A transmission method, network device and terminal device for multimedia broadcast multi-cast service data
A data transmission method and multimedia broadcasting technology, applied in the field of data transmission, can solve the problems of unguaranteed scheduling flexibility, high complexity, inability to transmit MBMS data, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
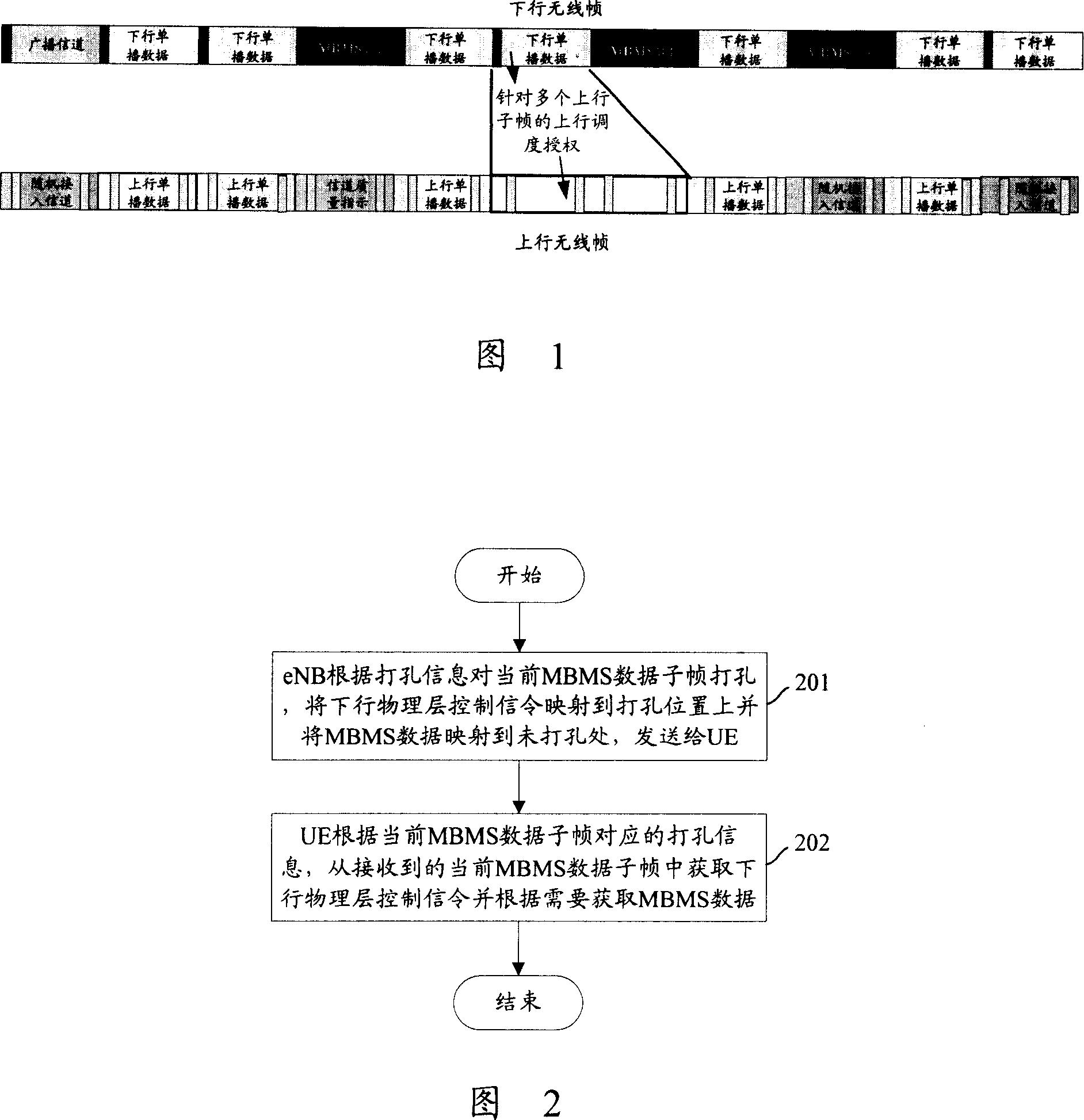
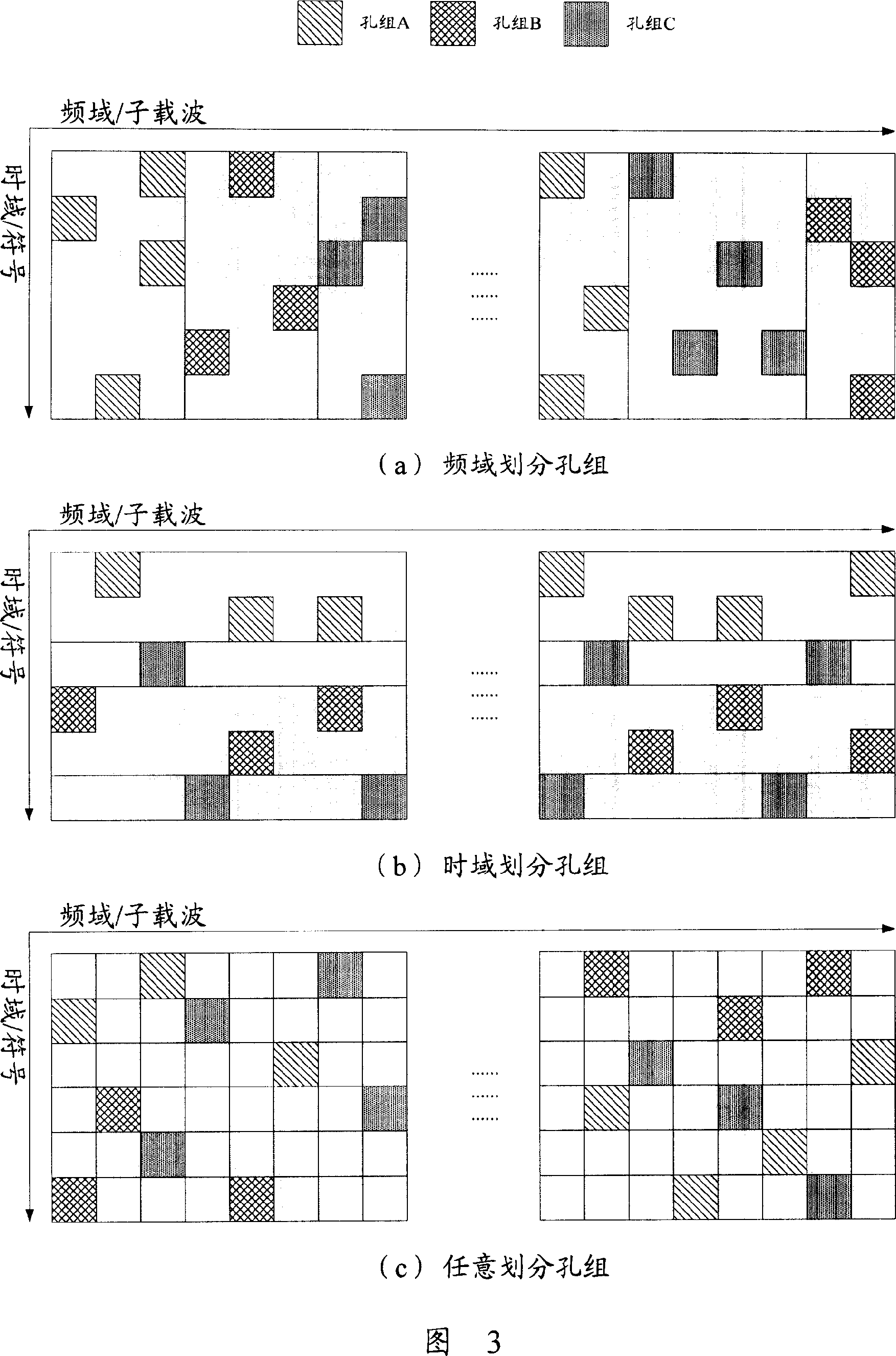
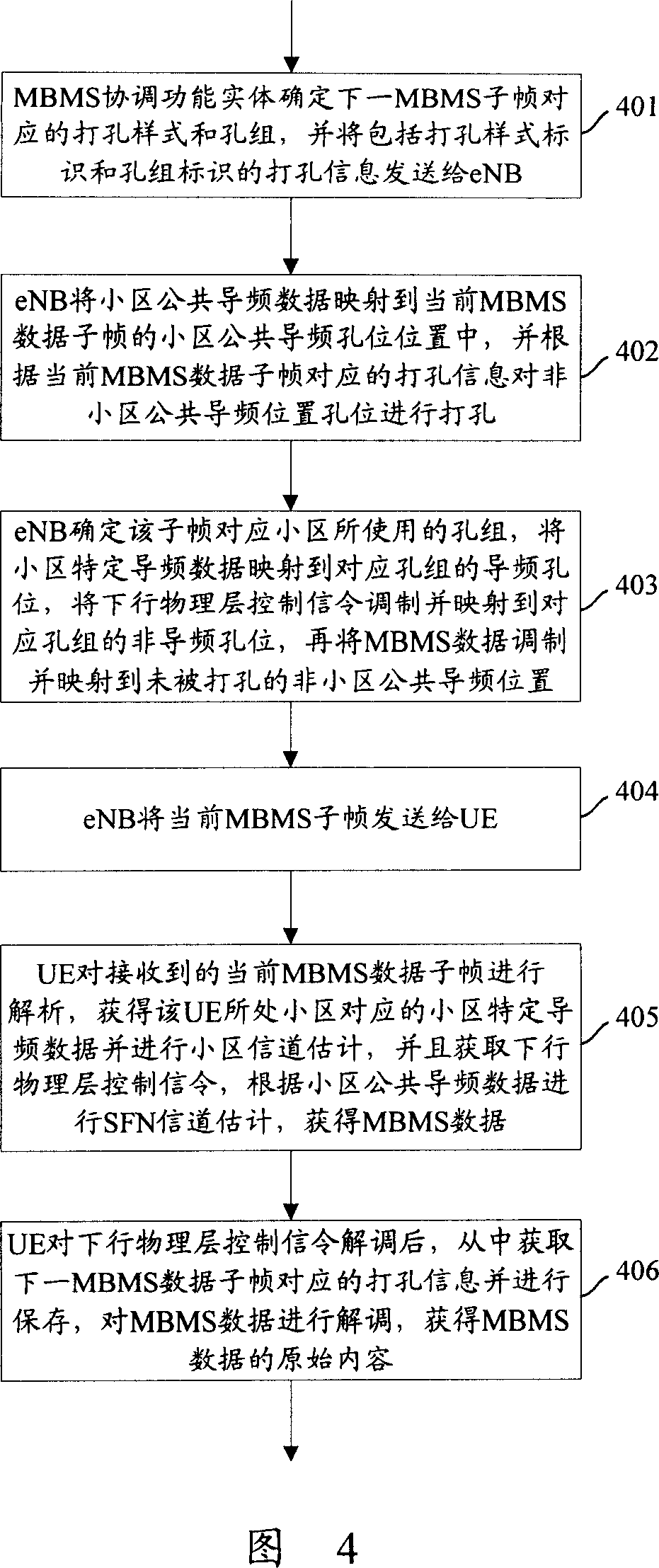
[0123] In this embodiment, the MBMS data is sent in the SFN mode, and the MBMS data subframes are punctured in the SFN puncturing mode sequence. The SFN puncturing pattern sequence here refers to dividing the punctured positions in the subframe into multiple puncturing groups, each puncturing group is represented by a unique puncturing group identifier, and adjacent cells are in the same Use different hole sets in the SFN hole punch pattern sequence at all times. For ease of description, the positions to be punched are referred to as hole positions for short below.
