Nano-PCR: methods and devices for nucleic acid amplification and detection
An oligonucleotide and nucleotide sequence technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid amplification and detection, which can solve the problems of overall speed, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and limitation of scope of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] Example 1: Method and Apparatus Using Opposite Coated Surfaces
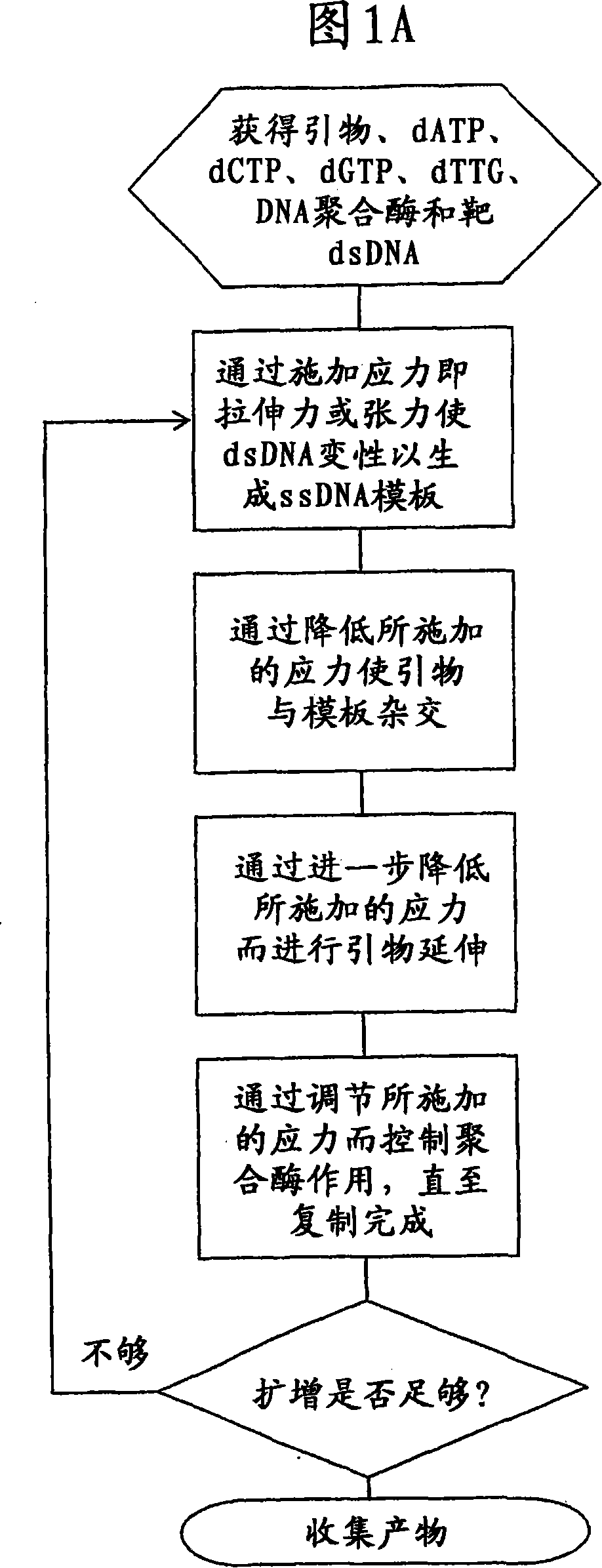
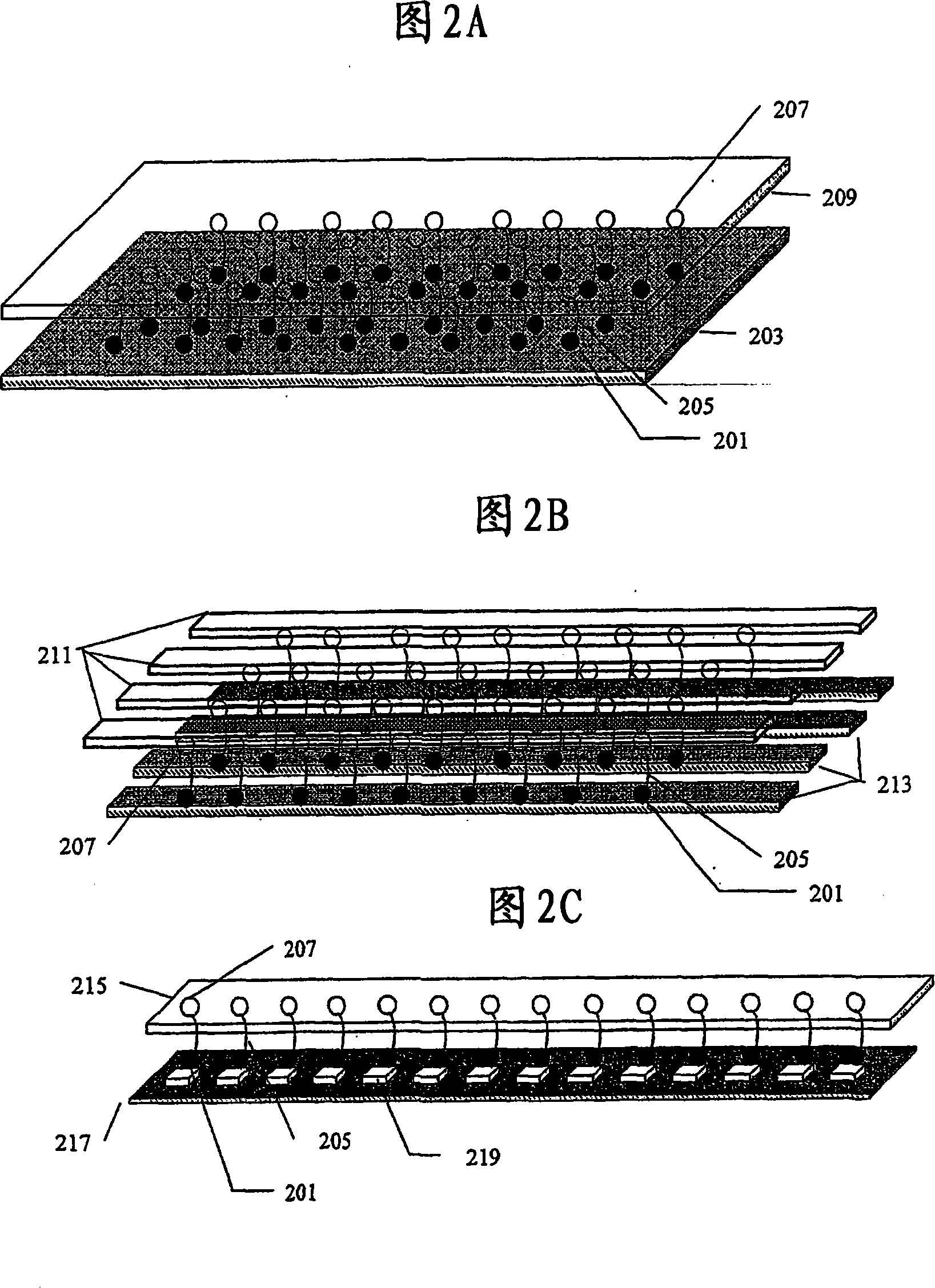
[0106] A pair of streptavidin-coated surfaces were fabricated according to standard methods (Sabanayagam, Smith, and Cantor. "Oligonucleotide immobilization on micropatterned streptavidin surfaces." Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, Vol.28, No.8 pp.i-iv ). Biotinylated dsDNA (biotinylated at both ends of one strand) was added to the above surfaces between which dsDNA was immobilized (Jeffrey M. Rothenberg and Meir Wilchek. p-Diazobenzoyl-biocytin: a new biotinylating reagent for DNA Nucleic Acids Research Volume 16 Number 14 1988). The surface density of DNA molecules can be controlled by adjusting the concentration of template applied to the surface. Tension greater than