Method for determining responsiveness to chk1 inhibitors
A technology of CHK1 and inhibitors, applied in the field of determining the response to CHK1 inhibitors, can solve the problems of limited practicality, strong side effects of normal tissues, tumor cell resistance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
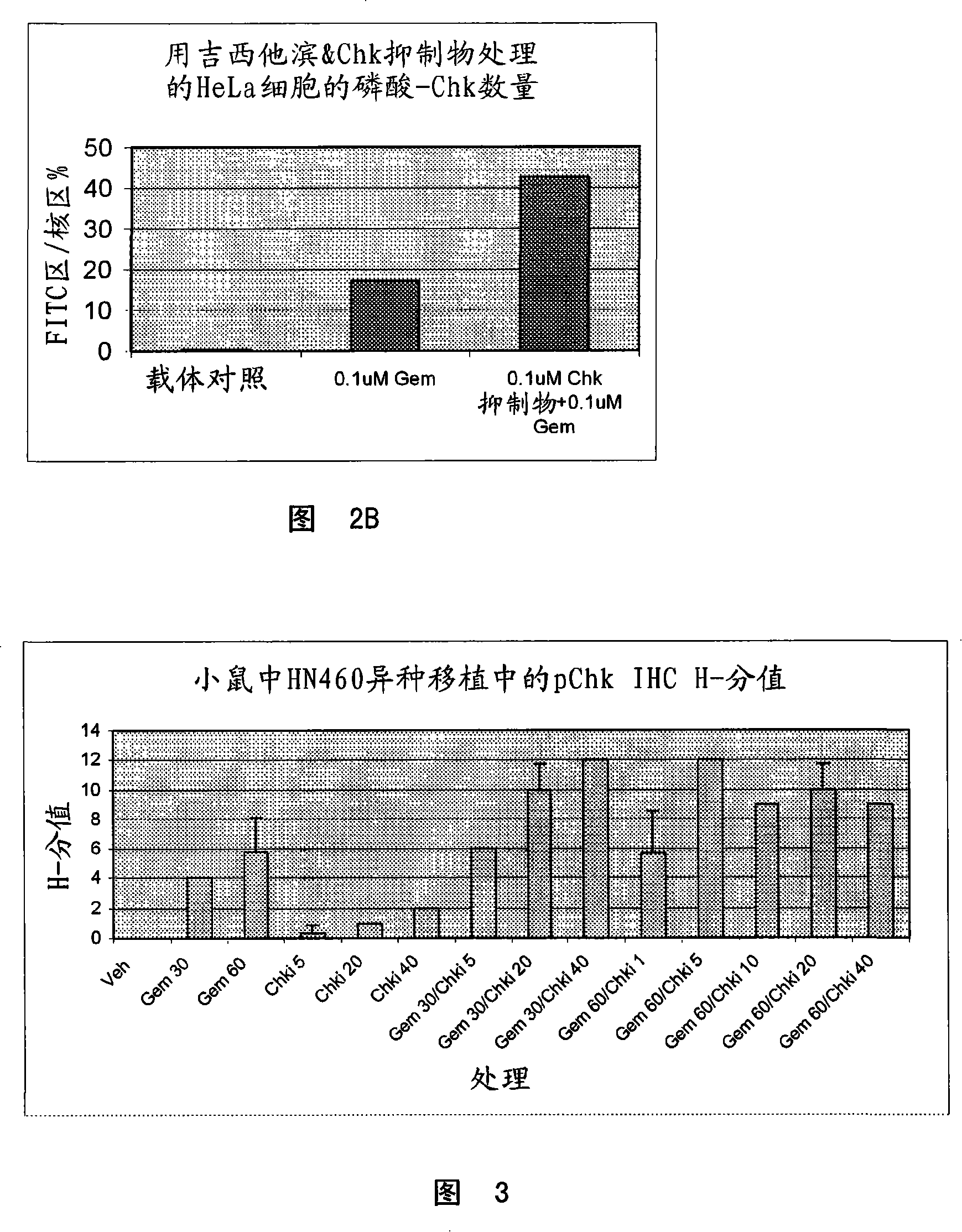
[0059] Example 1: Demonstration of CHK1 activation following DNA damage in tumor cell line S and xenograft samples
[0060] A. In vitro studies:
[0061] In short, the 3×10 6 SW620 and / or HT29 cells were seeded into 10 cm tissue culture dishes and allowed to attach for 24 hours at 37°C. Cells were then treated with titrations of DNA damaging reagents (SN-38 (CQ International, China), doxorubicin (Sigma-Aldrich, MO) or gemcitabine (CQ International, China)). Then, after 8 hours of incubation with DNA damaging reagents, cells were harvested in Onyx lysis buffer (20 mM Tris, 137 mM NaCl, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Triton-X, 10% glycerol, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1:100 dilution of CalbiochemPhophatase Inhibitor Cocktail Set II, 10 mM β-glycerol phosphate, 1 mM DTT, 7 μg / ml PMSF, 20 KIU / ml aprotinin, 1 mM Pefabloc, 0.1 mg / ml leupeptin) . Protein lysates were then generated, protein concentration was determined, an equal amount of protein was loaded, and phospho-CHK rabbit monoclonal antibody (Ser 345)...