[0124] Since in SFN mode, the cell common pilot contained in the MBMS data subframe cannot be used for channel estimation of a specific cell, so in this embodiment, the cell-specific pilot is also carried at the specific hole position (PuncturingPosition) of each hole group data, these specific slots are called pilot slots. For the completeness of the common pilot data of the cell, this embodiment performs hole ...
Embodiment 2
[0144] In this embodiment, the SFN mode is also used to send MBMS data. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, the hole positions in the MBMS data subframe are not divided into hole groups, but after the common pilot positions of the cells are pre-determined, the positions of the common pilots of the non-cells are punctured, and the The way of code division enables each cell to reuse all holes. In this case, it is still necessary to designate some specific holes to transmit cell-specific pilot data. These specific holes are still called pilot holes, and other holes are called non-pilot holes, but here The pilot hole position is no longer for a certain hole group. In this embodiment, a group of orthogonal sequences is allocated to adjacent cells, and different cells use mutually different but mutually orthogonal sequences to extend cell-specific pilot data and downlink physical layer control signaling, and the extended The cell-specific pilot data is map...
Embodiment 3
[0157] In this embodiment, the MBMS data is sent in a single-cell mode, and the MBMS data subframes are punctured in a single-cell puncturing mode sequence. The single-cell puncturing pattern sequence here means that all the hole positions in the MBMS data subframe are exclusively shared by one cell, so there is no need to divide hole groups.
[0158] Fig. 6 shows a schematic diagram of the distribution of pore positions in a single-cell puncturing pattern sequence. Referring to FIG. 6 , in this punching pattern sequence, the punching pattern identifier is used as punching information, the number of punching holes in each punching pattern can be the same, and the punched hole positions are evenly distributed. Since there is no situation in which multiple cells reuse MBMS data subframes in this embodiment, what is mapped in the pilot position is the cell-specific pilot data used as the basis for channel estimation of the cell, and the punctured hole positions can be Only the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com