Synchro motor drive device
A synchronous motor and driving device technology, applied in the control of electromechanical transmission, motor generator control, AC motor control, etc., can solve problems such as difficult starting, control phase error, motor reversal, etc., to avoid torque ripple, The effect of suppressing inversion and simple composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
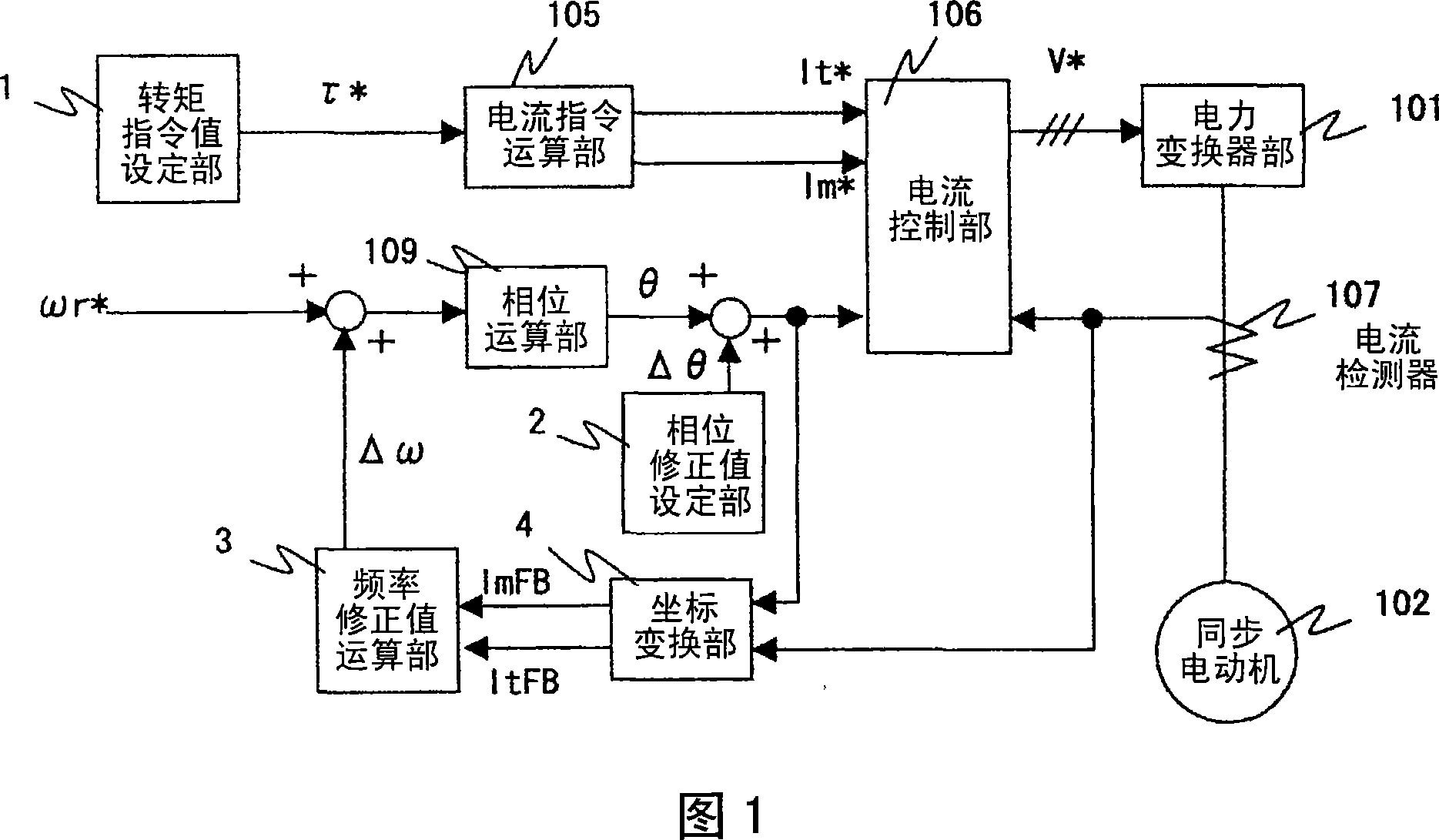
[0024] The differences between the induction motor drive device of this embodiment and the prior art shown in FIG. 10 will be described using FIGS. 1 to 3 . In addition, what is involved here is the control method from starting to accelerating to a given speed. In the torque command value setting section 1, let the torque command value τ * It corresponds to acceleration torque + load torque, and is set to, for example, about 60% of the rated torque. Next, in the current command computing unit 105, the torque current command It is set * = given value, excitation current command Im * =0. Since the magnetic flux is generated by the field current of another field device, it is generally controlled so that Im=0. At this time, the currents Id, Iq, magnetic fluxes Φd, Φq, and generated torque τm of the synchronous motor 102 are as shown in (Formula 2) to (Formula 6), respectively. In addition, the phase difference Δ is the phase deviation between the d-axis and the m-axis shown...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Differences between this example and example 1 will be described. In this embodiment, the phase correction value Δθ is gradually changed by degrees such as 90° or 45°, or 30°, or 10° below 90°. By doing this, the rotation becomes smoother.