Embodiment 2
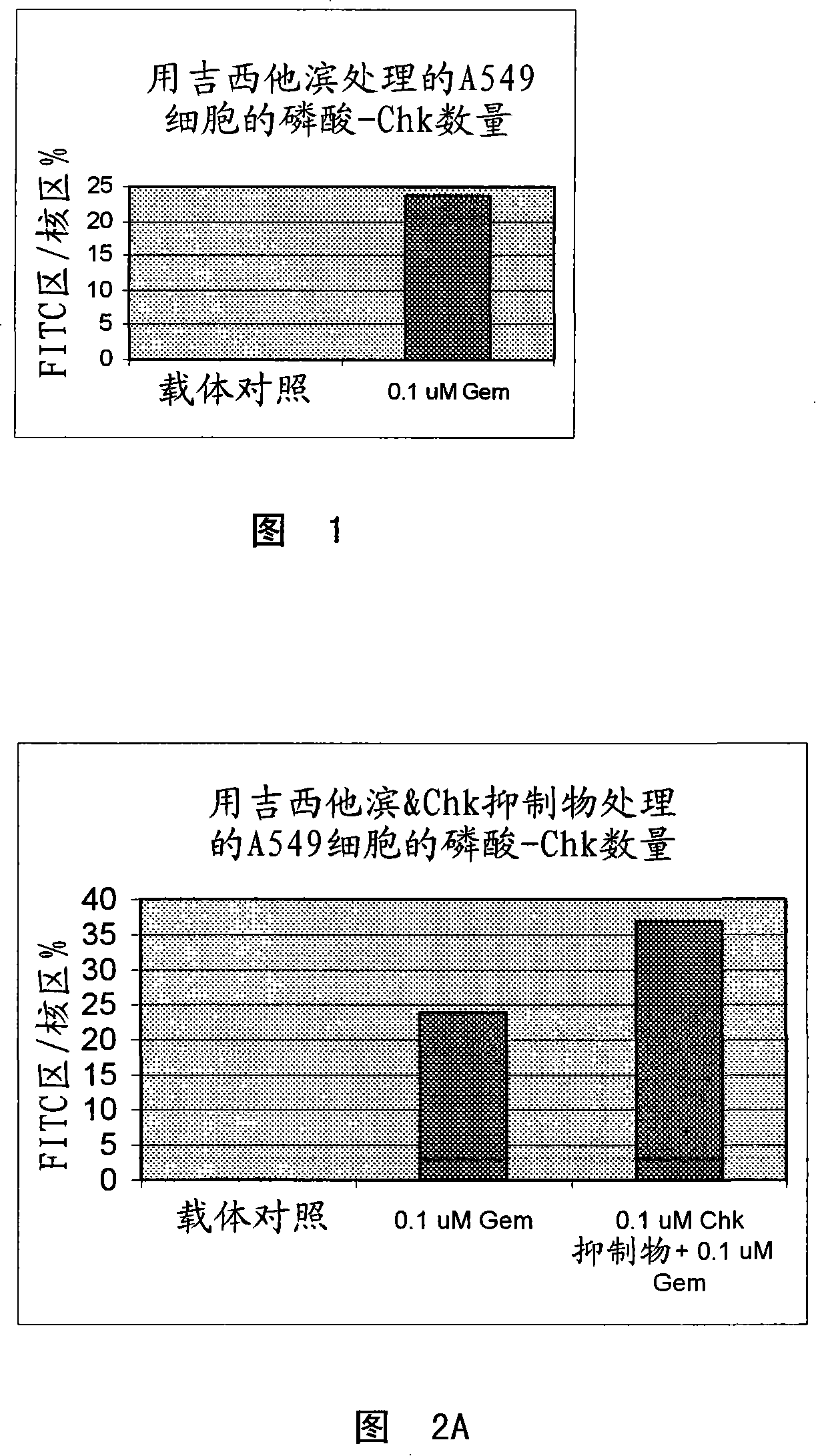
[0065] Example 2: Demonstration of increased phospho-CHK following combination treatment of gemcitabine and CHK1 inhibitors in tumor cell lines, xenograft samples and substitute tissues
[0066] A. In Vitro Studies
[0067] In short, the 3×10 6 SW620 cells were seeded in 10 cm tissue culture dishes and allowed to attach for 24 hours at 37°C. Cells were then treated for 8 hours with 100 nM gemcitabine or 30 nM, 100 nM or 500 nM CHK inhibitor, or 100 nM gemcitabine and 30 nM, 100 nM or 500 nM in combination. A panel of cells was then harvested for Western blot analysis. The medium containing the compound is removed from the remaining cells and fresh tissue culture medium is added back. Cells were then harvested 22 hours later and protein lysates were generated as described above and analyzed by Western blot analysis using a phospho-CHK antibody. Western blot analysis indicated an increase in phospho-CHK following gemcitabine treatment alone, and a dose-dependent increase in ...
