Porous electrode base material and process for producing the same
A technology of electrode base material and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of battery electrodes, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient fuel cell power generation, difficulty in controlling moisture, and low water retention, and achieves thickness and low cost , excellent bending strength, thin thickness effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
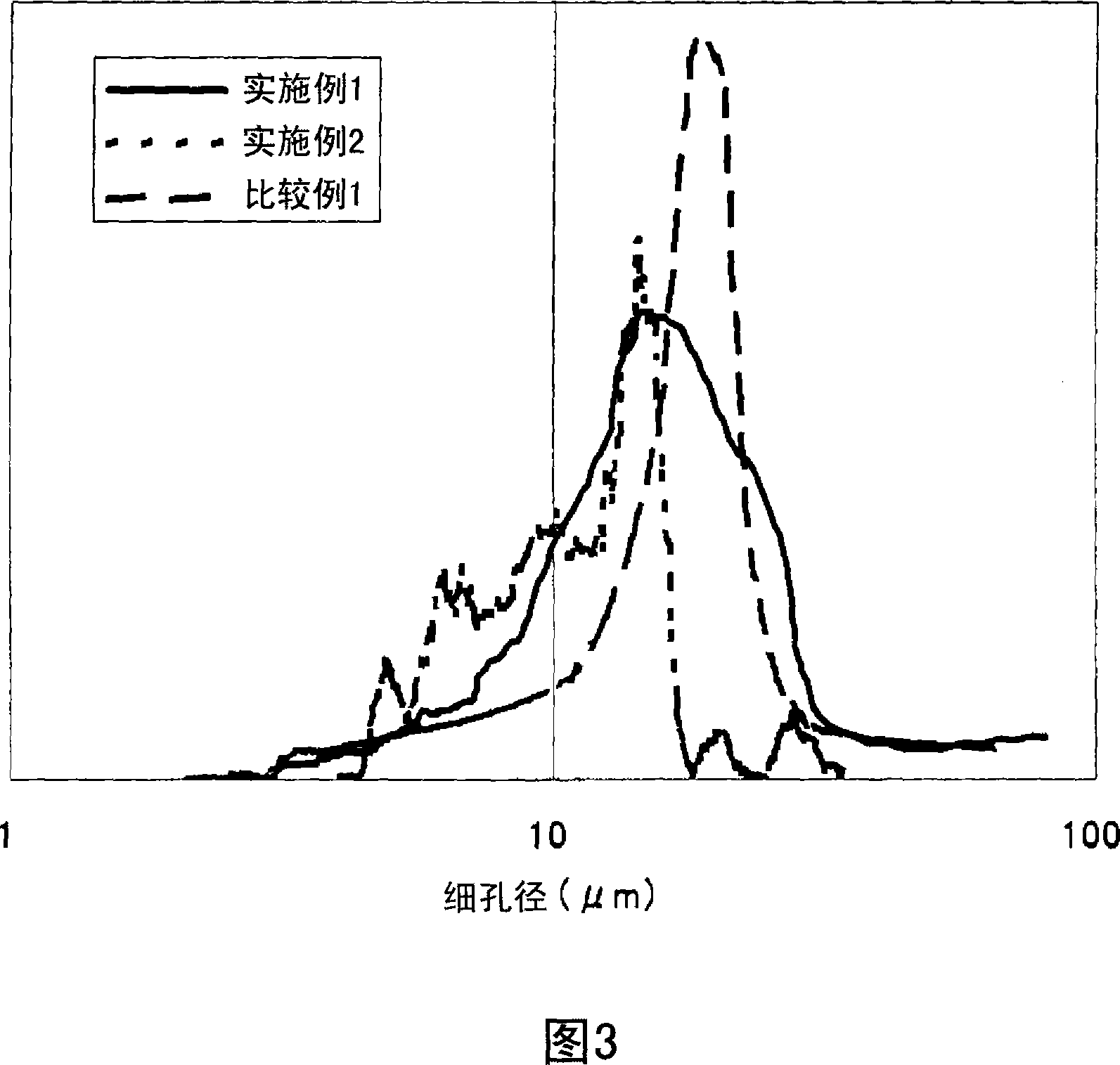
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0178] As short carbon fibers, polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based carbon fibers with an average fiber diameter of 7 μm and an average fiber length of 3 mm and PAN-based carbon fibers with an average fiber diameter of 4 μm and an average fiber length of 3 mm were prepared at a ratio of 70:30 (mass ratio). carbon staple.
[0179] Vinylon fibers of 1.1 dtex and a cut length of 5 mm (Unicka Vinylon F manufactured by Unitica Co., Ltd.) were prepared as vinylon fibers.
[0180] Short fibers of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (Kuraray Co., Ltd. VBP105-1, cut length 3 mm) were prepared as the organic polymer compound.
[0181] In the slurry tank of the wet short-wire continuous papermaking device, the carbon short fibers are evenly dispersed in water, and the filaments are divided into single fibers. After being fully dispersed, 18 mass parts, 32 parts by mass to evenly disperse PVA short fibers and vinylon short fibers, and output them in a net shape.
[0182] Let the output net pass through th...
Embodiment 2
[0189] A porous electrode substrate having a smooth surface was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the ratio of short carbon fibers was changed to 50 / 50 (mass ratio). The evaluation results are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
Embodiment 3
[0191] Except that the vinylon fibers were changed to 0.6dtex and vinylon staple fibers with a cut length of 5mm (Unitica Vinylon F manufactured by Unitica Co., Ltd.), a porous material with a smooth surface was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1. Electrode substrate. The evaluation results are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com