Hartman wave front sensor to realize alignment function by light splitter and testing method thereof
A spectroscopic device and sensor technology, which is used in the testing of machine/structural components, optical instrument testing, optical components, etc. It can solve the problem that the measured beam and the optical axis of the system deviate, it is difficult to adjust the incident wavefront, and the wavefront measurement error becomes larger. and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving measurement accuracy, small detection error, and reducing requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
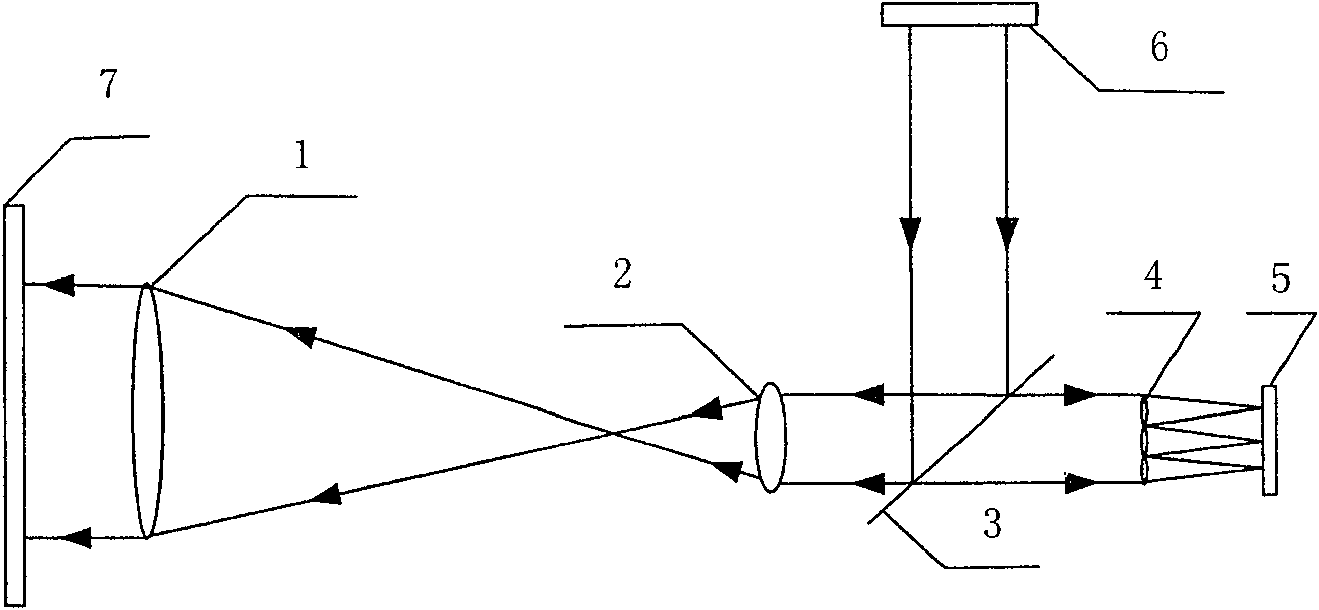
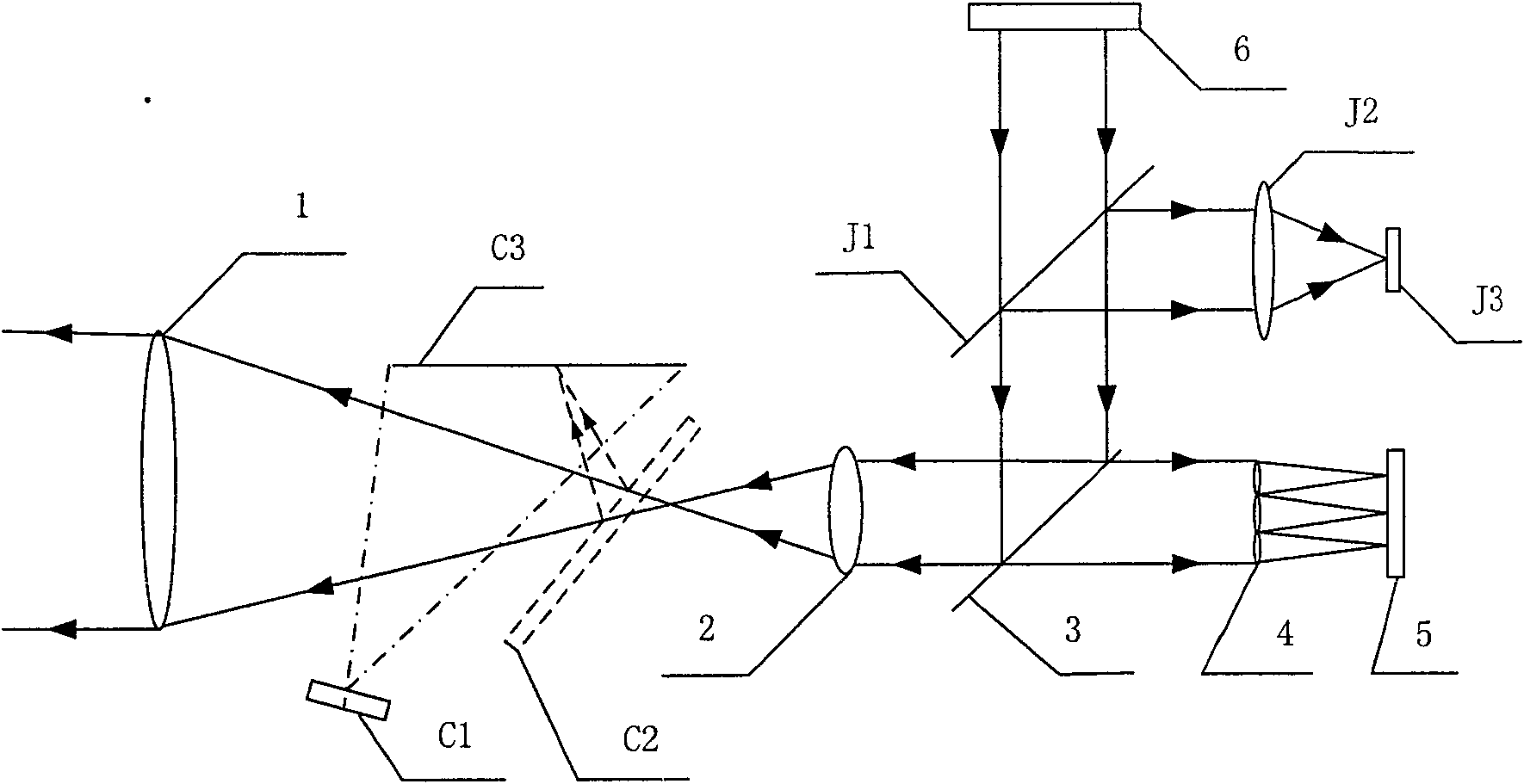
[0017] When the Hartmann wavefront sensor is working, the error of the system itself needs to be calibrated first.
