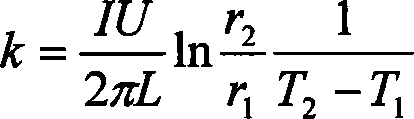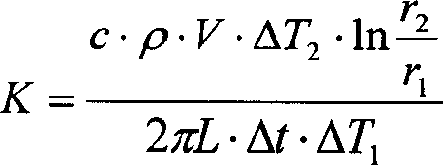Method and device for measuring liquid thermal conductivity factor
A technology of thermal conductivity and liquid, which is applied in the field of measuring liquid thermal conductivity, can solve the problems of low practical value and insufficient estimation of heat loss, etc., and achieve the effects of simple and easy testing, wide application range and simple formula derivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
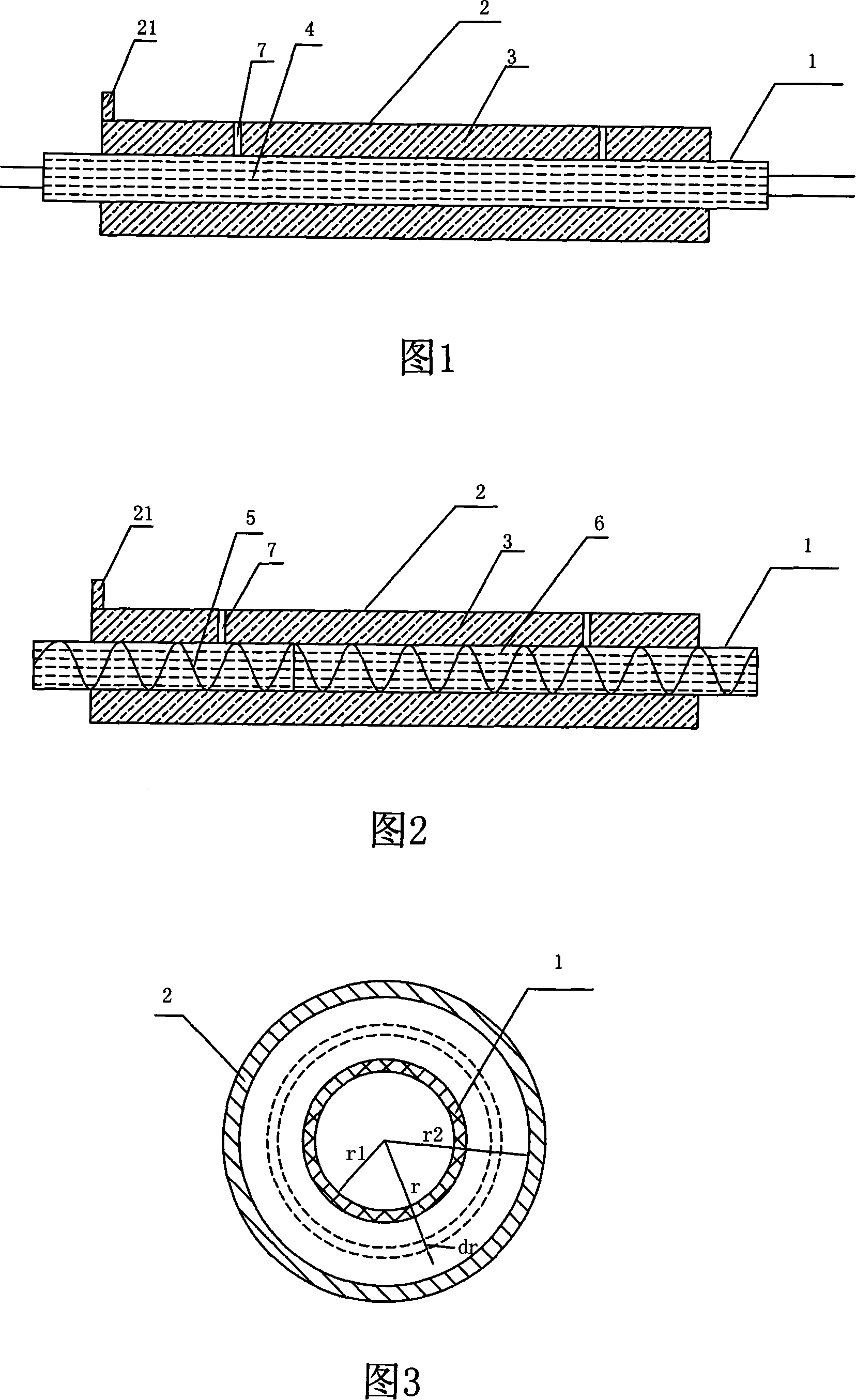
[0077] For the liquid to be tested is a high-temperature-resistant liquid, the center of the double-layer tube in this embodiment must be coaxial, and it must be resistant to a high temperature of at least 100 degrees. As shown in Figure 1, the outer tube 2 is long 2 to 5 centimeters, sealed, and the ratio of the outer tube length to the outer tube radius is greater than 10, and the outer wall is provided with an inlet 21 of the liquid to be measured (the height is 2 mm-8 mm, and the aperture is 8 mm. mm); the inner tube 1 is 33 cm long, and the two ends are respectively 4 cm longer than the outer tube, so as to connect other instruments. Two holes are respectively arranged on the side of the outer tube to install the thermocouple 7 . The diameter of the holes is 2 mm, the distance between the two holes is 135 mm, and the distance from the two ends of the tube is 55 mm. The thermocouple 7 is electrically connected with a microvoltage measuring instrument or a DC potentiometer...
Embodiment 2
[0112] For high temperature flammable liquids, the inner tube temperature is too high is very dangerous. Therefore, this embodiment is improved on the basis of the first embodiment, so as to be applicable to the measurement of the thermal conductivity of high-temperature flammable liquids.
[0113] As shown in Figure 2, the dimension structure of the double-layer pipe is the same as that of Embodiment 1, but the heating method of the inner pipe is different. The inner tube 1 is fixed with a heating wire 5 and filled with a high temperature resistant liquid 6 and sealed. The outer tube 2 is filled with the liquid 3 to be tested.
[0114] During the test, the liquid to be tested is injected from the injection port 21 of the outer tube. The inner tube 1 is provided with a heating wire 5 and injected with a high temperature resistant liquid 6, and the function of filling the high temperature resistant liquid 6 is to increase the heat conduction speed. The heating wire 5 is conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com