Embodiment 3
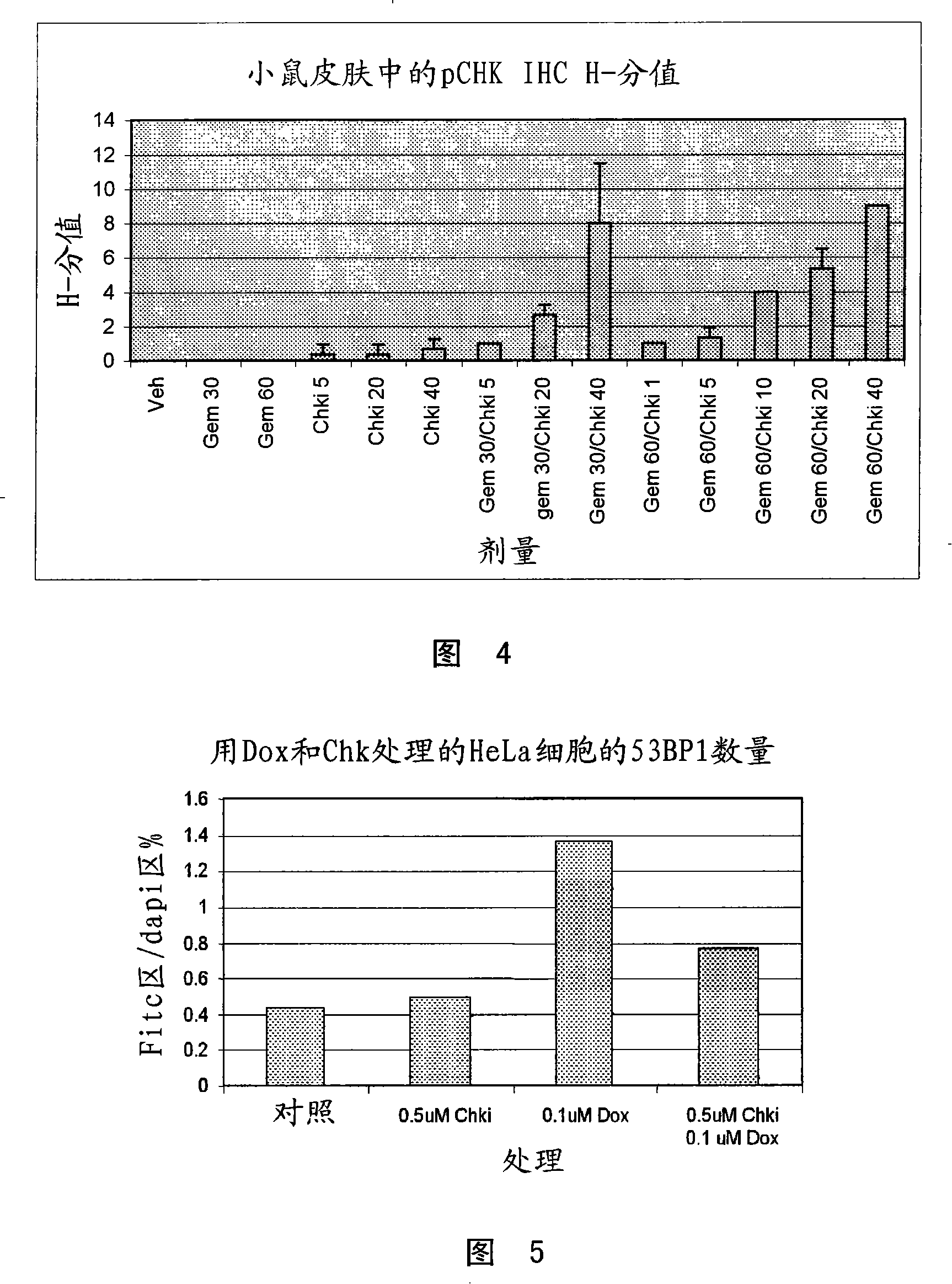
[0073]Similar combination studies have been done with irinotecan and Chk inhibitors. Data again indicated increased phospho-CHK staining compared to either reagent alone (data not shown). Example 3: Demonstration of Reduction of DNA Damage Nuclear Foci Following Inhibition of CHK1 Kinase
[0074] A. In vitro studies:
[0075] HeLa cells were seeded on coverslips and allowed to attach for 24 h at 37 °C. Then with 100nM Adriamycin TM The cells were treated with 500 nM CHK inhibitor for 5 hours. Cells were then treated as described in Example 1. The primary antibody used for the study was rabbit polyclonal anti-53BP1 (Novus, CO) diluted 1:120 and the secondary antibody was Alexa Fluor 488 anti-rabbit IgG (Molecular Probes, OR) diluted 1:300. Nuclear foci were quantified using Metaphorph analysis by measuring the fluorescence intensity per unit number of nuclei (determined by Hoescht staining). Figure 5 shows that when CHK inhibitors and doxorubicin hydrochloride (Adriamycin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com