Embodiment 3
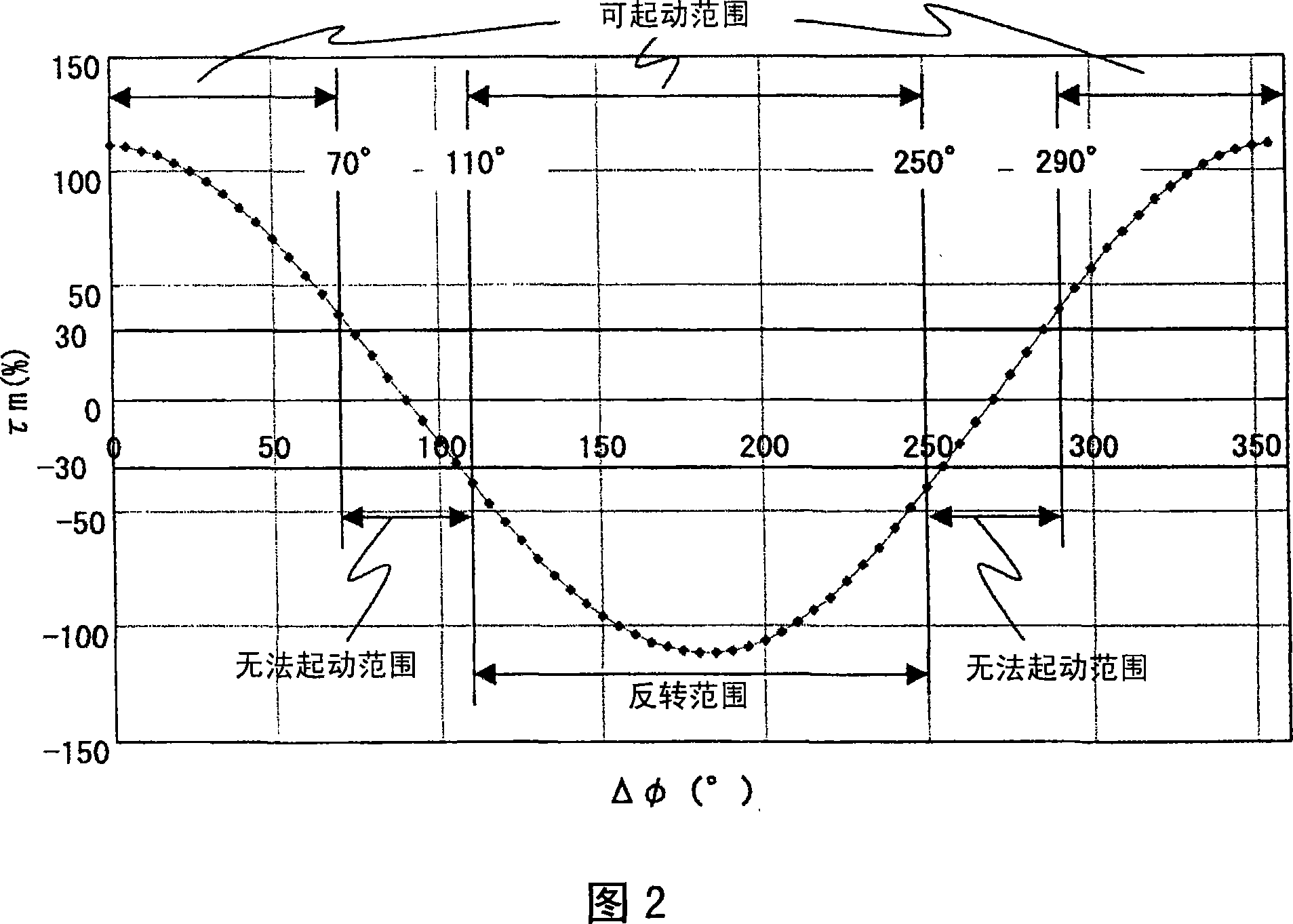
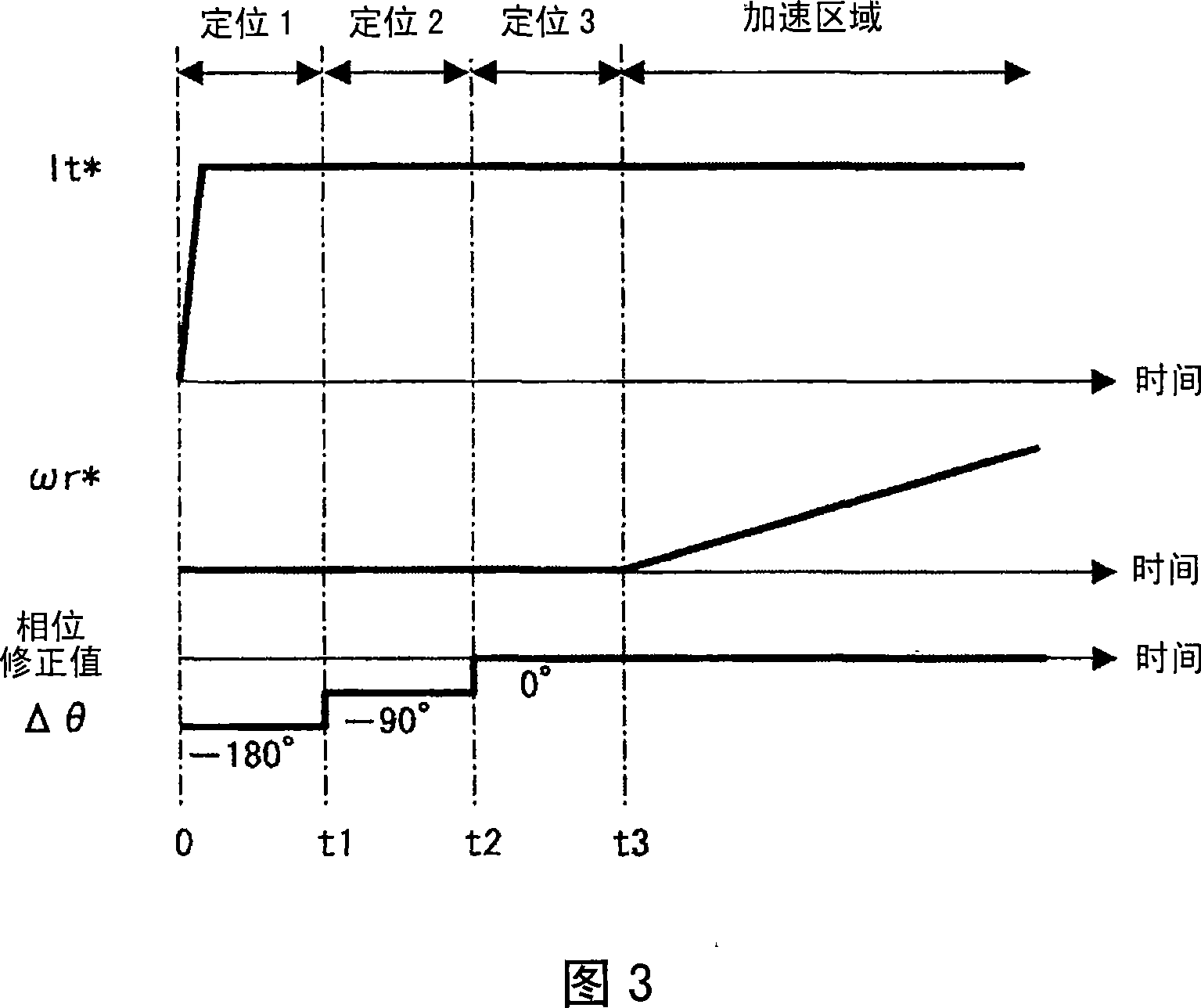
[0038] The differences between this example and example 1 and example 2 will be described using FIG. 4 . In FIG. 4, compared with FIG. 3 of the first embodiment, the time t1 for setting the phase correction value Δθ to the initial setting value is shorter than the time t2-t1 and t3-t2 for changing the phase correction value Δθ thereafter. This is because, in Fig. 11, starting at a position staggered by 180° from the t-axis (current axis) and the d-axis (magnetic pole axis) cannot start, and demagnetization is caused by the t-axis current, so the phase correction When the value Δθ changes and the t-axis (m-axis) moves, it may not start due to demagnetization. In addition, the reason why it can be started within t1 is that it is close to the phase correction value Δ=0, and then when the phase correction value Δθ moves by 90°, it is still within the startable range, as long as the demagnetization of the initial phase correction value Δθ is prevented. Can. In this embodiment, b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com