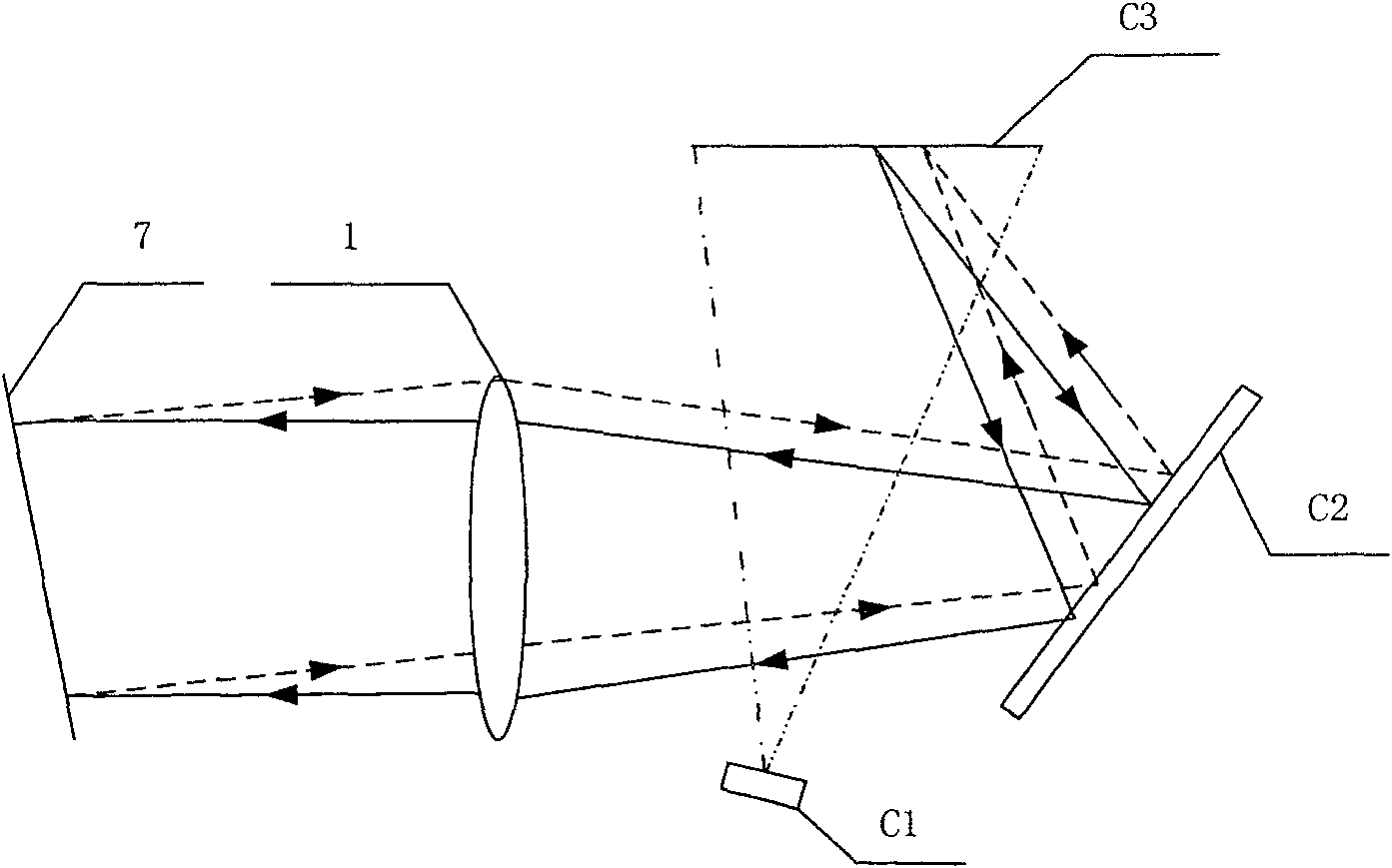
[0018] Such as figure 1 As shown, when calibrating the system error, the beam emitted by the measurement light source system 6 first passes through the beam splitter 3, then passes through the front mirror group 1 and rear mirror group 2 of the beam matching system, and finally exits the system. After being reflected by the standard plane mirror 7, it returns to the system, passes through the beam matching system, the beam splitter 3, and the microlens array 4, and forms an image on the photodetector 5. The position of the standard flat mirror 7 is adjusted to finally make the spot arrangement on the photodetector 5 meet the measurement requirements. But the area of microlens array 4 is about 1cm 2 , is very small compared to the overall optical path, resulting in a small adjustable range of the standard plane mirror 7, and the adjustment is very difficult. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com