Melt spun TPU fibers and process
A fiber and footwork technology, applied in the field of melt-spun TPU fiber production, can solve the problems of high cost and downtime, and achieve the effect of extending the time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 shows the preparation of a polyether TPU polymer using PTMEG as the hydroxyl terminated polyether polyol, MDI as the polyisocyanate, and 1,4-butanediol as the chain extender. The one-step process described above was used to prepare the TPU of Example 1. The TPU polymer from Example 1 was used in Examples 2-6 for melt spinning trials. Example 2 is a comparative example using a polyether crosslinker and Examples 3-6 use a polyester crosslinker according to the invention.
[0050] Example 1
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 (comparative example)
[0053] The TPU polymer of Example 1 was pre-dried in a vacuum batch dryer at 80°C for 12 hours. After drying the TPU polymer was melted in a 1.25 inch single screw extruder with an L / D ratio of 24. With loop control, the back pressure at the exit of the extruder is kept constant. The extruder contained four heating zones maintained between 180°C and 219°C. On exiting the extruder, the TPU polymer melt was mixed with 13.1 wt% of a polyether prepolymer crosslinker having a number average molecular weight of 1500 (Hyperlast 5196). Pump the crosslinker from the holding tank at a constant flow. The crosslinker was mixed with the TPU polymer melt in a dynamic mixer and then pumped through manifolds to 32 spinnerets. Each spinneret had an orifice size of 0.5 mm. The polymer stream exiting the spinneret was air cooled and the formed fibers were wound into bobbins at a winding speed of 480 m / min. The fibers on the aging spool were heated...
Embodiment 3
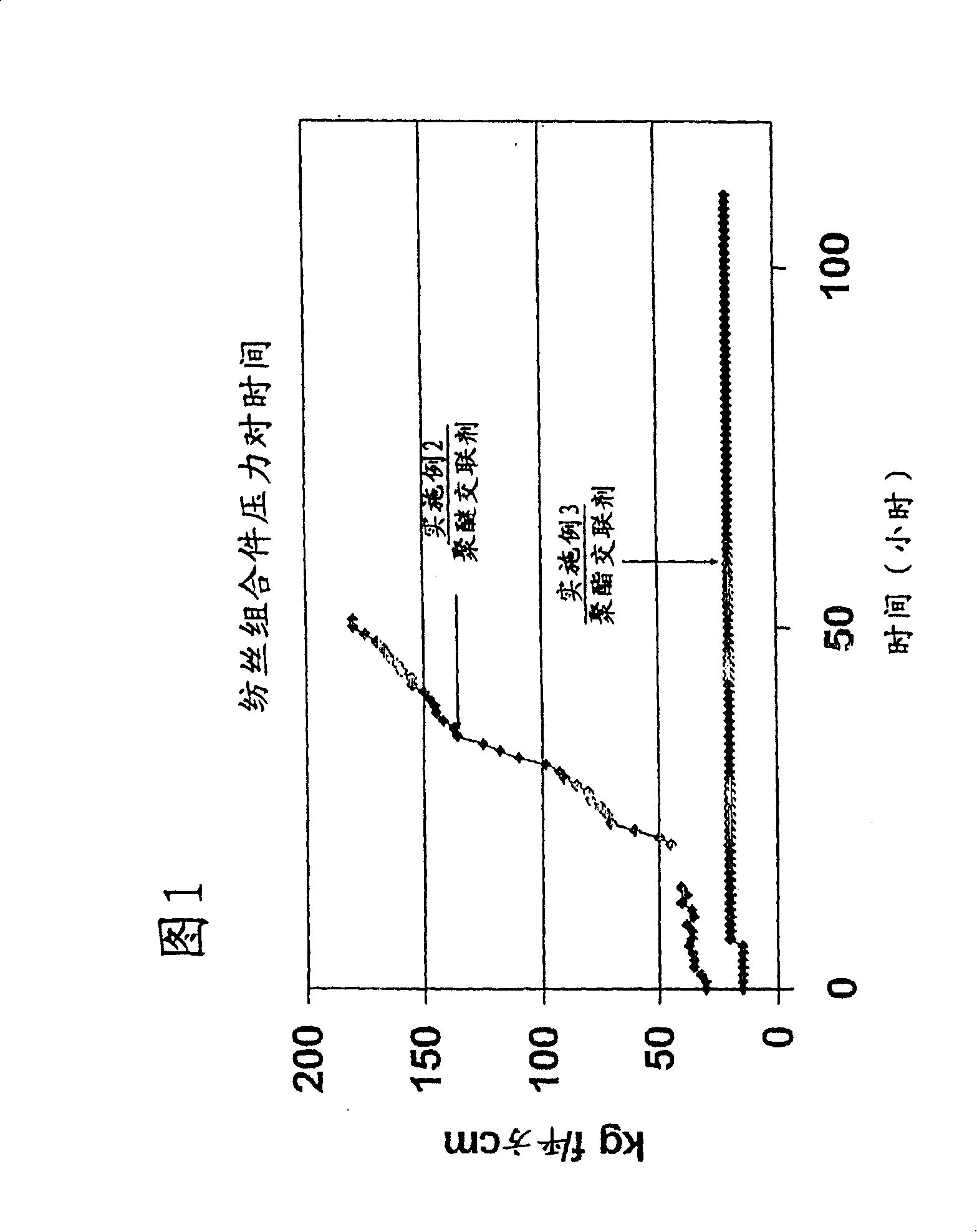
[0056] This example is presented to show that polyester crosslinkers give much less spinpack pressure buildup than the polyether crosslinkers used in Example 2.
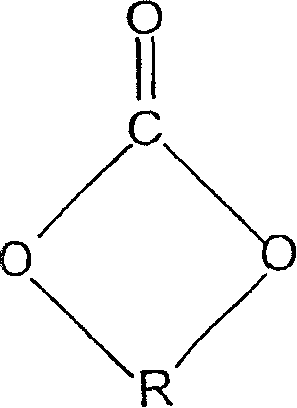
[0057] TPU polymer, melt spinning equipment and conditions were the same as described in Example 2 above. The only difference is the crosslinker used. In this example, 14.0 wt% polyester crosslinker was used. The polyester crosslinker used was purchased from Hyperlast Company 5128, its number average molecular weight is 2500.
[0058] The fibers produced were 20 denier and at the same speed as Example 1 (480 m / min).
[0059] Measure the spin pack pressure during the run. Figure 1 shows a graph of the pressure buildup during operation. The data shows that the spin pack pressure at the start of the run is about 15Kg / cm 2 . After about 8 hours, the spin pack pressure increased to 20 Kg / cm 2 . The run lasted a total of 110 hours and the spin pack pressure was maintained at 20 Kg / cm 2 . There were no fiber bre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com