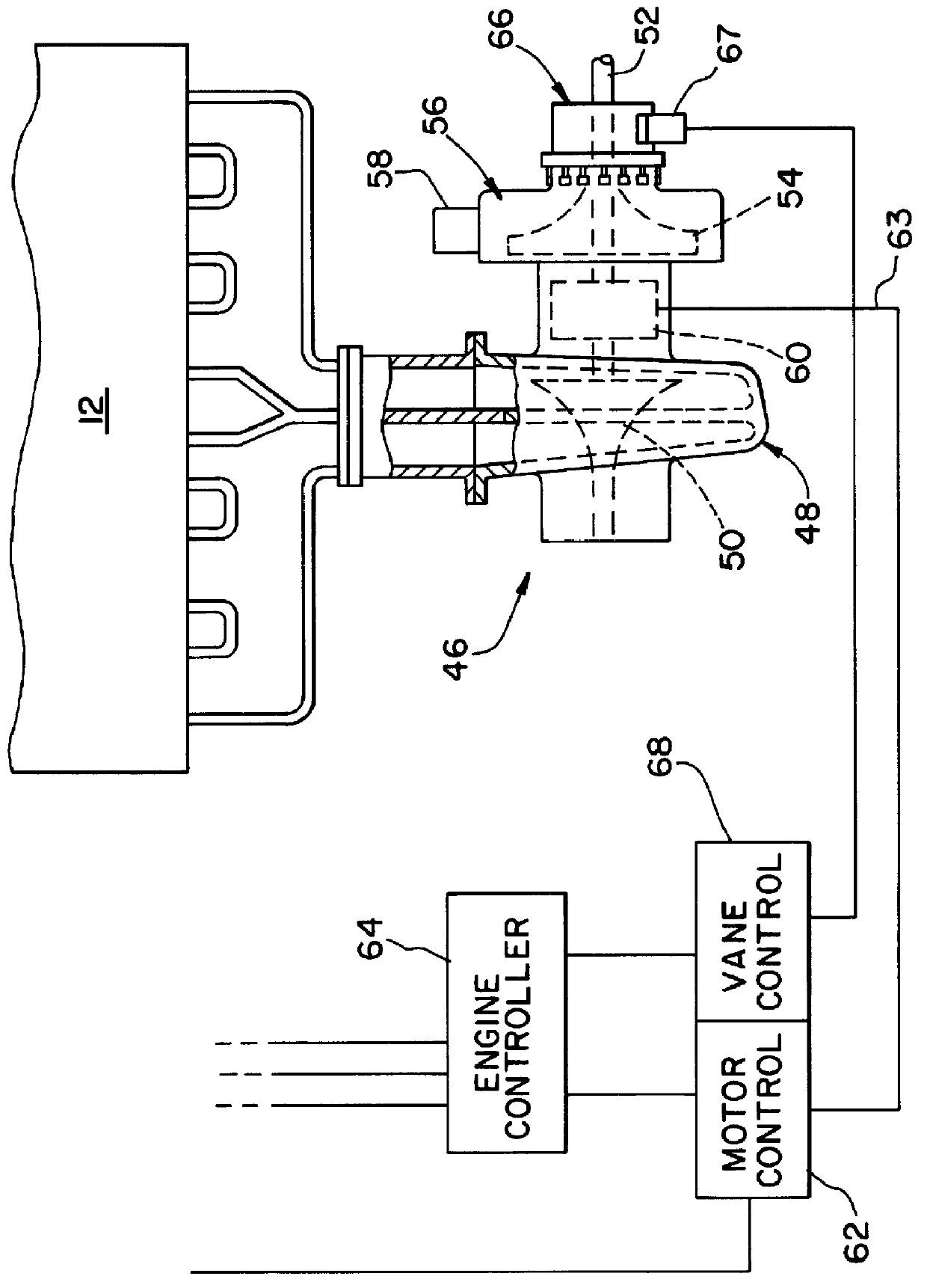
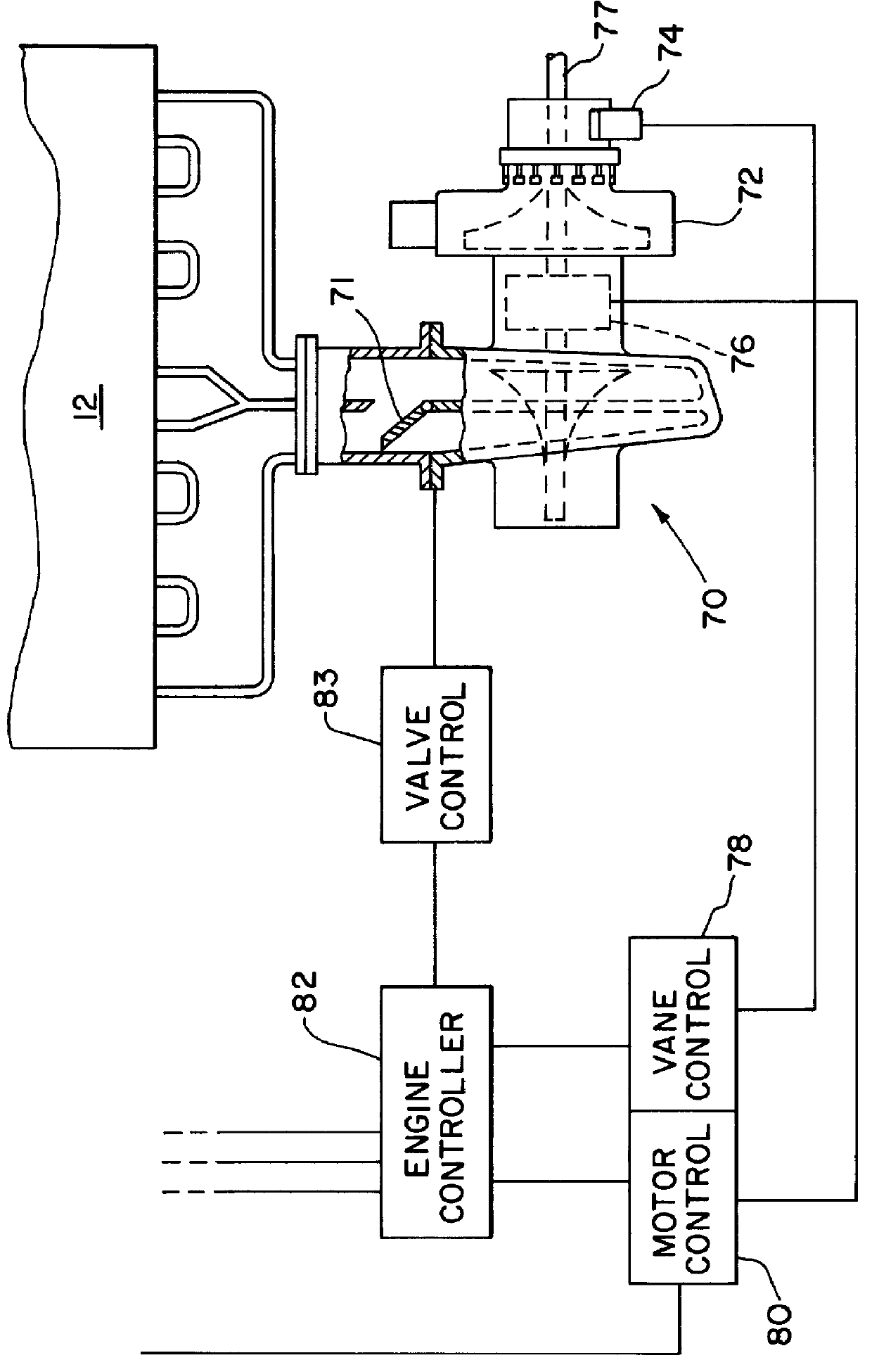
To improve engine and vehicle response to opening of the throttle, an external power source is needed to operate the turbocharger at higher speed at engine idle in order to provide increased boost levels in the engine intake system in preparation for quick acceleration. This external power source can be any convenient rotating power source, such as an electric motor, a hydraulic motor, a pneumatic motor, or the like, and particularly a motor which can have its power output controlled. A preferred example and the example given below of an external power source is an electric motor that engages the turbocharger rotor at engine idle and increases the idle speed of rotation of the rotating assembly.
Having higher boost pressure available at engine idle speed than the boost pressure the turbocharger can provide from exhaust gas energy alone, allows fuel to be injected into the engine cylinders sooner during acceleration and reduces smoke and emissions during the transient period. The engi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com