about 65 pN was exerted on the dsDNA by increasing the distance between the coated surfaces at room temperature. This denatures the dsDNA, leaving only the target ssDNA for amplification. The bound DNA is contacted with a primer containing a b...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2: Methods and devices utilizing immobilized polymerases
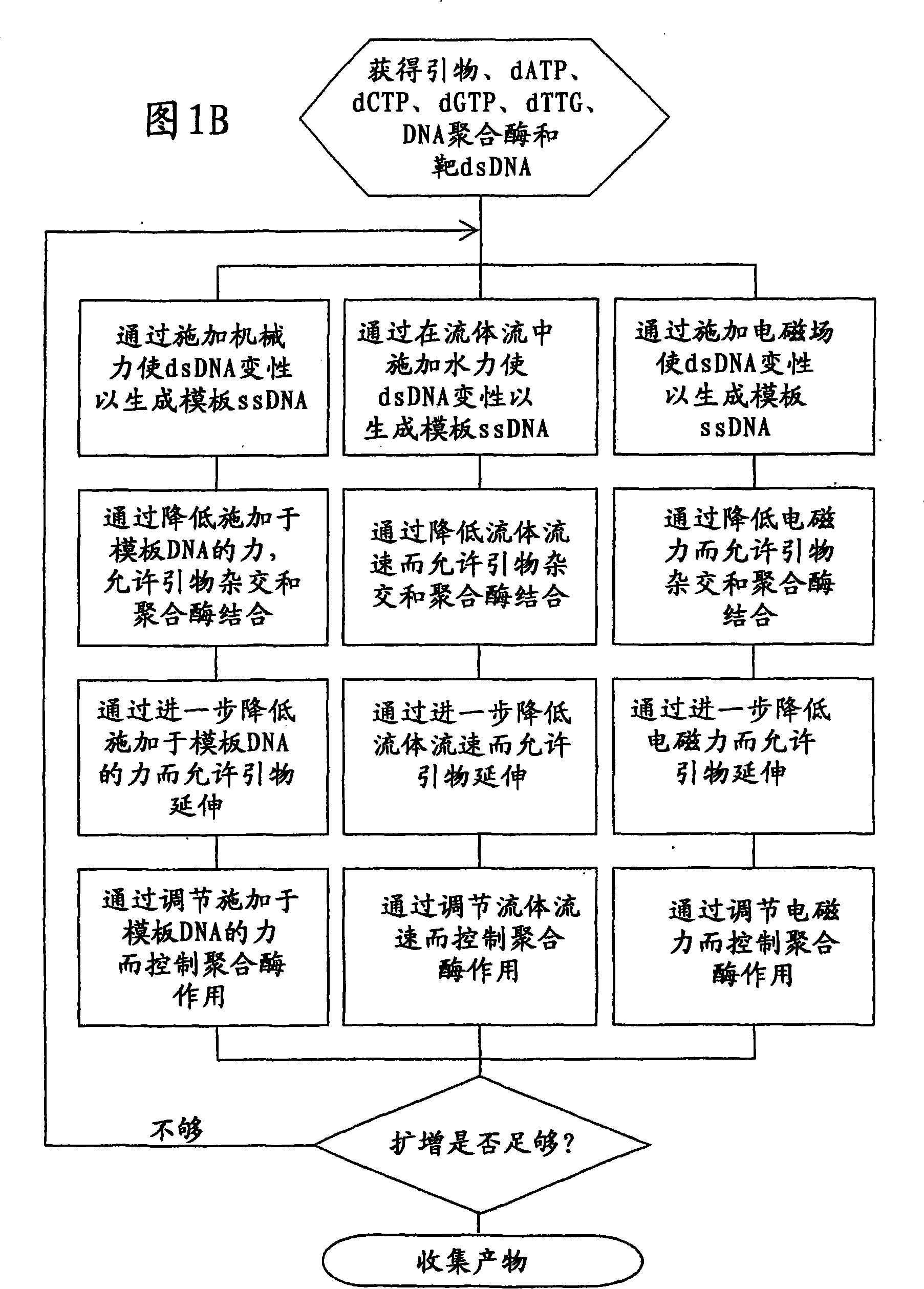
[0109] Streptavidin-coated microchannel surfaces were fabricated according to standard methods (Sabanayagam, Smith, and Cantor. "Oligonucleotide immobilization on micropatterned streptavidin surfaces." Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, Vol.28, No.8 pp.i-iv ). Biotinylated DNA polymerase was flowed into the microchannel and incubated to saturate the surface. Commercial kits for enzyme biotinylation are available, eg, from Pierce Labs. Unbound enzyme flows out of the microchannel and target nucleotides (eg, ssDNA, RNA) and primers flow in at a chamber flow rate such that a force greater than 60 pN is applied to the nucleotides. Reduce the flow rate so that a force of 30pN to 60pN is applied to the nucleotides to form polymerase / nucleotide / primer complexes. The chamber flow rate was further reduced to less than 30 pN for primer extension. After completion of primer extension, the flow rate was increased to apply...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Embodiment 3: Utilize the method and device of DNA immobilization
[0111]Streptavidin-coated microchannel surfaces were fabricated according to standard methods. (Sabanayagam, Smith, and Cantor. "Oligonucleotide immobilization on micropatterned streptavidin surfaces." Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, Vol. 28, No. 8 pp. i-iv). Biotinylated dsDNA (biotinylated at one end of one strand) was flowed into a microchannel and incubated to allow surface binding (Jeffrey M. Rothenberg and Meir Wilchek. p-Diazobenzoyl-biocytin: a new biotinylating reagent for DNA Nucleic Acids Research Volume 16 Number 14 1988). Chamber fluid flow rates were established that exert a force greater than 65 pN on bound dsDNA. This denatures the dsDNA, leaving only the target ssDNA for amplification. Flow DNA polymerase, nucleotides, and biotinylated primers into the microchannel. The biotin reagent used can be purchased from commercial suppliers such as Molecular Probes or Pierce. For example, a biotin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com