Superconductor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
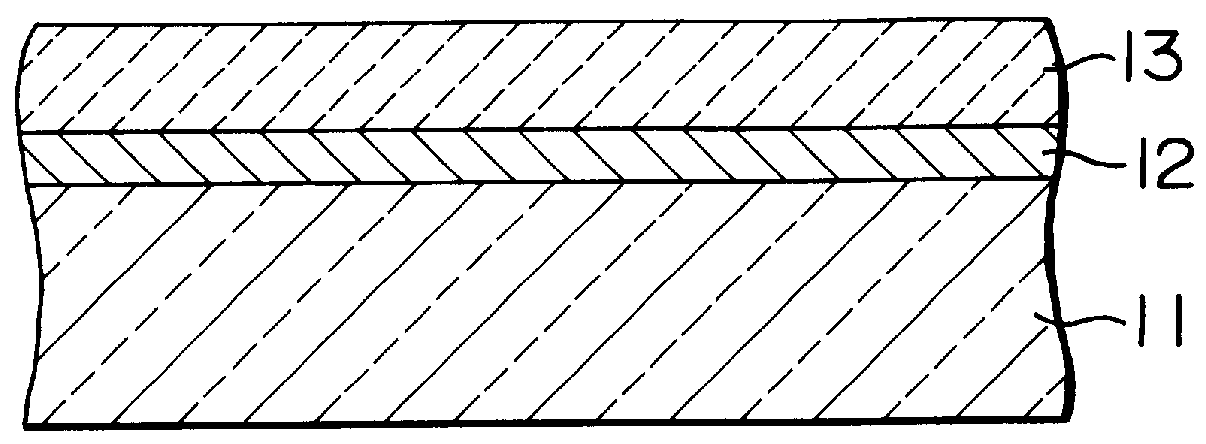
By using sapphire single crystal R plane as substrate 11 and a Pt plate as target, a Pt film 12 was deposited on the substrate by DC planar magnetron sputtering as shown in FIG. 1. Deposition was carried out at a sputtering power of 300 V.times.30 mA by using Ar gas pressurized to 8 Pa and maintaining the substrate temperature at 250.degree.-500.degree. C. to form a 0.1 .mu.m thick film. This Pt film was polycrystalline. On this Pt film 12 was deposited a compound film 13 by high frequency planer magnetron sputtering using sintered ErBa.sub.2 Cu.sub.4.sup...sub.5.sup.O.sub.8 as target. This sputtering deposition of compound film 13 was carried out under Ar gas pressure of 0.5 Pa at a sputtering power of 150 W for a period of one hour by maintaining the substrate temperature at 700.degree. C. to form a 0.5 .mu.m thick film.
This film showed a room-temperature resistance of 600 .OMEGA. and a superconducting transition temperature of 88 K.
Film formation on a glass coated substrate is de...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Superconductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com