Organic electroluminescence device
An electroluminescent device, an organic technology, applied in the direction of electroluminescent light source, electric light source, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems affecting the performance of the light-emitting layer, the complex energy band structure, and the performance of the device, so as to improve the transmission performance. Enhanced luminous efficiency and high binding energy effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
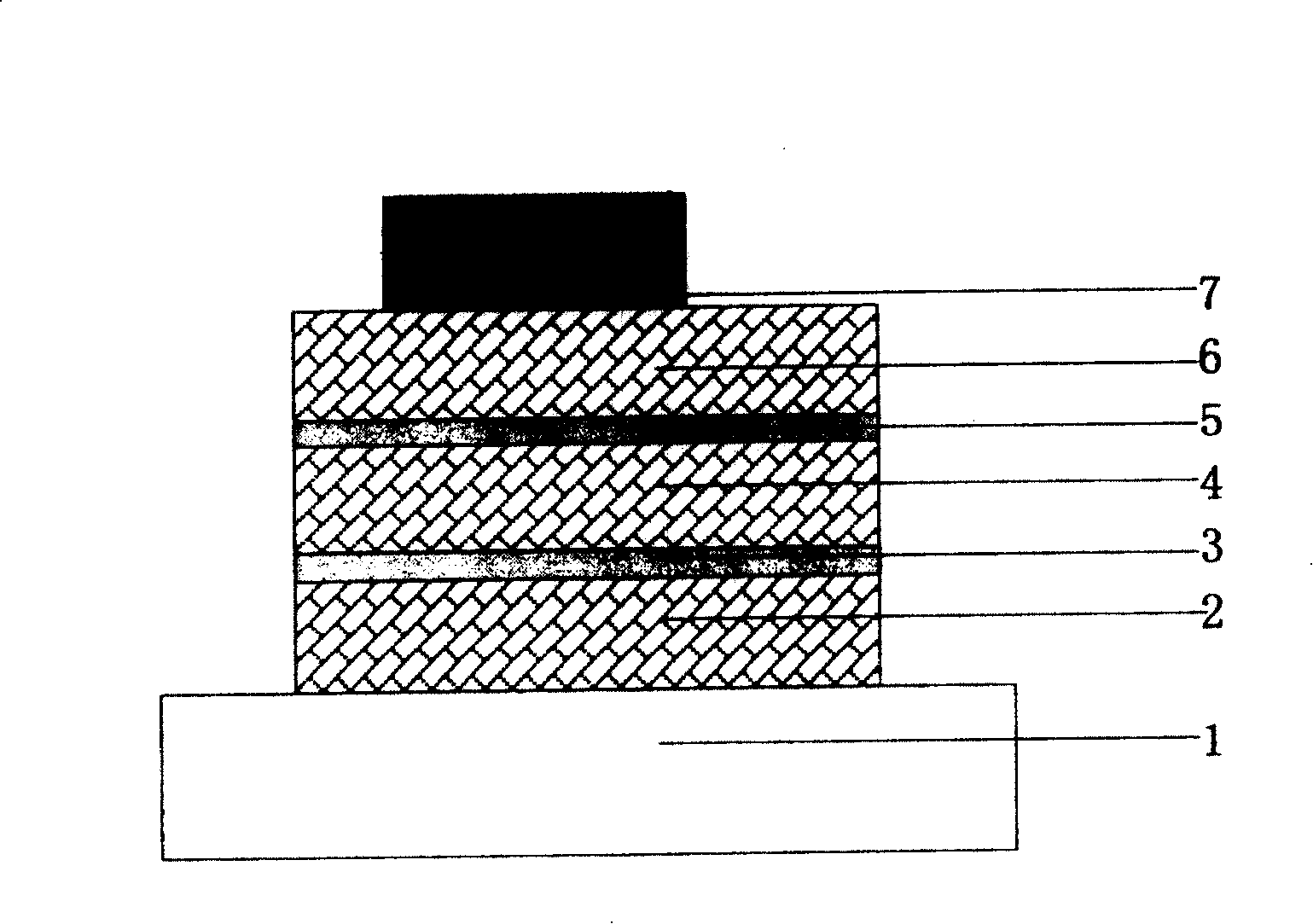
[0030]First, on the cleaned ITO conductive glass electrode (1) substrate, a layer of aromatic diamine derivative TPD with a thickness of 40nm is evaporated as a hole transport layer (2) by vacuum thermal evaporation coating method, and then evaporated on One deck thickness is the 8 quinoline aluminum Alq of 20nm as light-emitting layer (4), then vapor deposition last layer thickness is 0.5nm (device 1) or 1nm (device 2) thick LiF inorganic material thin layer ( 5) As a hole and exciton blocking layer, then vapor-deposited a layer of 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum Alq with a thickness of 40nm as the electron transport layer (6), and finally vapor-deposited with a layer of metal aluminum Al with a thickness of 100nm as Back electrode (7). In the device, the inorganic material thin layer (3) may not be used, and the light emitting layer (4) and the electron transport layer (6) may be of the same material. Compared with the conventional devices prepared by the prior art under the sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com